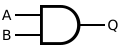
AND gate
| INPUT | OUTPUT | |
| A | B | A AND B |
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
The AND gate is a basic digital logic gate that implements logical conjunction - it behaves according to the truth table to the right. A HIGH output (1) results only if both the inputs to the AND gate are HIGH (1). If neither or only one input to the AND gate is HIGH, a LOW output results. In another sense, the function of AND effectively finds the minimum between two binary digits, just as the OR function finds the maximum. Therefore, the output is always 0 except when all the inputs are 1s.
Symbols
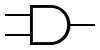
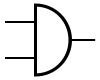
There are three symbols for AND gates: the American (ANSI or 'military') symbol and the IEC ('European' or 'rectangular') symbol, as well as the deprecated DIN symbol. For more information see Logic Gate Symbols.
|

|
|
| MIL/ANSI Symbol | IEC Symbol | DIN Symbol |
The AND gate with inputs A and B and output C implements the logical expression .
Implementations
 |
 |
 |
An AND gate is usually designed using N-channel (pictured) or P-channel MOSFETs. The digital inputs a and b cause the output F to have the same result as the AND function.
Alternatives
If no specific AND gates are available, one can be made from NAND or NOR gates, because NAND and NOR gates are considered the "universal gates," [1] meaning that they can be used to make all the others. XOR Gates can also be used to simulate AND functions, but are rarely used to do so.
| Desired gate | NAND construction | NOR construction |
|---|---|---|
 |
 |

|
See also
References
- ^ Mano, M. Morris and Charles R. Kime. Logic and Computer Design Fundamentals, Third Edition. Prentice Hall, 2004. p. 73.















