Naked mole-rat: Difference between revisions
m Journal cites, added 1 PMC, templated 1 journal cites using AWB (11771) |
m Journal cites, Added 3 dois to journal cites using AWB (11769) |
||
| Line 49: | Line 49: | ||
===Size=== |
===Size=== |
||
Reproducing females become the dominant female, usually, by founding new colonies, fighting for the dominant position, or taking over once the reproducing female dies. These reproducing females tend to have longer bodies than that of their non-reproducing counterparts of the same skull width. Interestingly enough, the measurements of females before they became reproductive and after show significant increases in body size. It is believed that this trait does not occur due to pre-existing morphological differences but to the actual attainment of the dominant female position.<ref>{{cite journal | last1 = Young | first1 = A. J. | last2 = Bennett | first2 = N. C. | year = 2010 | title = Morphological Divergence of Breeders and Helpers in Wild Damaraland Mole Rat Societies | url = | journal = Evolution | volume = 64 | issue = 11| pages = 3190–3197 }}</ref> As with the reproductive females, the reproductive males also appear to be bigger in size than their non-reproducing counterparts but not as much so as in the case of the females. These males also have visible outlines of the testes through the skin of their abdomens. Unlike the females, there are usually multiple reproducing males <ref name="Jarvis, J. U. M. 1993">{{cite journal | last1 = Jarvis | first1 = J. U. M. | last2 = Bennett | first2 = N. C. | year = 1993 | title = Eusociality has evolved independently in two genera of bathyergid mole-rats — but occurs in no other subterranean mammal | url = | journal = Behavioral Ecology and Sociobiology | volume = 33 | issue = 4| pages = 253–260 }}</ref> |
Reproducing females become the dominant female, usually, by founding new colonies, fighting for the dominant position, or taking over once the reproducing female dies. These reproducing females tend to have longer bodies than that of their non-reproducing counterparts of the same skull width. Interestingly enough, the measurements of females before they became reproductive and after show significant increases in body size. It is believed that this trait does not occur due to pre-existing morphological differences but to the actual attainment of the dominant female position.<ref>{{cite journal | last1 = Young | first1 = A. J. | last2 = Bennett | first2 = N. C. | year = 2010 | title = Morphological Divergence of Breeders and Helpers in Wild Damaraland Mole Rat Societies | url = | journal = Evolution | volume = 64 | issue = 11| pages = 3190–3197 | doi=10.1111/j.1558-5646.2010.01066.x}}</ref> As with the reproductive females, the reproductive males also appear to be bigger in size than their non-reproducing counterparts but not as much so as in the case of the females. These males also have visible outlines of the testes through the skin of their abdomens. Unlike the females, there are usually multiple reproducing males <ref name="Jarvis, J. U. M. 1993">{{cite journal | last1 = Jarvis | first1 = J. U. M. | last2 = Bennett | first2 = N. C. | year = 1993 | title = Eusociality has evolved independently in two genera of bathyergid mole-rats — but occurs in no other subterranean mammal | url = | journal = Behavioral Ecology and Sociobiology | volume = 33 | issue = 4| pages = 253–260 | doi=10.1007/bf02027122}}</ref> |
||
==Ecology and behavior== |
==Ecology and behavior== |
||
| Line 69: | Line 69: | ||
==== Workers ==== |
==== Workers ==== |
||
Smaller workers focus on acquiring food and maintaining tunnels, while the larger workers are more reactive in case of attacks.<ref>{{cite news|url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/science_and_environment/10088502.stm|title=Meet the 'sabre-toothed sausage'|author=Rebecca Morelle|publisher=BBC News|date=May 5, 2010}}</ref> As in certain bee species, the workers are divided along a continuum of different worker-caste behaviors instead of discrete groups.<ref name=selfish_gene/> Some function primarily as tunnellers, expanding the large network of tunnels within the burrow system, and some primarily as [[soldier]]s, protecting the group from outside [[predation|predators]]. There are two main types of worker, the "frequent workers" who frequently perform tasks such as foraging and nest building and "infrequent workers" that show role overlap with the "frequent workers" but perform at a much slower rate.<ref>{{cite journal | last1 = Jarvis | first1 = J. U. M. | year = 1981 | title = Eusociality in a Mammal: Cooperative Breeding in Naked Mole-Rat Colonies | journal = Science | volume = 212 | issue = 4494| pages = 571–573 | jstor=1686202}}</ref> Workers are sterile when there is no new reproductive role to fill. |
Smaller workers focus on acquiring food and maintaining tunnels, while the larger workers are more reactive in case of attacks.<ref>{{cite news|url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/science_and_environment/10088502.stm|title=Meet the 'sabre-toothed sausage'|author=Rebecca Morelle|publisher=BBC News|date=May 5, 2010}}</ref> As in certain bee species, the workers are divided along a continuum of different worker-caste behaviors instead of discrete groups.<ref name=selfish_gene/> Some function primarily as tunnellers, expanding the large network of tunnels within the burrow system, and some primarily as [[soldier]]s, protecting the group from outside [[predation|predators]]. There are two main types of worker, the "frequent workers" who frequently perform tasks such as foraging and nest building and "infrequent workers" that show role overlap with the "frequent workers" but perform at a much slower rate.<ref>{{cite journal | last1 = Jarvis | first1 = J. U. M. | year = 1981 | title = Eusociality in a Mammal: Cooperative Breeding in Naked Mole-Rat Colonies | journal = Science | volume = 212 | issue = 4494| pages = 571–573 | jstor=1686202 | doi=10.1126/science.7209555}}</ref> Workers are sterile when there is no new reproductive role to fill. |
||
==== Colonies ==== |
==== Colonies ==== |
||
Revision as of 22:06, 8 January 2016
| Naked mole-rat Temporal range: Early Pliocene - Recent
| |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Missing taxonomy template (fix): | Heterocephalus glaber |
| Binomial name | |
| Heterocephalus glaber Rüppell, 1842
| |
| |
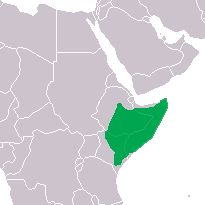
| Distribution of the naked mole-rat | |
The naked mole-rat (Heterocephalus glaber), also known as the sand puppy[citation needed] or desert mole rat, is a burrowing mammal native to parts of East Africa and is the only species currently classified in the genus Heterocephalus.[2] The naked mole-rat and the Damaraland mole-rat are the only known eusocial mammals.[3] It has a highly unusual set of physical traits that enable it to thrive in an otherwise harsh underground environment; it is the only mammalian thermoconformer.[4] (A thermoconforming organism adopts the surrounding temperature as its own body temperature, thus avoiding the need for internal thermoregulation).
The mole rat also lacks pain sensitivity in its skin, and has very low metabolic and respiratory rates. It is also remarkable for its resistance to cancer and its longevity. While traditionally considered to belong to the same family as other African mole-rats, the Bathyergidae, more recent investigation suggests that the naked mole-rat is sufficiently divergent to be placed in a new, separate family, Heterocephalidae.[5]
Description
Typical individuals are 8 to 10 cm (3 to 4 in) long and weigh 30 to 35 grams (1.1 to 1.2 oz). Queens are larger and may weigh well over 50 grams (1.8 oz), the largest reaching 80 grams (2.8 oz). They are well-adapted to their underground existence. Their eyes are quite small, and their visual acuity is poor. Their legs are thin and short; however, they are highly adept at moving underground and can move backward as fast as they can move forward. Their large, protruding teeth are used to dig and their lips are sealed just behind the teeth, preventing soil from filling their mouths while digging.[6] About a quarter of their musculature is used in the closing of their jaws while they dig - about the same proportion that is utilized in the human leg.[citation needed] They have little hair (hence the common name) and wrinkled pink or yellowish skin. They lack an insulating layer in the skin.
Physiology
The naked mole-rat is well adapted for the limited availability of oxygen within the tunnels of its typical habitat; its lungs are very small and its blood has a very strong affinity for oxygen, increasing the efficiency of oxygen uptake. It has a very low respiration and metabolic rate for an animal of its size, about 2/3 that of a similarly sized mouse, thus using oxygen minimally. In response to long periods of hunger, its metabolic rate can be reduced by up to 25 percent.
Thermoregulation
The naked mole-rat does not regulate its body temperature in typical mammalian fashion. They are thermoconformers rather than thermoregulators in that, unlike other mammals, body temperature tracks ambient temperatures. However, it has also been claimed that "the Naked Mole-Rat has a distinct temperature and activity rhythm that is not coupled to environmental conditions."[7] The relationship between oxygen consumption and ambient temperature switches from a typical poikilothermic pattern to a homeothermic mode when temperature is at 28 °C or higher.[8] At lower temperatures naked mole-rats can use behavioral thermoregulation. For example, cold naked mole-rats huddle together or seek shallow parts of the burrows that are warmed by the sun. Conversely, when they get too hot, naked mole-rats retreat to the deeper, cooler parts of the burrows.
Pain insensitivity

The skin of naked mole-rats lacks a key neurotransmitter called substance P that is responsible in mammals for sending pain signals to the central nervous system. As a result, the naked mole-rats feel no pain, even when they are exposed to acid or capsaicin. When they are injected with substance P, however, the pain signaling works as it does in other mammals, but only with capsaicin and not with acids. This is proposed to be an adaptation to the animal living in high levels of carbon dioxide due to poorly ventilated living spaces, which would cause acid to build up in their body tissues.[9]
Naked mole-rats' substance P deficiency has also been tied to their lack of the histamine-induced itching and scratching behavior typical of rodents.[10]
Resistance to cancer
Naked mole-rats appear to have a high resistance to tumours; there are no known cases of cancer-infected naked mole rats.[11] A potential mechanism that averts cancer is an "over-crowding" gene, p16, which prevents cell division once individual cells come into contact (known as "contact inhibition"). The cells of most mammals, including naked mole-rats, undergo contact inhibition via the gene p27 which prevents cellular reproduction at a much higher cell density than p16 does. The combination of p16 and p27 in naked mole-rat cells is a double barrier to uncontrolled cell proliferation, one of the hallmarks of cancer.[12]
On June 19, 2013, scientists reported that the reason naked mole-rats do not get cancer may be because they produce an "extremely high-molecular-mass hyaluronan" (HMW-HA) (a natural sugary substance), which is over "five times larger" than that in cancer-prone humans and cancer-susceptible laboratory animals.[13][14][15] The breakthrough scientific report was published a month later as the cover story of the journal Nature.[16] A few months later, the same University of Rochester research team announced that naked mole-rats have ribosomes that produce extremely error-free proteins.[17] Because of both of these discoveries, the journal Science named the naked mole-rat "Vertebrate of the Year" for 2013.[18]
Blind mole-rats Spalax golani and Spalax judaei also appear to be immune to cancer but by a different mechanism.[19]
Longevity
The naked mole-rat is also of interest because it is extraordinarily long-lived for a rodent of its size (up to 31 years[20]) and holds the record for the longest living rodent.[21] Naked mole-rats are highly resistant to cancer[11] and maintain healthy vascular function longer in their lifespan than shorter-living rats.[22] The reason for their longevity is debated, but is thought to be related to their ability to substantially reduce their metabolism during hard times, and so prevent aging-induced damage from oxidative stress. This has been referred to as "living their life in pulses".[23] Their longevity has also been attributed to “protein stability.”[24] Because of their extraordinary longevity, an international effort was put into place to sequence the genome of the naked mole-rat.[25] A draft genome was made available in 2011[26][27][28] with an improved version released in 2014.[29] Further transcriptome sequencing revealed genes related to mitochondria and oxidation reduction processes to have high expression levels in the naked mole-rat when compared to mice, which may contribute to their longevity.[30]
Size
Reproducing females become the dominant female, usually, by founding new colonies, fighting for the dominant position, or taking over once the reproducing female dies. These reproducing females tend to have longer bodies than that of their non-reproducing counterparts of the same skull width. Interestingly enough, the measurements of females before they became reproductive and after show significant increases in body size. It is believed that this trait does not occur due to pre-existing morphological differences but to the actual attainment of the dominant female position.[31] As with the reproductive females, the reproductive males also appear to be bigger in size than their non-reproducing counterparts but not as much so as in the case of the females. These males also have visible outlines of the testes through the skin of their abdomens. Unlike the females, there are usually multiple reproducing males [32]
Ecology and behavior
Distribution and habitat
The naked mole-rat is native to the drier parts of the tropical grasslands of East Africa, predominantly southern Ethiopia, Kenya, and Somalia.[33]
Clusters averaging 75 to 80 individuals live together in complex systems of burrows in arid African deserts. The tunnel systems built by naked mole-rats can stretch up to three to five kilometres (2–3 mi) in cumulative length.[34]
Roles
The naked mole-rat is the first mammal discovered to exhibit eusociality. This eusocial structure is similar to that found in ants, termites, and some bees and wasps.[35][36] Only one female (the queen) and one to three males reproduce, while the rest of the members of the colony function as workers. The queen and breeding males are able to breed at one year of age. Workers are sterile,[36] with the smaller focusing on gathering food and maintaining the nest, while larger workers are more reactive in case of attack. The non-reproducing females appear to be reproductively suppressed, meaning the ovaries do not fully mature, and do not have the same levels of certain hormones as the reproducing females. On the other hand, there is little difference of hormone concentration between reproducing and non-reproducing males. In experiments where the reproductive female was removed or died, one of the non-reproducing females would take over and become sexually active. Non-reproducing members of the colony are involved in cooperative care of the pups produced by the reproducing female. This occurs through the workers keeping the pups from straying, foraging for food, grooming, contributing to extension of tunnels, and keeping them warm.[32]
The Damaraland mole-rat (Cryptomys damarensis) is the only other eusocial mammal currently known.
Queen and gestation
The relationships between the queen and the breeding males may last for many years; other females are temporarily sterile. Queens live from 13 to 18 years, and are extremely hostile to other females behaving like queens, or producing hormones for becoming queens. When the queen dies, another female takes her place, sometimes after a violent struggle with her competitors. Once established, the new queen stretches the space between the vertebrae in her backbone to become longer and ready to bear pups.[37]
Gestation is about 70 days. A litter typically ranges from three to twelve pups, but may be as large as twenty-eight. The average litter size is eleven.[38] In the wild, naked mole-rats usually breed once a year, if the litter survives. In captivity, they breed all year long and can produce a litter every 80 days.[39] The young are born blind and weigh about 2 grams (0.07 oz). The queen nurses them for the first month; after which the other members of the colony feed them feces until they are old enough to eat solid food.
Workers
Smaller workers focus on acquiring food and maintaining tunnels, while the larger workers are more reactive in case of attacks.[40] As in certain bee species, the workers are divided along a continuum of different worker-caste behaviors instead of discrete groups.[34] Some function primarily as tunnellers, expanding the large network of tunnels within the burrow system, and some primarily as soldiers, protecting the group from outside predators. There are two main types of worker, the "frequent workers" who frequently perform tasks such as foraging and nest building and "infrequent workers" that show role overlap with the "frequent workers" but perform at a much slower rate.[41] Workers are sterile when there is no new reproductive role to fill.
Colonies
Colonies range in size from 20 to 300 individuals, with an average of 75.[42]
Diet

Naked mole-rats feed primarily on very large tubers (weighing as much as a thousand times the body weight of a typical mole-rat) that they find deep underground through their mining operations. A single tuber can provide a colony with a long-term source of food—lasting for months, or even years,[34] as they eat the inside but leave the outside, allowing the tuber to regenerate. Symbiotic bacteria in their intestines ferment the fibres, allowing otherwise indigestible cellulose to be turned into volatile fatty acids.
Naked mole-rats sometimes also eat their own feces.[34] This may be part of their eusocial behavior and a means of sharing hormones from the queen.[43]
Conservation status
Naked mole-rats are not threatened. They are widespread and numerous in the drier regions of East Africa.[44]
References
- ^ Template:IUCN2008
- ^ a b Woods, C.A.; Kilpatrick, C.W. (2005). "Infraorder Hystricognathi". In Wilson, D.E.; Reeder, D.M (eds.). Mammal Species of the World: A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference (3rd ed.). Johns Hopkins University Press. p. 1542. ISBN 978-0-8018-8221-0. OCLC 62265494.
- ^ O'Riain, M. Justin; Faulkes, Chris G. (2008). "African mole rats: eusociality, relatedness and ecological constraints". In Korb, Judith; Heinze, Jörgen (eds.). Ecology of Social Evolution. Springer. pp. 207–223. doi:10.1007/978-3-540-75957-7_10. ISBN 978-3-540-75956-0.
- ^ Welsh, Jennifer (2011-10-12). "Naked Mole Rat Genome May Hold Key to Long Life". Human Health & Longevity. LiveScience. Retrieved 2013-03-23.
- ^ Patterson, Bruce D.; Upham, Nathan S. (December 2014). "A newly recognized family from the Horn of Africa, the Heterocephalidae (Rodentia: Ctenohystrica)". Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society. 172 (4): 942–963. doi:10.1111/zoj.12201.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: postscript (link) - ^ "Naked Mole-Rat". Meet Our Animals. Smithsonian National Zoo Park.
- ^ "Uncovering the secrets of the naked mole-rat". DataScience.com. 2014. Retrieved February 9, 2015.
- ^ Daly, T. Joseph M.; Williams, Laura A.; Buffenstein, Rochelle (April 1997). "Catecholaminergic innervation of interscapular brown adipose tissue in the naked mole-rat (Heterocephalus glaber)". Journal of Anatomy. 190 (3): 321–326. doi:10.1046/j.1469-7580.1997.19030321.x.
- ^ Park, Thomas J.; Lu, Ying; Jüttner, René; St. J. Smith, Ewan; Hu, Jing; Brand, Antje; Wetzel, Christiane; Milenkovic, Nevena; Erdmann, Bettina; Heppenstall, Paul A.; Laurito, Charles E.; Wilson, Steven P.; Lewin, Gary R. (2008). "Selective Inflammatory Pain Insensitivity in the African Naked Mole-Rat (Heterocephalus glaber)". PLoS Biology. 6 (1): e13. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.0060013 (inactive 2015-06-22). PMC 2214810. PMID 18232734.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: DOI inactive as of June 2015 (link) CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ St John Smith, E; Blass, GR; Lewin, GR; Park, TJ (2010). "Absence of histamine-induced itch in the African naked mole-rat and "rescue" by Substance P." Molecular Pain. 6 (1): 29. doi:10.1186/1744-8069-6-29. PMC 2886013. PMID 20497578.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ a b Buffenstein R. (2008). "Negligible senescence in the longest living rodent, the naked mole-rat: insights from a successfully aging species". J Comp Physiol B. 178 (4): 439–45. doi:10.1007/s00360-007-0237-5. PMID 18180931.
- ^ Seluanov A, Hine C, Azpurua J, Feigenson M, Bozzella M, Mao Z, Catania KC, Gorbunova V (2009). "Hypersensitivity to contact inhibition provides a clue to cancer resistance of naked mole-rat". Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 106 (46): 19352–7. doi:10.1073/pnas.0905252106. PMC 2780760. PMID 19858485.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Zimmer, Carl (19 June 2013). "A Homely Rodent May Hold Cancer-Fighting Clues". New York Times. Retrieved 20 June 2013.
- ^ Callaway, E. (19 June 2013). "Simple molecule prevents mole rats from getting cancer". Nature. Retrieved 21 June 2013.
- ^ Briggs, H. (19 June 2013). "Naked mole-rat gives cancer clues". BBC News. Retrieved 21 June 2013.
- ^ "High-molecular-mass hyaluronan mediates the cancer resistance of the naked mole rat". Nature. 499 (7458): 346–349. 19 June 2013. doi:10.1038/nature12234. PMID 23783513.
{{cite journal}}: Cite uses deprecated parameter|authors=(help) - ^ Azpurua J, Ke Z, Chen IX, Zhang Q, Ermolenko DN, Zhang ZD, Gorbunova V, Seluanov A (2013). "Naked mole-rat has increased translational fidelity compared with the mouse, as well as a unique 28S ribosomal RNA cleavage". PNAS. 110 (43): 17350–17355. doi:10.1073/pnas.1313473110. PMID 24082110.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ "Breakthrough of the year 2013. Notable developments". Science. 342 (6165): 1435–1441. 2013. doi:10.1126/science.342.6165.1444. PMID 24357296.
- ^ Cormier, Zoe (November 5, 2012). "Blind mole rats may hold key to cancer". Nature. Retrieved November 15, 2012.
- ^ "Naked mole-rat (Heterocephalus glaber) longevity, ageing, and life history". Retrieved 2013-11-07.
- ^ Buffenstein R, Jarvis JU (May 2002). "The naked mole rat—a new record for the oldest living rodent". Sci Aging Knowledge Environ. 2002 (21): pe7. doi:10.1126/sageke.2002.21.pe7. PMID 14602989.
- ^ Csiszar, A; Labinskyy, N; Orosz, Z; Xiangmin, Z; Buffenstein, R; Ungvari, Z (2007). "Vascular aging in the longest-living rodent, the naked mole rat". American journal of physiology. Heart and circulatory physiology. 293 (2): H919–27. doi:10.1152/ajpheart.01287.2006. PMID 17468332.
- ^ "Ugly Duckling Mole Rats Might Hold Key To Longevity". Sciencedaily.com. 2007-10-16. Retrieved 2009-03-11.
- ^ Viviana Perez, Rochelle Buffenstein, Venkata Masamsetti, Shanique Leonard, Adam Salmon, James Mele, Blazej Andziak, Ting Yang, Yael Edrey, Bertrand Friguet, Walter Ward, Arlan Richardson, Asish Chaudhuri. "Protein stability and resistance to oxidative stress are determinants of longevity in the longest-living rodent, the naked mole rat". (March 3, 2009). Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences This reference requires further details
- ^ "Proposal to Sequence an Organism of Unique Interest for Research on Aging: Heterocephalus glaber, the Naked Mole-Rat". Genomics.senescence.info. Retrieved 2009-04-30.
- ^ "Naked Mole-Rat Database". Naked Mole-Rat Database 2011. Retrieved 5 July 2011.
- ^ "Naked Mole-Rat Genome Resource". Naked Mole-Rat Genome Resource 2011. Retrieved 5 July 2011.
- ^ Kim; et al. (Oct 2011). "Genome sequencing reveals insights into physiology and longevity of the naked mole rat". Nature. 2011 (21): 223–7. doi:10.1038/nature10533. PMC 3319411. PMID 21993625.
- ^ Keane; et al. (2014). "The Naked Mole Rat Genome Resource: facilitating analyses of cancer and longevity-related adaptations". Bioinformatics. 30 (24): 3558–3360. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btu579. PMC 4253829. PMID 25172923.
- ^ Yu C, Li Y, Holmes A, Szafranski K, Faulkes CG, Coen CW, Buffenstein R, Platzer M, de Magalhães JP, Church GM (2011). "RNA sequencing reveals differential expression of mitochondrial and oxidation reduction genes in the long-lived naked mole-rat (Heterocephalus glaber) when compared to mice". PLoS ONE. 6 (11): e26729. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0026729. PMID 22073188.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Young, A. J.; Bennett, N. C. (2010). "Morphological Divergence of Breeders and Helpers in Wild Damaraland Mole Rat Societies". Evolution. 64 (11): 3190–3197. doi:10.1111/j.1558-5646.2010.01066.x.
- ^ a b Jarvis, J. U. M.; Bennett, N. C. (1993). "Eusociality has evolved independently in two genera of bathyergid mole-rats — but occurs in no other subterranean mammal". Behavioral Ecology and Sociobiology. 33 (4): 253–260. doi:10.1007/bf02027122.
- ^ Sherman, Paul W.; Jennifer Jarvis; Richard Alexander (1991). The Biology of the Naked Mole-rat. Princeton, N.J.: Princeton University Press. ISBN 0691024480.
- ^ a b c d Dawkins, Richard (2006) [1976]. The Selfish Gene (30th anniversary ed.). Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-286092-5.
- ^ Jarvis, Jennifer (May 1981). "Eusociality in a Mammal: Cooperative Breeding in Naked Mole-Rat Colonies". Science. 212 (4494): 571–573. doi:10.1126/science.7209555. JSTOR 1686202.
- ^ a b Marshall, Presented by Michael (17 October 2014). "Eight ugly animals we should save anyway". BBC Earth. Retrieved 3 January 2015.
- ^ "San Diego's Animals. Mammals: Naked Mole-rat". Sandiegozoo.org. Retrieved 2013-03-23.
- ^ Counting mole-rat mammaries and hungry pups, biologists explain why naked rodents break the rules, Roger Segelken, Cornell News, August 9, 1999
- ^ Ross Piper (2007). Extraordinary Animals: An Encyclopedia of Curious and Unusual Animals. Westport, Conn: Greenwood Press. ISBN 0-313-33922-8.
- ^ Rebecca Morelle (May 5, 2010). "Meet the 'sabre-toothed sausage'". BBC News.
- ^ Jarvis, J. U. M. (1981). "Eusociality in a Mammal: Cooperative Breeding in Naked Mole-Rat Colonies". Science. 212 (4494): 571–573. doi:10.1126/science.7209555. JSTOR 1686202.
- ^ The Naked Truth About Mole-Rats, Jill Locantore, Smithsonian Zoogoer, May/June 2002
- ^ Reardon, Sara (20 October 2015). "Poo turns naked mole rats into better babysitters". Nature (journal). Retrieved 21 October 2015.
- ^ International Union for Conservation of Nature Red List: Heterocephalus Glaber listed as "least concern".
External links
- Ciszek, Deborah (1999). "Heterocephalus glaber, naked mole rat". Animal Diversity Web. Retrieved January 2010.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help)
- "Heterocephalus glaber: Cooperation is Key". Brookfield Zoo. Retrieved January 2010.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help) - "Naked Mole Rat Queen". Chicago Zoological Society. Retrieved January 2010.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help) (For MSIE only?) - Baskauf, Steve (2003). "Naked mole rat (Heterocephalus glaber) images". Bioimages at Vanderbilt University. Retrieved January 2010.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help) - Bryner, Jeanna (October 2006). "Naked Mole-rats Hold Clues to Human Aging". LiveScience. Retrieved January 2010.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help) - Sherman, Paul W.; Jarvis, Jennifer U. M. (November 2002). "Extraordinary life spans of naked mole-rats (Heterocephalus glaber)". Journal of Zoology. 258 (3): 307–311. doi:10.1017/S0952836902001437.
{{cite journal}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help) - Shuster, Gabriela; Sherman, P. W. (1998). "Tool use by naked mole-rats". Animal Cognition. 1 (1). Springer Berlin / Heidelberg: 71–74. doi:10.1007/s100710050009.
- Choi, Charles Q. (January 2008). "Strange Creature Immune to Pain". LiveScience. Retrieved January 2010.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help) - "Small Mammals (with a naked mole-rat webcam)". Smithsonian National Zoological Park. Retrieved January 2010.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help)

