Greater hoopoe-lark
| Greater hoopoe-lark | |
|---|---|

| |
| Individual from Little Rann of Kutch | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| Phylum: | |
| Class: | |
| Order: | |
| Family: | |
| Genus: | |
| Species: | A. alaudipes
|
| Binomial name | |
| Alaemon alaudipes (Desfontaines, 1789)
| |
| Subspecies | |
| |
| |
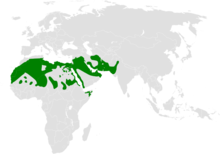
| resident range | |
| Synonyms | |
|
Certhilauda desertorum | |
The greater hoopoe-lark (Alaemon alaudipes), is a passerine bird which is a breeding resident of arid, desert and semi-desert regions from the Cape Verde Islands across much of north Africa, through the Arabian peninsula, Syria, Afghanistan, Pakistan and India. It was formerly known as the bifasciated lark.
Description

This lark is large, long-legged and slender-bodied with a distinctive down-curved bill. The face has dark markings including a line through the eye and whisker like-lines from the base of bill running under the eye. The breast is spotted and the underside is buffy white while the upper-parts are sandy grey. The female is slightly smaller with less prominent markings and the bill is slightly shorter.[2] The hind claw is short and straight.[3] The curved upper beak has the nostril opening exposed.[4] The tongue is bifid at the tip.[5]
Behaviour and ecology

Birds are seen singly or in pairs as they forage by running or walking in spurts, probing and digging the ground. They have been recorded to feed on the fruiting bodies of certain fungi.[6] The breeding season is mainly after the first rains, in India most records are from March to July. Late records in August when the rains were delayed have been noted in India.[7] The courtship display of the male consists of rising with fluttering wing-strokes and then diving down with closed wings to a perch. The slow flappy start to the song flight recall a hoopoe for which this species is named. The striking wing pattern of black wing feathers with a white base and trailing edge; and a white tail with black outer feathers are displayed in flight. The male also sings with rising and falling notes consisting of trilled whistles and clicks that have been transcribed as a tee-tee-tee followed by a prolonged tee-hoo while nosediving. The typical call is a rolling zreee or too. The nest is a cup made up of small sticks and placed on a low bush or on the ground, sometimes at the base of a bush.[2][8] The nest is prominent and often placed on an isolated bush.[9] Two or three eggs are laid and both sexes take turns in incubation. They feed on insects and other invertebrates, small lizards and seeds. Young birds are capable of swift running even before they can fly. The female may perform distraction displays when the young or nest are threatened.[5]

During the heat of the day, they may shelter in the burrows of Uromastyx lizards.[10][11] The water loss through their skin varies with temperature and they are able to live in very arid conditions.[12] Their breeding is dependent on the rains and in very dry years they may not breed.[13]
Distribution and populations
The wide distribution consists of several populations that have been designated as subspecies. These include boavistae of the Cape Verde Islands, the nominate alaudipes of the north African Sahara region and northern Arabia. Subspecies desertorum has been assigned to the populations along the Red Sea coast while the eastern population of Iraq, Pakistan and north-western India are assigned to doriae. Forms like pallida and variety cinerea are included in doriae.[14][15][16]
References
- ^ Template:IUCN
- ^ a b Rasmussen PC; JC Anderton (2005). Birds of South Asia: The Ripley Guide. Volume 2. Smithsonian Institution & Lynx Edicions. p. 309.
- ^ Ramsay, Wardlaw (1923). Guide to the birds of Europe and North Africa. Gurney and Jackson, London. p. 52.
- ^ Oates, EW (1890). Fauna of British India. Birds. Volume 2. Taylor and Francis, London. pp. 316–318.
- ^ a b Ali S; SD Ripley (1986). Handbook of the Birds of India and Pakistan. Volume 5 (2nd ed.). Oxford University Press. pp. 16–19.
- ^ Alsheikh, A.M.; Trappe, J.M. (1983). "Taxonomy of Phaeangium lefebvrei, a desert truffle eaten by birds". Canadian Journal of Botany. 61: 1919–1925. doi:10.1139/b83-204.
- ^ Bulkley, H (1902). "Nidification of the Desert Sand Lark Alaemon desertorum". J. Bombay Nat. Hist. Soc. 14 (1): 179–180.
- ^ Tieleman BI; H J Van Noordwijk; JB Williams (2008). "Nest site selection in a hot desert: trade-off between microclimate and predation risk?". The Condor. 110 (1): 116–124. doi:10.1525/cond.2008.110.1.116.
- ^ Betham, RM (1920). "The Desert Lark (Alaemon desertorum)". J. Bombay Nat. Hist. Soc. 27 (2): 400–401.
- ^ Cunningham P L (2000). "The use of burrows by Hoopoe Lark (Alaemon alaudipes)". Tribulus. 10: 21.
- ^ Williams, J. B.; Tieleman, B. I.; Shobrak, M. (1999). "Lizard burrows provide thermal refugia for larks in the Arabian desert". Condor. 101: 714–717. doi:10.2307/1370208.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|last-author-amp=ignored (|name-list-style=suggested) (help) - ^ Haugen, Michael J.; Tieleman, B. Irene; Williams, Joseph B. (2003). "Phenotypic flexibility in cutaneous water loss and lipids of the stratum corneum". J. Exp. Biol. 206: 3581–3588. doi:10.1242/jeb.00596.
- ^ Tieleman BI; JB Williams (2002). "Effects of food supplementation on behavioural decisions of hoopoe-larks in the Arabian Desert: balancing water, energy and thermoregulation" (PDF). Animal Behaviour. 63: 519–529. doi:10.1006/anbe.2001.1927.
- ^ Dickinson, E.C.; R.W.R.J. Dekker; S. Eck; S. Somadikarta (2001). "Systematic notes on Asian birds. 12. Types of the Alaudidae". Zool. Verh. Leiden. 335: 85–126.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|last-author-amp=ignored (|name-list-style=suggested) (help) - ^ Vaurie, C (1951). "A study of Asiatic larks". Bull. Am. Mus. Nat. Hist. 97: 431–526. hdl:2246/952.
- ^ Mayr E; JC Greenway Jr, eds. (1960). Check-list of birds of the World. Volume 9. Museum of Comparative Zoology, Cambridge, Massachusetts. p. 39.
External links
- Photographs and videos - The Internet Bird Collection

