Portal:North America
The North America Portal
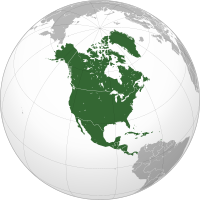
North America is a continent in the Northern and Western Hemispheres. North America is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the Caribbean Sea, and to the west and south by the Pacific Ocean. The region includes the Bahamas, Bermuda, Canada, the Caribbean, Central America, Clipperton Island, Greenland, Mexico, Saint Pierre and Miquelon, Turks and Caicos Islands, and the United States.
North America covers an area of about 24,709,000 square kilometers (9,540,000 square miles), representing approximately 16.5% of the Earth's land area and 4.8% of its total surface area. It is the third-largest continent by size after Asia and Africa, and the fourth-largest continent by population after Asia, Africa, and Europe. , North America's population was estimated as over 592 million people in 23 independent states, or about 7.5% of the world's population. In human geography, the terms "North America" and "North American" sometimes refer to just Canada, the United States, Mexico, and Greenland.
It is unknown with certainty how and when first human populations first reached North America. People were known to live in the Americas at least 20,000 years ago, but various evidence points to possibly earlier dates. The Paleo-Indian period in North America followed the Last Glacial Period, and lasted until about 10,000 years ago when the Archaic period began. The classic stage followed the Archaic period, and lasted from approximately the 6th to 13th centuries. Beginning in 1000 AD, the Norse were the first Europeans to begin exploring and ultimately colonizing areas of North America.
In 1492, the exploratory voyages of Christopher Columbus led to a transatlantic exchange, including migrations of European settlers during the Age of Discovery and the early modern period. Present-day cultural and ethnic patterns reflect interactions between European colonists, indigenous peoples, enslaved Africans, immigrants from Europe, Asia, and descendants of these respective groups. (Full article...)
The Gettysburg Address is a speech that U.S. President Abraham Lincoln delivered during the American Civil War at the dedication of the Soldiers' National Cemetery, now known as Gettysburg National Cemetery, in Gettysburg, Pennsylvania on the afternoon of November 19, 1863, four and a half months after the Union armies defeated Confederate forces in the Battle of Gettysburg, the Civil War's deadliest battle. It remains one of the most notable and famous speeches in American history.
Lincoln's carefully crafted and brief address, which was not scheduled as the day's primary speech, came to be seen as one of the greatest and most influential statements on the American national purpose. In just 271 words, beginning with the now famous phrase "Four score and seven years ago", referring to the signing of the Declaration of Independence 87 years earlier, Lincoln described the U.S. as a nation "conceived in Liberty, and dedicated to the proposition that all men are created equal", and represented the Civil War as a test that would determine whether such a nation could endure. Lincoln extolled the sacrifices of those who died at Gettysburg in defense of those principles, and then urged that the nation ensure: (Full article...)
Harold Adams Innis FRSC (November 5, 1894 – November 8, 1952) was a Canadian professor of political economy at the University of Toronto and the author of seminal works on media, communication theory, and Canadian economic history. He helped develop the staples thesis, which holds that Canada's culture, political history, and economy have been decisively influenced by the exploitation and export of a series of "staples" such as fur, fish, lumber, wheat, mined metals, and coal. The staple thesis dominated economic history in Canada from the 1930s to 1960s, and continues to be a fundamental part of the Canadian political economic tradition.
Innis's writings on communication explore the role of media in shaping the culture and development of civilizations. He argued, for example, that a balance between oral and written forms of communication contributed to the flourishing of Greek civilization in the 5th century BC. He warned, however, that Western civilization is now imperiled by powerful, advertising-driven media obsessed by "present-mindedness" and the "continuous, systematic, ruthless destruction of elements of permanence essential to cultural activity." His intellectual bond with Eric A. Havelock formed the foundations of the Toronto School of communication theory, which provided a source of inspiration for future members of the school Marshall McLuhan and Edmund Snow Carpenter. (Full article...)The Gadsden Purchase (Spanish: Venta de La Mesilla "La Mesilla sale") is a 29,640-square-mile (76,800 km2) region of present-day southern Arizona and southwestern New Mexico that the United States acquired from Mexico by the Treaty of Mesilla, which took effect on June 8, 1854. The purchase included lands south of the Gila River and west of the Rio Grande where the U.S. wanted to build a transcontinental railroad along a deep southern route, which the Southern Pacific Railroad later completed in 1881–1883. The purchase also aimed to resolve other border issues.
The first draft was signed on December 30, 1853, by James Gadsden, U.S. minister to Mexico, and by Antonio López de Santa Anna, president of Mexico. The U.S. Senate voted in favor of ratifying it with amendments on April 25, 1854, and then sent it to President Franklin Pierce. Mexico's government and its General Congress or Congress of the Union took final approval action on June 8, 1854, when the treaty took effect. The purchase was the last substantial territorial acquisition in the contiguous United States, and defined the Mexico–United States border. The Arizona cities of Tucson, Yuma and Tombstone are on territory acquired by the U.S. in the Gadsden Purchase. (Full article...)Did you know...
- ...that the Cuban night lizard is less than 4 cm long and lives exclusively in the west corner of the southern-most coast of Cuba?
- ... that tequila was first produced in the 16th century?
- ...that the Soufrière Hills volcano is an active complex stratovolcano with many lava domes forming its summit on the Caribbean island of Montserrat?
- ... that the Chontal Maya of Tabasco consider themselves the direct descendants of the Olmec civilization?
- ...that Jacob Piatt Dunn in 1886 wrote the first scholarly history concerning the Indian Wars?
Selected panorama

Topics
Categories
List articles
Related portals
Northern America
Central America
Caribbean
WikiProjects
 North America
North America-
 Canada
Canada -
 Greenland
Greenland -
 Mexico
Mexico -
 Saint Pierre and Miquelon
Saint Pierre and Miquelon -
 United States
United States  Central America
Central America-
 Belize
Belize -
 Costa Rica
Costa Rica -
 El Salvador
El Salvador -
 Guatemala
Guatemala -
 Honduras
Honduras -
 Nicaragua
Nicaragua -
 Panama
Panama  Mesoamerica
Mesoamerica Caribbean
Caribbean-
 Antigua and Barbuda
Antigua and Barbuda -
 Bahamas
Bahamas -
 Barbados
Barbados -
 Bermuda
Bermuda -
 Cuba
Cuba -
 Dominica
Dominica -
 Dominican Republic
Dominican Republic -
 Grenada
Grenada -
 Haiti
Haiti -
 Jamaica
Jamaica -
 Puerto Rico
Puerto Rico -
 Saint Kitts and Nevis
Saint Kitts and Nevis -
 Saint Lucia
Saint Lucia -
 Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
Saint Vincent and the Grenadines -
 Trinidad and Tobago
Trinidad and Tobago
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wikivoyage
Free travel guide -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus



























