Synovial bursa
This article needs additional citations for verification. (September 2012) |
| Synovial Bursa | |
|---|---|
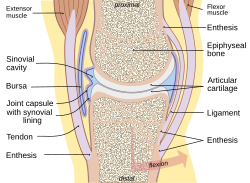 Typical joint | |
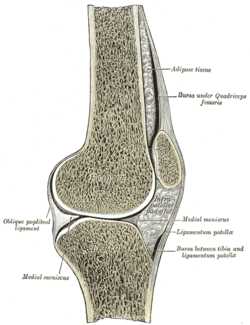 Within the knee joint: bursae visible top right and bottom right | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | bursa synovialis |
| MeSH | D002061 |
| TA98 | A03.0.00.039 A04.8.01.004 |
| TA2 | 2028 |
| TH | H3.03.00.0.00039 |
| FMA | 9692 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
A bursa (plural bursae or bursas) is a small fluid-filled sac lined by synovial membrane with an inner capillary layer of viscous fluid (similar in consistency to that of a raw egg white). It provides a cushion between bones and tendons and/or muscles around a joint. This helps to reduce friction between the bones and allows free movement. Bursae are filled with synovial fluid and are found around most major joints of the body.
Structure
There are four types of bursa: adventitious, subcutaneous, synovial, and sub-muscular. Among these, only adventitious is non-native. When any surface of the body is subjected to repeated stress, an adventitious bursa develops under it. Examples are Students' elbow and bunion.
Clinical significance
Infection or irritation of a bursa leads to bursitis (inflammation of a bursa). The general term for disease of bursae is "bursopathy".
History
Etymology
Bursa is Latin for purse, so named for the resemblance of an anatomical bursa to a purse. Bursae or bursas is its plural form.
See also
- Bursa of Fabricius (a lymphatic organ in birds)
- Bursectomy
- Knee bursae
External links
- Image
- Diagram of elbow with olecranon bursa (broken link?)
- . GPnotebook https://www.gpnotebook.co.uk/simplepage.cfm?ID=-831848371.
{{cite web}}: Missing or empty|title=(help)
