Foreign relations of San Marino
 |
|---|
San Marino is an independent and sovereign member of the international community. It maintains an extensive diplomatic network relative to its diminutive size, as well as an active foreign policy and international presence.
International organizations[edit]
Among other international organizations, San Marino is a full member of the following international organizations:
- United Nations
- International Court of Justice
- United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO)
- International Monetary Fund (IMF)
- World Health Organization (WHO)
- World Tourism Organization (WTO)
- Council of Europe
- International Committee of the Red Cross
- International Criminal Court (ICC)
- International Institution for the Unification of Private Law (UNIDROIT)
It also cooperates with UNICEF and the United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees and has official relations with the European Union.[1][2][3]
From May 10 until November 6, 1990, San Marino held the semi-annual presidency of the Committee of Ministers of the Council of Europe. The second San Marino Chairmanship of the Committee of Ministers of the Council of Europe was from November 2006 until May 2007.
Diplomatic relations[edit]
List of countries which San Marino maintains diplomatic relations with: (consular relations with Haiti)
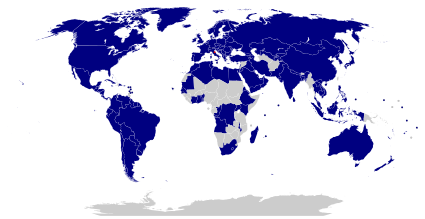
| ||
|---|---|---|
| # | Country | Date[4] |
| 1 | 15 May 1965 | |
| 2 | 18 May 1974 | |
| 3 | 21 June 1976 | |
| 4 | 30 July 1976 | |
| 5 | 28 October 1978 | |
| 6 | 14 May 1984 | |
| 7 | 26 March 1985 | |
| – | 18 January 1986 | |
| – | 4 March 1986 | |
| 8 | 2 April 1987 | |
| 9 | 1 August 1988[5] | |
| 10 | 13 December 1988 | |
| 11 | 27 April 1989 | |
| 12 | 15 April 1991 | |
| 13 | 24 May 1991 | |
| 14 | 18 June 1991 | |
| 15 | 14 January 1992 | |
| 16 | 29 April 1992 | |
| 17 | 10 June 1992 | |
| 18 | 13 July 1992 | |
| 19 | 20 October 1992 | |
| 20 | 3 November 1992 | |
| 21 | 1 January 1993 | |
| 22 | 30 April 1993 | |
| 23 | 23 July 1993 | |
| 24 | 30 September 1993 | |
| 25 | 6 October 1994[6] | |
| 26 | 14 November 1994 | |
| 27 | 15 November 1994 | |
| 28 | 13 January 1995 | |
| 29 | 27 March 1995[7] | |
| 30 | 10 July 1995 | |
| 31 | 17 July 1995 | |
| 32 | 13 September 1995 | |
| 33 | 15 September 1995 | |
| 34 | 30 October 1995 | |
| 35 | 30 October 1995[8] | |
| 36 | 30 November 1995[9] | |
| 37 | 1995[10] | |
| 38 | 27 February 1996 | |
| 39 | 27 May 1996 | |
| 40 | 28 May 1996 | |
| 41 | 21 November 1996 | |
| 42 | 11 December 1996 | |
| 43 | 24 November 1997 | |
| 44 | 18 November 1998 | |
| 45 | 22 September 1999[7] | |
| 46 | 20 October 1999 | |
| 47 | 22 November 1999 | |
| 48 | 17 April 2000 | |
| 49 | 18 May 2000 | |
| 50 | 22 August 2000 | |
| 51 | 8 February 2001 | |
| 52 | 14 February 2002 | |
| 53 | 14 March 2002 | |
| 54 | 13 February 2003 | |
| 55 | 3 April 2003 | |
| 56 | 3 April 2003 | |
| 57 | 3 April 2003 | |
| 58 | 3 April 2003 | |
| 59 | 3 April 2003 | |
| 60 | 3 May 2003 | |
| 61 | 12 September 2003 | |
| 62 | 15 October 2003 | |
| 63 | 19 October 2003 | |
| 64 | 20 November 2003[11] | |
| 65 | 22 January 2004 | |
| 66 | 29 January 2004 | |
| 67 | 20 September 2004[12] | |
| 68 | 28 September 2004[7] | |
| 69 | 14 October 2004 | |
| 70 | 29 October 2004 | |
| 71 | 22 February 2005 | |
| 72 | 14 March 2005 | |
| 73 | 5 May 2005 | |
| 74 | 5 May 2005 | |
| 75 | 10 August 2005[13] | |
| 76 | 29 September 2005 | |
| 77 | 12 October 2005[14] | |
| 78 | 28 October 2005 | |
| 79 | 9 December 2005 | |
| 80 | 17 December 2005 | |
| 81 | 12 April 2006[15] | |
| 82 | 1 June 2006 | |
| 83 | 17 October 2006 | |
| 84 | 17 October 2006 | |
| 85 | 22 November 2006[7] | |
| 86 | 22 November 2006[16] | |
| 87 | 29 March 2007 | |
| 88 | 30 March 2007 | |
| 89 | 22 May 2007 | |
| 90 | 6 July 2007[17] | |
| 91 | 10 July 2007 | |
| 92 | 16 November 2007 | |
| 93 | 5 November 2008 | |
| 94 | 9 February 2009[18] | |
| 95 | 26 March 2009 | |
| 96 | 30 March 2009[7] | |
| 97 | 31 March 2009[7] | |
| 98 | 6 April 2009 | |
| 99 | 6 July 2009 | |
| 100 | 11 July 2009 | |
| 101 | 2 October 2009 | |
| 102 | 30 November 2010 | |
| 103 | 12 April 2011[19] | |
| 104 | 26 September 2011 | |
| 105 | 26 September 2011[20] | |
| 106 | 7 October 2011 | |
| 107 | 21 October 2011 | |
| 108 | 9 December 2011 | |
| — | 3 May 2012[21] | |
| 109 | 5 November 2012 | |
| 110 | 13 February 2013 | |
| 111 | 15 March 2013[22] | |
| 112 | 19 March 2013[23] | |
| 113 | 29 April 2013[24] | |
| 114 | 1 October 2013 | |
| 115 | 16 December 2013[23] | |
| 116 | 24 April 2014[25] | |
| 117 | 10 November 2014 | |
| 118 | 17 December 2014 | |
| 119 | 31 May 2017 | |
| 120 | 9 November 2017 | |
| 121 | 20 April 2018[7] | |
| 122 | 3 August 2018[26] | |
| 123 | 25 September 2018[27] | |
| 124 | 25 September 2018[28] | |
| 125 | 25 September 2018[29] | |
| 126 | 26 September 2018[29] | |
| 127 | 26 September 2018[30] | |
| 128 | 27 September 2018[29] | |
| 129 | 7 November 2018[29] | |
| 130 | 12 December 2018[30] | |
| 131 | 17 December 2018[7] | |
| 132 | 22 January 2019[30] | |
| 133 | 17 February 2019[31] | |
| 134 | 28 February 2019[32] | |
| 135 | 28 February 2019[30] | |
| 136 | 24 September 2019[30] | |
| 137 | 25 September 2019[30] | |
| 138 | 25 September 2019[30] | |
| 139 | 25 September 2019[33] | |
| 140 | 26 September 2019[34] | |
| 141 | 3 October 2019[35] | |
| 142 | 8 October 2019[30] | |
| 143 | 7 February 2020[30] | |
| 144 | 29 September 2020[7] | |
| 145 | 23 October 2020[7] | |
| 146 | 6 February 2021[36] | |
| 147 | 12 May 2021[37] | |
| 148 | 2 August 2021[38] | |
| 149 | 20 October 2021[39][7] | |
| 150 | 1 February 2023[7] | |
| 151 | 8 December 2023[7] | |
UN Secretary General visits and remarks[edit]
On 31 March-1 April 2013, United Nations Secretary-General Ban Ki-moon was the official orator on the occasion of the newly elected Captains Regent. “Although this country is small, your importance to the United Nations stands as tall as Mount Titano,” the Secretary-General told the country's highest officials, the two Captains Regent, in reference to the country's 739 meter UNESCO World Heritage Site. Mr. Ban also noted that the country accepted five times as many refugees as its population during the Second World War, and praised its emphasis on protecting human rights.[40] This has been the second visit to San Marino by a UN Secretary General, the first being Boutrous Boutrous-Gali's visit in 1996.
Multilateral relations[edit]
| Organization | Formal Relations Began | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| See San Marino–European Union relations |
Bilateral relations[edit]
| Country | Formal relations began on | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| 30 November 1995[4] |
| |
| 17 October 2006[4] |
| |
| 2 April 1987[4] |
| |
| 19 April 2002[41] |
| |
| 26 March 1985[4] |
| |
| 21 November 1996[4] |
| |
| 1926[4] |
| |
| 6 May 1971[4] | See China–San Marino relations
| |
| 3 November 1992[4] |
| |
| 27 February 1996[4] |
| |
| 15 May 1965[4] |
| |
| 1 October 1995[42] | See Germany–San Marino relations
| |
| 20 November 1979[4] |
| |
| 18 January 1986[4] |
| |
See Italy–San Marino relations
| ||
| 9 December 2011[4] |
| |
| 1961[4] | See Japan–San Marino relations
| |
| 7 December 1981[4] |
| |
| 1 June 2006[4] |
| |
| 17 January 1977[4] |
| |
| ||
| 3 December 1979[4] |
| |
| 30 September 1993[4] |
On 1 March 2023, the Grand and General Council of San Marino authorised the country's government to take sanctions against Russia for the invasion of Ukraine. Russia has included San Marino in an Unfriendly List. | |
| 22 August 2000[4] |
| |
| 31 March 1978[4] |
| |
| 10 July 1995[4] |
| |
| 17 December 2005[4] | See San Marino–Turkey relations
| |
| 24 March 1995[4] |
| |
| 18 November 1998[4] | See San Marino–United Kingdom relations
| |
| 16 January 1925[4] | See San Marino–United States relations
United States was the first non-European state recognizing official diplomatic relations with San Marino.[45] |
See also[edit]
References[edit]
- ^ "/eeas.europa.eu".
- ^ "San Marino: Thanks but No Thanks, EU Accession!". europeanpublicaffairs.eu. 21 October 2013. Retrieved 11 April 2017.
- ^ "UNICEF. At a glance: San Marino". unicef.org. 2 February 2007. Retrieved 11 April 2017.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z aa "Rapporti bilaterali della Repubblica di San Marino" (in Italian). Retrieved 15 December 2021.
- ^ "Stati di servizio del personale della carriera diplomatica e della dirigenza del ministero degli affari esteri e della cooperazione internazionale che ha cessato di far parte dell'amministrazione dal 1° Gennaio 2000 al 5 Luglio 2016" (PDF) (in Italian). p. 94. Retrieved 27 October 2023.
- ^ Mensaje presidencial del ... a la Honorable Asamblea (in Spanish). 1995. p. 64.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m "Diplomatic relations between San Marino and ..." United Nations Digital Library. Retrieved 3 December 2021.
- ^ "Relazione politiche". Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Ukraine (in Italian). 25 March 2021. Retrieved 3 December 2021.
- ^ "Diplomatic relations". Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Andorra. Retrieved 3 July 2021.
- ^ "Nederlandse diplomatieke vertegenwoordiging in Italië te Rome en consulaat-generaal in Italië te Milaan" (in Dutch). Retrieved 5 January 2022.
Nederland heeft sinds 1995 diplomatieke betrekkingen met San Marino.
- ^ "Acordo bilaterale - Exchange of Notes on the establishment of official diplomatic relations". Retrieved 30 January 2024.
- ^ "Список стран, с которыми КР установил дипломатические отношения" (in Russian). Retrieved 10 October 2021.
- ^ "Bilateral Relations". Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Nepal. Retrieved 25 June 2021.
- ^ "Relations between Turkey and San Marino". Retrieved 2 December 2021.
- ^ "Ministry of Foreign Affairs". Mofa.gov.pk. Archived from the original on 3 March 2012. Retrieved 24 November 2012.
- ^ "A Guide to the United States' History of Recognition, Diplomatic, and Consular Relations, by Country, since 1776: San Marino". Retrieved 21 July 2023.
- ^ "Bilateral relations". Retrieved 3 December 2021.
- ^ "9 February 2009". Belarus, San Marino establish diplomatic relations. Retrieved 3 December 2021.
- ^ "LIST OF MEMBER STATES OF THE UNITED NATIONS (193) HAVING DIPLOMATIC RELATIONS WITH CAMBODIA". mfaic.gov.kh. Retrieved 2 October 2021.
- ^ "Bilateral Relations". RSM Indonesia. Retrieved 11 February 2024.
- ^ Gëzim Visoka (2018). Acting Like a State: Kosovo and the Everyday Making of Statehood. Abingdon: Routledge. pp. 219–221. ISBN 9781138285330.
- ^ "Formal diplomatic relations list" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 27 August 2019. Retrieved 31 March 2018.
- ^ a b "E' convocata una sessione del CONSIGLIO GRANDE E GENERALE che si terrà nei giornidi giovedì 10 aprile dalle ore 13.00 alle ore 20.00..." (in Italian). Retrieved 3 December 2013.
- ^ "Ratifica dell'Accordo tra la Repubblica di San Marino e la Nuova Zelanda sulle relazioni diplomatiche" (in Italian). Retrieved 3 December 2021.
- ^ "Countries with which the Republic of Maldives has established Diplomatic Relations" (PDF). Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Maldives. 30 March 2021. Retrieved 2 April 2021.
- ^ "LIST OF STATES WITH WHICH THE REPUBLIC OF TAJIKISTAN ESTABLISHED DIPLOMATIC RELATIONS" (PDF). November 2018. Retrieved 30 April 2021.
- ^ "FSM Diplomatic Relations List". Government of the Federated States of Micronesia.
- ^ "Diplomatic Relations". Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Saint Kitts and Nevis. Retrieved 1 April 2021.
- ^ a b c d "Relazione sugli Accordi di Stabilimento della relazioni diplomatiche" (in Italian). Retrieved 3 December 2021.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i "16-17-18-21-22-23-24 settembre 2020" (in Italian). pp. 15–16. Retrieved 3 December 2021.
- ^ "Guyana establishes diplomatic ties with San Marino". Guyana Chronicle. 17 February 2019. Retrieved 21 April 2021.
- ^ "Accordo tra la Repubblica di San Marino e lo Stato Indipendente di Samoa sullo stabilimento delle relazioni diplomatiche, firmato a New York il 28 febbraio 2019 – Consiglio Grande e Generale". consigliograndeegenerale.sm (in Italian). Retrieved 13 July 2019.
- ^ "RATIFICA DELL'ACCORDO TRA LA REPUBBLICA DI SAN MARINO E LA REPUBBLICA DI CABO VERDE SULLO STABILIMENTO DELLE RELAZIONI DIPLOMATICHE" (in Italian). Retrieved 3 December 2021.
- ^ "Ratifica dell'Accordo tra la Repubblica di San Marino e la Repubblica di Macedonia del Nord sullo stabilimento delle relazioni diplomatiche". esteri.sm (in Italian). Retrieved 3 April 2021.
- ^ "Relazione CGG stabilimento relazioni diplomatiche RSM - JamaicaApri". Esteri.sm (in Italian). Retrieved 18 April 2021.
Accordo tra la Repubblica di San Marino e la Jamaica sullo stabilimento delle relazioni diplomatiche, concluso tramite Scambio di Note del 22 giugno 2020.
- ^ "Uzbekistan, San Marino establish diplomatic relations". 6 February 2021. Retrieved 3 December 2021.
- ^ "Stabilimento delle relazioni diplomatiche con la Repubblica del Kenya" (in Italian). Retrieved 3 December 2021.
- ^ "Stabilimento delle relazioni diplomatiche con il Commonwealth della Dominica" (in Italian). Retrieved 21 August 2021.
- ^ "Agreement between the Republic of San Marino and the Republic of Kiribati on the establishment of diplomatic relations". Retrieved 8 June 2022.
- ^ https://www.un.org/apps/news/story.asp?NewsID=44531&Cr=San+Marino&Cr1=#.UV9F_o5FsV8 UN News Centre
- ^ "San Marino". mfa.gov.az. Retrieved 20 January 2021.
- ^ "San Marino: Steckbrief".
- ^ "San Marino".
- ^ "국가/지역 검색 | 외교부".
- ^ Storia di San Marino (History of San Marino) (Rimini: Bookstone, 2022), pp. 127-128)

