TOM (psychedelic)
| TOM | |
|---|---|
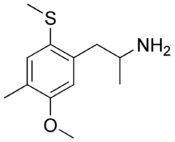
| Chemical name | Thiomescaline |
| Chemical formula | C12H19NOS |
| |
TOM, or methylthio-methyl-methoxyamphetamine, is a series of lesser-known psychedelic drugs and substituted amphetamines. 2-TOM and 5-TOM are the 2 and 5 methylthio analogs of DOM/STP, respectively. They were first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin and written up in his book PiHKAL (Phenethylamines i Have Known And Loved). Very little is known about their dangers or toxicity.
TOM compounds


2-TOM
Dosage: 60–100 mg
Duration: 8–10 hours
Effects: strong closed-eye visuals upon listening to music, ++ on the Shulgin Rating Scale
5-TOM
Dosage: 30–50 mg
Duration: 6–10 hours
Effects: open and closed-eye visuals, psychedelia, hallucinations
See also
- Phenethylamine
- Psychedelics, dissociatives and deliriants
- PiHKAL
- 2,5-Dimethoxy-4-methylamphetamine
- TOMSO
