Fragmentation (weaponry)


Fragmentation is the process by which the casing, shot, or other components of an anti-personnel weapon, bomb, barrel bomb, land mine, IED, artillery, mortar, tank gun, or autocannon shell, rocket, missile, grenade, etc. are dispersed and/or shattered by the detonation of the explosive filler.
The correct term for these pieces is "fragmentation"; "shards" or "splinters" can be used for non-preformed fragments. Preformed fragments can be of various shapes (spheres, cubes, rods, etc.) and sizes, and are normally held rigidly within some form of matrix or body until the high explosive (HE) filling is detonated. The resulting high-velocity fragments produced by either method are the main lethal mechanisms of these weapons, rather than the heat or overpressure caused by detonation, although offensive grenades are often constructed without a frag matrix.
These casing pieces are often incorrectly referred to as "shrapnel", particularly by non-military media sources.[1][2]
History
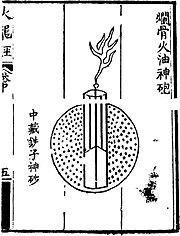
The use of fragmentation in bombs dates to the 14th century, and appears in the Ming Dynasty text Huolongjing. The fragmentation bombs were filled with iron pellets and pieces of broken porcelain. Once the bomb explodes, the resulting fragments are capable of piercing the skin and blinding enemy soldiers.[3]
For this bomb you take tung oil, yin hsiu, salammoniac, chin chih, scallion juice, and heat them so as to coat a lot of iron pellets and bits of broken porcelain. Then fill in (with a gunpowder core) to a case of cast iron making a fragmentation bomb. When it bursts, it breaks into pieces that wound the skin and break the bones (of enemy soldiers) and blinds their eyes.
— Huolongjing, Part 1 Chapter 2[3]
The modern fragmentation grenade was developed during the 20th century. The Mills bomb, first adopted in 1915 by the British army, is an early fragmentation grenade used in World War I. The Mk 2 grenade was a fragmentation grenade adopted by the American military based on the Mills bomb, and was in use during World War II.[4]
Difference between fragmentation and shrapnel shells

shrapnel shell
The term "shrapnel" is commonly, although incorrectly from a technical standpoint, used to refer to fragments produced by any explosive weapon. However, the shrapnel shell, named for Major General Henry Shrapnel of the British Royal Artillery, predates the modern high-explosive shell and operates by an entirely different process.[1]
A shrapnel shell consists of a shell casing filled with steel or lead balls suspended in a resin matrix, with a small explosive charge at the base of the shell. When the projectile is fired, it travels a pre-set distance along a ballistic trajectory, then the fuse ignites a relatively weak secondary charge (often black powder or cordite) in the base of the shell. This charge fractures the matrix holding the balls in place and expels the nose of the shell to open a path for the balls, which are then propelled out of the front of the shell without rupturing the casing (which falls to earth relatively unharmed and can be retrieved and reused).[5] These balls continue onward to the target, spreading out in a cone-shaped pattern at ground level, with most of their energy coming from the original velocity of the shell itself rather than the lesser force of the secondary charge that freed them from the shell. Since the cone of impact is relatively small, no more than 10 to 15 times the diameter of the shell, true shrapnel shells needed to be carefully sighted and judiciously used in order to maximize their impact on the enemy.
In contrast, a high-explosive shell contains a relatively large and energetic secondary charge of high explosive (known as a burster charge) which, when ignited by the fuse, produces a powerful supersonic shock wave that shatters the entire shell casing into many fragments that fly in all directions.[6] The use of high explosives with a fragmenting case improves efficiency as well as propelling a larger number of fragments at a higher velocity over a much wider area (40-60 times the diameter of the shell), giving high-explosive shells a vastly superior battlefield lethality that was largely impossible before the Industrial Era. World War I was the first major conflict in which HE shells were the dominant form of artillery; the failure to adapt infantry tactics to the massive increase in lethality they produced was a major element in producing the ghastly subterranean stalemate conditions of trench warfare, in which neither side could risk movement above ground without the guarantee of instant casualties from the constant, indiscriminate hail of HE shell fragments.
One easy comparison between fragmenting HE and shrapnel shells would be to imagine a shell of each type standing stationary and base-first on the ground; a high-explosive shell would be equally lethal if detonated in this state vs. detonating on impact after being fired, whereas a shrapnel shell would ineffectually fire its contents only a few feet into the air in a cone-shaped pattern (while the casing itself remained intact).[1] However, the reduced area of effect of shrapnel shells can be exploited, such as in the creeping barrage tactics of World War I, where shrapnel shells were able to be used much closer to friendly infantry than HE shells could.
Gallery of images
-
Early artillery shell, with the fragments it would generate. 1900
-
Artillery shell fragment from the Gulf War
-
Grenade fragments in the soft tissue of the lower leg (along with an old fracture of the fibula)
References
- ^ a b c "What is the difference between artillery shrapnel and shell fragments?". Combat Forces Journal. March 1952. Archived from the original on 10 February 2017.
- ^ [1] Archived 1 February 2014 at the Wayback Machine [2] Examples of use of "shrapnel" for casing fragments
- ^ a b Joseph Needham (1986). Military Technology: The Gunpowder Epic. Cambridge University Press. pp. 180–181. ISBN 978-0-521-30358-3.
- ^ The New Weapons of the World Encyclopedia: An International Encyclopedia from 5000 B.C. to the 21st Century. St. Martin's Press. 21 August 2007. p. 88. ISBN 978-0-312-36832-6.
- ^ U.S. War Department Technical Manual 9-1900 ‘'Ammunition, General'’. 18 June 1945. p. 106. Available: http://90thidpg.us/Reference/Manuals/index.html
- ^ What forensic conclusions can be drawn from the analysis of shell fragments: https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/pdf/10.1179/1574077313Z.00000000029?needAccess=true



