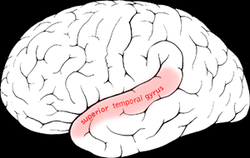
Superior temporal gyrus
| Superior temporal gyrus | |
|---|---|
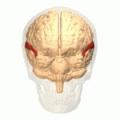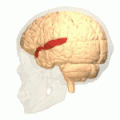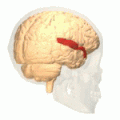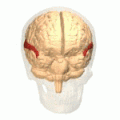
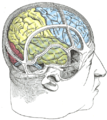
 Superior temporal gyrus of the human brain. | |
 Right temporal lobe (shown in green). Superior temporal gyrus is visible at the top of the green area. | |
| Details | |
| Part of | Temporal lobe |
| Artery | middle cerebral |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | gyrus temporalis superior |
| NeuroNames | 136 |
| NeuroLex ID | birnlex_1648 |
| TA98 | A14.1.09.138 |
| TA2 | 5489 |
| FMA | 61905 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
The superior temporal gyrus is one of three (sometimes two) gyri in the temporal lobe of the human brain, which is located laterally to the head, situated somewhat above the external ear.
The superior temporal gyrus is bounded by:
- the lateral sulcus above;
- the superior temporal sulcus (not always present or visible) below;
- an imaginary line drawn from the preoccipital notch to the lateral sulcus posteriorly.
The superior temporal gyrus contains several important structures of the brain, including:
- Brodmann areas 41 and 42, marking the location of the primary auditory cortex, the cortical region responsible for the sensation of sound;
- Wernicke's area, Brodmann 22p, an important region for the processing of speech so that it can be understood as language.
The superior temporal gyrus contains the primary auditory cortex, which is responsible for processing sounds. Specific sound frequencies map precisely onto the primary auditory cortex. This auditory (or tonotopic) map is similar to the homunculus map of the primary motor cortex. Some areas of the superior temporal gyrus are specialized for processing combinations of frequencies, and other areas are specialized for processing changes in amplitude or frequency. The superior temporal gyrus also includes the Wernicke's area, which (in most people) is located in the left hemisphere. It is the major area involved in the comprehension of language. The superior temporal gyrus (STG) is involved in auditory processing, including language, but also has been implicated as a critical structure in social cognition.[1][2]
Function
The superior temporal gyrus has been involved in the perception of emotions in facial stimuli.[1] [3]) Furthermore, the superior temporal gyrus is an essential structure involved in auditory processing, as well as in the function of language in individuals who may have an impaired vocabulary, or are developing a sense of language. The superior temporal gyrus has been discovered to be an important structure in the pathway consisting of the amygdala and prefrontal cortex, which are all involved in social cognition processes.[4][5][6] Including the superior temporal gyrus, areas more anterior and dorsal within the temporal lobe have been linked to the ability of processing information the many changeable characteristics of a face.[7] Research conducted with the use of neuroimaging have found patients with schizophrenia have structural abnormalities in their superior temporal gyrus.[8]
Social Context
The superior temporal gyrus (STG) is important for language comprehension, but studies also suggest that is plays a functional role in the cocktail party scene. A magnetoencephalography study was conducted on participants that were exposed to 5 differing listening conditions each with a different level of background noise. It was discovered that the STG has a strong connection with the attended speech stream in a cocktail party setting. When the attended speech stream wasn’t disrupted by background noise a bilateral connection was displayed, but as more background noise was introduced the connection became left-hemisphere dependent.[9]
Additional images
-
Position of superior temporal gyrus (shown in red).
-
Superior temporal gyrus shown in yellow. Lateral aspect of the left cerebrl hemisphere.
-
Lateral view of a human brain, main gyri labeled.
-
Drawing of a cast to illustrate the relations of the brain to the skull. (Superior temporal gyrus labeled at center, in green section.)
-
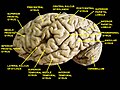
Cerebrum. Lateral view. Deep dissection. Superior temporal gyrus is visible at the center.
See also
References
- ^ a b Erin D. Bigler, Sherstin Mortensen, E. Shannon Neeley, Sally Ozonoff, Lori Krasny, Michael Johnson, Jeffrey Lu, Sherri L. Provencal, William McMahon & Janet E. Lainhart (2007): Superior Temporal Gyrus, Language Function, and Autism, Developmental Neuropsychology, 31:2, 217-238
- ^ Jou, RJ.; Minshew, NJ.; Keshavan, MS.; Vitale, MP.; Hardan, AY. (Nov 2010). "Enlarged right superior temporal gyrus in children and adolescents with autism". Brain Res. 1360: 205–12. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2010.09.005. PMC 2990401. PMID 20833154.
- ^ Radua, Joaquim; Phillips, Mary L.; Russell, Tamara; Lawrence, Natalia; Marshall, Nicolette; Kalidindi, Sridevi; El-Hage, Wissam; McDonald, Colm; Giampietro, Vincent; Brammer, Michael J.; David, Anthony S.; Surguladze, Simon A. (2010). "Neural response to specific components of fearful faces in healthy and schizophrenic adults". NeuroImage. 49 (1): 939–946. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2009.08.030. PMID 19699306.
- ^ Adolphs, R. (Apr 2003). "Is the human amygdala specialized for processing social information?". Ann N Y Acad Sci. 985: 326–40. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.2003.tb07091.x. PMID 12724168.
- ^ Takahashi et al., 2004
- ^ Bigler, E. et al. (2007) Superior Temporal Gyrus, Language Function, and Autism Developmental Neuropsychology, 31(2), 217-238
- ^ Bigler ED, Mortensen S, Neeley ES, Ozonoff S, Krasny L, Johnson M, Lu J, Provencal SL, McMahon W, Lainhart JE. 2007. Superior temporal gyrus, language function, and autism. 31 (2): 217-238
- ^ Kasai K, Shenton ME, Salisbury DF, Hirayasu Y, Lee C-U, Ciszewski AA, et al. Progressive decrease of left superior temporal gyrus gray matter volume in patients with first-episode schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry 2003a;160:156–64.
- ^ . PMID 26843641.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help); Missing or empty|title=(help)
[1] Erin D. Bigler, Sherstin Mortensen, E. Shannon Neeley, Sally Ozonoff, Lori Krasny, Michael Johnson, Jeffrey Lu, Sherri L. Provençal, William McMahon & Janet E. Lainhart (2007): Superior Temporal Gyrus, Language Function, and Autism, Developmental Neuropsychology, 31:2, 217-238