Worthing Borough Council
Worthing Borough Council | |
|---|---|
 | |
 | |
| Type | |
| Type | |
| Leadership | |
Catherine Howe since 2021[2] | |
| Structure | |
| Seats | 37 councillors |
 | |
Political groups |
|
Joint committees | Various joint committees of Adur and Worthing Councils Greater Brighton City Board |
| Elections | |
| First past the post | |
Last election | 4 May 2023 |
Next election | 2 May 2024 |
| Motto | |
| "Ex terra copiam e mari salutem" (Latin for "From the land plenty and from the sea health") | |
| Meeting place | |
 | |
| Town Hall, Chapel Road, Worthing, BN11 1HA | |
| Website | |
| www | |
Worthing Borough Council is the local authority for Worthing in West Sussex, England. Worthing is a non-metropolitan district with borough status. It forms the lower tier of local government in Worthing, responsible for local services such as housing, planning, leisure and tourism. The council is currently led by the Labour Party. It is based at Worthing Town Hall.
History[edit]
Commissioners (1803–1852)[edit]
Worthing was historically a hamlet in the ancient parish of Broadwater. Until 1803 it was administered by the Broadwater parish vestry, in the same way as most rural areas.[3]

Worthing's first form of urban local government was a body of improvement commissioners, established in 1803 with responsibility for street paving and lighting, sewerage and policing.[4] The first chairman of the commissioners was Timothy Shelley.[5] The commissioners' responsibilities were gradually expanded by subsequent Acts of Parliament.[6][7] The commissioners initially met at hotels in the town until 1835 when they built Worthing's first town hall at the northern end of South Street.[8][5]
Local board (1852–1890)[edit]
The commissioners were replaced in 1852 when Worthing was made a local board district.[9][10] A separate body of improvement commissioners was established in 1865 covering West Worthing, which was being developed as a new town in the neighbouring parish of Heene.[11]
Municipal borough (1890–1974)[edit]
In 1890 Worthing and West Worthing were merged and incorporated as a municipal borough called Worthing. The borough was governed by a body formally called the "mayor, aldermen and burgesses of the borough of Worthing", generally known as the corporation, town council or borough council. The first mayor was Alfred Cortis.[12] The borough initially covered the whole of the parish of Heene and the part of the parish of Broadwater which had been the old local board district. The part of Broadwater within the borough became a separate parish called Worthing in 1894, which was enlarged to cover the whole borough in 1902. The borough was enlarged on several occasions, notably in 1902 when West Tarring and the residual parish of Broadwater were abolished, and in 1929 when the borough absorbed Goring-by-Sea and Durrington.[3]
In 1910 Ellen Chapman became Worthing's first woman councillor and one of the first women councillors in the UK. She subsequently became the first female mayor of Worthing in 1920.[12]
The Labour Party first put up candidates in Worthing in 1919, and its first councillor, Charles Barber, was elected in 1922.[13] Worthing was the first town in the UK to establish a branch of the Middle Class Union, which in Worthing was largely made up of retired army personnel. An MCU candidate, Colonel Connolly, was elected in 1921. The elections of Connolly and Barber brought about an end to the tradition in Worthing of non-party participation in elections.[14]
In 1933, Charles Bentinck Budd, who had been elected as an independent councillor to both Worthing Borough Council and West Sussex County Council in 1930, joined the British Union of Fascists. He was subsequently re-elected to the borough council in the 1933 elections, and the national press reported that Worthing was the first town in the country to elect a fascist councillor.[15][16] Over the next few months tensions rose, culminating on 9 October 1934 when anti-fascist protesters met outside a blackshirt rally at the Pavilion Theatre, in what became known as the Battle of South Street.[17]
Between 1933 and 1939 the Worthing Corporation purchased 1,000 acres (405 ha) of downland to the north of Worthing, which forms the Worthing Downland Estate.[18] In 1939 the Worthing Corporation purchased 72 acres (29 ha) acres of land at High Salvington. This land adjoined another 59 acres (24 ha) acres that were purchased around the same time.[19]
Modern borough (1974 onwards)[edit]
Worthing was reformed to become a non-metropolitan district in 1974 under the Local Government Act 1972. It kept the same boundaries, but there were changes to its responsibilities.[20] Worthing retained its borough status, allowing the chair of the reformed council to take the title of mayor, continuing Worthing's series of mayors dating back to 1890.[8][21]
Since 2008 Worthing Borough Council has worked in partnership with Adur District Council, as Adur and Worthing Councils, sharing a joint management structure, with a single Chief Executive.[22] In 2014 the council also became a constituent member of the Greater Brighton City Region.[23]
On 18 July 2019,[24] Worthing Borough Council declared a climate emergency, which aims to see the council become carbon-neutral by 2030.[25]
Governance[edit]
Worthing Borough Council provides district-level services. County-level services are provided by West Sussex County Council. There are no civil parishes in the borough, which has been an unparished area since 1974.[26][27]
Political control[edit]
The council has been under Labour majority control since 2022.[28]
Political control of the council since the 1974 reforms has been as follows:[29][30]
| Party in control | Years | |
|---|---|---|
| No overall control | 1974–1976 | |
| Conservative | 1976–1994 | |
| Liberal Democrats | 1994–1999 | |
| Conservative | 1999–2002 | |
| Liberal Democrats | 2002–2003 | |
| No overall control | 2003–2004 | |
| Conservative | 2004–2021 | |
| No overall control | 2021–2022 | |
| Labour | 2022–present | |
Leadership[edit]
The role of mayor is largely ceremonial in Worthing. Political leadership is instead provided by the leader of the council. The leaders since 2002 have been:[31]
| Councillor | Party | From | To | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Keith Mercer[32] | Conservative | Oct 2002 | 20 Jul 2009 | |
| Paul Yallop | Conservative | Jul 2009 | 26 Jan 2015 | |
| Daniel Humphreys | Conservative | 26 Jan 2015 | 10 Nov 2021 | |
| Kevin Jenkins | Conservative | 10 Nov 2021 | 20 May 2022 | |
| Beccy Cooper | Labour | 20 May 2022 | ||
Composition[edit]
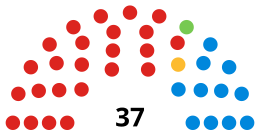
Following the 2023 election, the composition of the council was:[33]
| Party | Councillors | |
|---|---|---|
| Labour | 24 | |
| Conservative | 11 | |
| Green | 1 | |
| Liberal Democrats | 1 | |
| Total | 37 | |
The next election is due in 2024.
Elections[edit]
Since the last boundary changes in 2004 the council has comprised 37 councillors representing 13 wards, with each ward electing two or three councillors. Elections are held three years out of every four, with roughly a third of the council being elected each time for a four-year term of office. West Sussex County Council elections are held in the fourth year of the cycle when there are no borough council elections.[34]
Wards and councillors[edit]
| Ward | 2021—24 term | 2022—26 term | 2023—27 term | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Broadwater | Cathy Glynn-Davies (Labour) | Margaret Howard (Labour) | Dawn Smith (Labour) | |||
| Castle | Sam Theodoridi (Labour and Co-operative) | Ibsha Choudhury (Labour) | Sophie Cox (Labour) | |||
| Central | Rosey Whorlow (Labour) | Odul Bozkurt (Labour) | Caroline Baxter (Labour) | |||
| Durrington | Dan Coxhill (Conservative) | Charles James (Conservative) | ||||
| Gaisford | John Turley (Labour) | Dale Overton (Labour) | Henna Chowdhury (Labour) | |||
| Goring | Steve Waight (Conservative) | Kevin Jenkins (Conservative) | Claire Hunt (Green) | |||
| Heene | Emma Taylor (Labour) | Richard Mulholland (Labour) | Helen Abrahams (Labour) | |||
| Marine | Rebecca Cooper (Labour) | Andy Whight (Labour) | Vicki Wells (Labour) | |||
| Northbrook | Russ Cochran (Conservative) | Mike Barrett (Labour) | ||||
| Offington | Elizabeth Sparkes (Conservative) | Nigel Morgan (Conservative) | Daniel Humphreys (Conservative) | |||
| Salvington | Richard Nowak (Conservative) | Heather Mercer (Conservative) | Noel Atkins (Conservative) | |||
| Selden | Jon Roser (Labour) | Dan Hermitage (Labour) | Carl Walker (Labour) | |||
| Tarring | Hazel Thorpe (Liberal Democrat) | Rita Garner (Labour and Co-operative) | Hilary Schan (Labour) | |||
Premises[edit]
The council is based at Worthing Town Hall on Chapel Road. The building was purpose-built for the council and opened in 1933.[35][36]
Coat of arms[edit]

The borough's coat of arms includes three silver mackerel, a Horn of Plenty overflowing with corn and fruit on a cloth of gold, and the figure of a woman, considered likely to be Hygieia, the ancient Greek goddess of health, holding a snake. The images represent the health given from the seas, the fullness and riches gained from the earth and the power of healing. Worthing's motto is the Latin Ex terra copiam e mari salutem, which translates as 'From the land plenty and from the sea health'. The design was created in 1890 shortly after the town's incorporation as a borough, to serve as its official seal.[37] The design was formally granted as a coat of arms by the College of Arms in 1919.[38][39]
See also[edit]
- Adur and Worthing Councils
- Worthing Borough Council elections
- History of local government in Sussex
- West Sussex County Council
- Worthing Rural District
Bibliography[edit]
- Hare, Chris (1991). Historic Worthing: The Untold Story. Cassell Reference. ISBN 9780900075919.
References[edit]
- ^ "Council minutes, 23 May 2023". Adur and Worthing Councils. Retrieved 30 January 2024.
- ^ Ford, Martin (12 October 2021). "Adur and Worthing appoint permanent chief executive". The MJ. Retrieved 5 November 2023.
- ^ a b "Worthing Township / Civil Parish". A Vision of Britain through Time. GB Historical GIS / University of Portsmouth. Retrieved 30 January 2024.
- ^ "Worthing Improvement Act 1803". legislation.gov.uk. The National Archives. Retrieved 30 January 2024.
- ^ a b Hare 1991, p. 1
- ^ "Worthing Municpial Borough". National Archives. Retrieved 26 June 2018.
- ^ "Worthing: Local government and public services | British History Online".
- ^ a b "Worthing: Local government and public services". Victoria County History, British History Online. Retrieved 27 June 2018.
- ^ Reports of Cases Argued and Determined in the Court of Queen's Bench. 1865. p. 993. Retrieved 30 January 2024.
- ^ Hare 1991, p. 108
- ^ "Worthing Municipal Borough". The National Archives. Retrieved 30 January 2024.
- ^ a b "Past Mayors and Honorary Aldermen and Alderwomen". Adur and Worthing Councils. Retrieved 5 June 2018.
- ^ Hare 1991, p. 158
- ^ Hare 1991, p. 160
- ^ "The notorious Charles Bentinck Budd and the British Union of Fascists". www.worthingherald.co.uk.
- ^ "Charles Bentinck Budd".
- ^ "Friend of the Nazis who fate left behind". The Argus. 23 January 2003. Retrieved 6 May 2018.
- ^ Feest, Freddie (2012). "Rapid expansion between World Wars". HA Design. Retrieved 23 September 2017.
- ^ Municipal Journal, Volume 48, Part 2. 1939.
- ^ "The English Non-metropolitan Districts (Definition) Order 1972", legislation.gov.uk, The National Archives, SI 1972/2039, retrieved 22 June 2023
- ^ "District Councils and Boroughs". Parliamentary Debates (Hansard). 28 March 1974. Retrieved 4 December 2021.
- ^ "Senior Management structure". Adur & Worthing Councils. Retrieved 25 August 2015.
- ^ "City Deal; The beginning of a great city region". Brighton and Hove City Council. 11 March 2019. Retrieved 5 December 2019.
- ^ "List of Councils Who Have Declared a Climate Emergency". Retrieved 12 February 2020.
- ^ "Climate Emergency Declared By Adur & Worthing Councils". Adur and Worthing Councils. 10 July 2019. Retrieved 12 February 2020.
- ^ "Local Government Act 1972", legislation.gov.uk, The National Archives, 1972 c. 70, retrieved 31 May 2023
- ^ "Election Maps". Ordnance Survey. Retrieved 25 January 2024.
- ^ "Sussex election results 2022: Labour wins control of Worthing for first time". BBC News. 6 May 2022. Retrieved 6 May 2022.
- ^ "Compositions calculator". The Elections Centre. Retrieved 9 September 2022.
- ^ "Worthing". BBC News Online. 19 April 2008. Retrieved 8 October 2009.
- ^ "Council minutes". Adur and Worthing Councils. Retrieved 23 July 2022.
- ^ Holden, Paul (7 July 2009). "Worthing council leader to resign". The Argus. Retrieved 23 July 2022.
- ^ "Local elections 2023: live council results for England". The Guardian.
- ^ "The Borough of Worthing (Electoral Changes) Order 2002", legislation.gov.uk, The National Archives, SI 2002/2884, retrieved 30 January 2024
- ^ Historic England. "Worthing Town Hall including Assembly Hall and Worthing Room (1250786)". National Heritage List for England. Retrieved 31 January 2021.
- ^ "Programme and Souvenir for the opening of Worthing Town Hall". National Archives. Retrieved 31 January 2021.
- ^ "Untitled". Worthing Gazette. 17 December 1890. p. 5. Retrieved 31 January 2024.
- ^ "Arms of the Borough of Worthing". Worthing Borough Council website. Worthing Borough Council. Archived from the original on 5 May 2013. Retrieved 16 April 2009.
- ^ Young, Robert. "South East Region". Civic Heraldry of England and Wales. Retrieved 31 January 2024.
