Thorpe reaction
The Thorpe reaction is a chemical reaction described as a self-condensation of aliphatic nitriles catalyzed by base to form enamines.[1][2][3] The reaction was discovered by Jocelyn Field Thorpe.
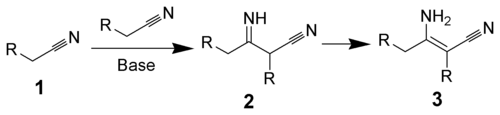
Thorpe–Ziegler reaction[edit]
The Thorpe–Ziegler reaction (named after Jocelyn Field Thorpe and Karl Ziegler), or Ziegler method, is the intramolecular modification with a dinitrile as a reactant and a cyclic ketone as the final reaction product after acidic hydrolysis. The reaction is conceptually related to the Dieckmann condensation.[3]

References[edit]
- ^ Baron, Harold; Remfry, Frederick George Percy; Thorpe, Jocelyn Field (1904). "CLXXV.—The formation and reactions of imino-compounds. Part I. Condensation of ethyl cyanoacetate with its sodium derivative". Journal of the Chemical Society, Transactions. 85: 1726–1761. doi:10.1039/CT9048501726. ISSN 0368-1645.
- ^ Ziegler, K.; Eberle, H.; Ohlinger, H. (1933). "Über vielgliedrige Ringsysteme. I. Die präparativ ergiebige Synthese der Polymethylenketone mit mehr als 6 Ringgliedern". Justus Liebig's Annalen der Chemie (in German). 504 (1): 94–130. doi:10.1002/jlac.19335040109. ISSN 0075-4617.
- ^ a b Schaefer, John P.; Bloomfield, Jordan J. (2011). "The Dieckmann Condensation (Including the Thorpe-Ziegler Condensation)". Organic Reactions. pp. 1–203. doi:10.1002/0471264180.or015.01. ISBN 978-0471264187.
External links[edit]
- Thorpe-Ziegler reaction: 4-Phosphorinanone, 1-phenyl- Organic Syntheses, Coll. Vol. 6, p. 932 (1988); Vol. 53, p. 98 (1973) Link
