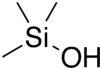Trimethylsilanol
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Hydroxytrimethylsilane
| |||
| Other names
Trimethylhydroxysilane
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.012.650 | ||
PubChem CID
|
|||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C3H10OSi | |||
| Molar mass | 90.196 g/mol | ||
| Boiling point | 98.6 - 99 °C | ||
| Related compounds | |||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
Trimethylsilanol (TMS), also trimethylhydroxysilane, is a silanol with the formula (CH3)3SiOH, or C3H10OSi. It is an organosilicon derivative of silane substituted with three methyls and one hydroxyl group. It is a volatile organic liquid with boiling point between 98.6-99 °C.
TMS is used to apply hydrophobic coating on silicate surfaces. It reacts with the silicon atoms of the substrate, coating the surface with a layer of methyl groups. A commercial example is Magic Sand.
TMS is a common contaminant in spacecraft atmospheres, where it is present due to outgassing of silicone-based materials.[1] It is a potential end group hydrolysis product of polydimethylsiloxane chains.
TMS, together with other silanols, is also being investigated as an antimicrobial agent.[2]
References
- ^ Trimethylsilanol, Harold L. Kaplan, Martin E. Coleman, and John T. James Spacecraft Maximum Allowable Concentrations for Selected Airborne Contaminants, Volume 1 (1994)
- ^ Yun-mi Kim, Samuel Farrah, Ronald H. Baney (2006). "Silanol - A novel class of antimicrobial agent". Electronic Journal of Biotechnology. 9 (2): 176. doi:10.2225/vol9-issue2-fulltext-4.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)