Jacob Dircksz de Graeff
| Jacob Dircksz de Graeff | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Regent and Mayor of Amsterdam | |
| Reign | 1613–1638 |
| Predecessor | Reinier Pauw |
| Successor | Andries Bicker |
| Born | 1 January 1579 Emden |
| Died | 6 October 1638 (aged 69) Amsterdam |
| Burial | Oude Kerk, Amsterdam |
| Consort | Aaltje Boelens Loen |
| Issue | Cornelis de Graeff (1599–1664) Dirk de Graeff (1601–1633) Agneta de Graeff van Polsbroek (1603–1656) Wendela de Graeff Christina de Graeff (1609–1679) Andries de Graeff (1611–1678) |
| House | De Graeff |
| Father | Diederik Jansz. Graeff |
| Mother | Agnies Pietresdr van Neck |
Jacob Dircksz de Graeff, free lord of Zuid-Polsbroek (Emden 1571 – Amsterdam, 6 October 1638) was an illustrious member of the patrician De Graeff family. He was a powerful politician of the States Faction, regent and mayor of Amsterdam after the political collapse of Reynier Pauw in 1627.[1]
In the mid 17th century, during the Dutch Golden Age, De Graeff controlled the city's politics in close cooperation with his nephew Andries Bicker.[2][3] Jacob de Graeff was very critical of the Orange family's influence. He was a member of a family of regents who belonged to the republican political movement also referred to as the ‘state oriented’, the Dutch States Party, as opposed to the Royalists.[4]
Biography
Political background
During the Dutch Golden Age, the De Graeff and Bicker families were very critical of the Orange family's influence in the Netherlands. Together with the Republican-minded brothers and their cousins Andries, Cornelis and Jan Bicker, the family De Graeff strived for the abolition of stadtholdership. They desired the full sovereignty of the individual regions in a form in which the Republic of the United Seven Netherlands was not ruled by a single person. Instead of a sovereign (or stadtholder) the political and military power was lodged with the States General and with the regents of the cities in Holland. Jacob de Graeffs two sons Cornelis and Andries de Graeff became the strongest Dutch regents during the First Stadtholderless Period.[4][5]
Family
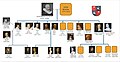
-
Overview of the personal family relationships of the Amsterdam oligarchy between the regent-dynasties Boelens Loen, De Graeff, Bicker (van Swieten), Witsen and Johan de Witt in the Dutch Golden Age
-
Descendants of Jacob Dircksz de Graeff and Aeltje Boelens Loen
Jacob Dircksz de Graeff was born in Emden, Lower Saxony, the Exile of his parents Dirck Jansz Graeff and Agnies Pietresdr van Neck. He grew up in Emden and later in Amsterdam, at the house De Keyser in the Niezel, a small street not far from the Oude Kerk. In 1597 he married to Aaltje Boelens Loen (27 February 1579 at Emden; † 29 August 1630 at Amsterdam), daughter of the politician Cornelis Andriesz Boelens Loen, descendant of Andries Boelens (1455–1519), a famous regent of Amsterdam. The couple had six children reaching adulthood:[6][7]
- Cornelis de Graeff (1599–1664), regent and burgomaster of Amsterdam, Dutch statesman
- Dirk de Graeff (1601–1637), Vroedschap and Schepen of Amsterdam
- Agneta de Graeff van Polsbroek (1603–1656), married Jan Bicker; her daughter Wendela Bicker married Johan de Witt, while her daughter Jacoba Bicker married her full cousin Pieter de Graeff
- Wendela de Graeff (1607–1652), painted by Rembrandt für his painting Jacob Blessing the Sons of Joseph
- Christina de Graeff (1609–1679), lady of Engelenburg (heiress to her uncle Pieter Dircksz Graeff) married in 1642 with Jacob Bicker and in 1648 to Pieter Trip
- Andries de Graeff (1611–1678), regent and burgomaster of Amsterdam, Dutch statesman
Feudality

On September 18, 1610, Jacob Dircksz de Graeff acquired the High Lordship of Zuid-Polsbroek from Charles of Aremberg,[8] which was freely inheritable and sellable as an allod.[9] Their acquisition increased the reputation and contributed to the aristocratization of the family, in which De Graeff and his heirs could be addressed as Vrijheer(en) van Zuid-Polsbroek ever since. De Graeff was also from 1604 Ambachtsheer (Lord of the manor) of Sloten, Sloterdijk, Nieuwer-Amstel, Osdorp and Amstelveen,[10] but not the owner of these glories. Rather, the city of Amsterdam bought them in 1529 from Reinoud III van Brederode,[11] and then gave it in fief to one of their council members. He was also chieflandholder of the Zijpe- en Hazepolder, Watergraafs- and Wiemermeer.[12] He also had the tithe in fief at Rietveld, Poldertienden (Oliviersblok), Groot-Rietveld, Klein-Rietveld, Tournooisveld, Oudeland and Bredeveld (Bredeveld).
Coat of arms
The coat of arms of Jacob Dircksz de Graeff is quartered with a heart shield and shows the following symbols:
- heart shield shows the three silver rhombuses on red (originally from the family Van Woerdern van Vliet) of the High Lordship Zuid-Polsbroek
- field 1 (left above) shows the silver shovel on red of their paternal ancestors, the Herren von Graben
- field 2 (right above) shows the silver swan on blue of the Fief Vredenhof [or that one (Waterland) of their maternal ancestors, the De Grebber]
- field 3 (left below), same as field 2
- field 4 (right below), same as field 1
- helmet covers in red and silver
- helm adornment shows an upright silver spade with ostrich feathers (Herren von Graben)
- motto: MORS SCEPTRA LIGONIBUS AEQUAT (DEATH MAKES SEPTRES AND HOES EQUAL)
-
Full coat of arms as "Vrijheer van Zuid-Polsbroek"
-
Gravestone of Jacob and his father Diederik Jansz. Graeff at Amsterdam's Oude Kerk
Career
Jacob de Graeff studied Classical language at Leiden University. In De Graeff was a merchant, and in 1598 became Schepen (alderman), from 1603 a member of the Vroedschap and in 1613–1638 mayor of Amsterdam six times.[13] He was first named as mayor of Amsterdam in 1611.[14]
During his councillorship in the States of Holland and West Friesland (1615–1617) De Graeff get sympathy with Oldenbarnevelt. In 1618, as regent-mayor of Amsterdam, Jacob de Graeff was deeply involved in the political crisis that engulfed the Oldenbarnevelt regime and brought about its fall.[13] Amsterdam was one of the Holland cities whose regents were partisans of the Remonstrants and had agitated for the Sharp Resolution of 1617 which authorized city governments to raise private armies, called waardgelders. The Counter-Remonstrants (enemies of the Remonstrants) opposed this, and the stadtholder, Maurice of Nassau viewed this policy as a challenge to his authority as commander-in-chief of the States Army. On 23 August 1618, by order of the States-General, Oldenbarnevelt and his chief supporters such as Hugo Grotius, Gilles van Ledenberg, Rombout Hogerbeets were arrested. Jacob de Graeff lost his political position in the government for some years. After the political collapse of the royalist Reynier Pauw in 1627 De Graeff returned to power again. During the late 1620s and the 1630s he controlled the city's politics in close cooperation with his nephew Andries Bicker.[13] Together with Bicker he was also the leader of the Arminian faction of the city.[3]
De Graeff died in Amsterdam and his tomb chapel can be found in the Oude Kerk floor, plots number 108 and 109. After his death his son Cornelis de Graeff and his cousins, the hardcore republican brothers Andries and Cornelis Bicker took over his role on the council.[4][5]
Trivia
Dirck Jansz Graeff play a role in the historic roman Krone der Welt by Sabine Weiß.[15]
Notes
- ^ Biografie Andries Bicker at the dutch DBNL
- ^ Google: De Republiek: 1477-1806, by J.I. Israel
- ^ a b Google: Geschiedenis van Holland, Part 2, book 2, from Eelco Beukers
- ^ a b c "Triomf der Vrede (nl)". Archived from the original on 2016-10-31. Retrieved 2009-12-04.
- ^ a b Pieter C. Vies Andries de Graeff (1611-1678) `t Gezagh is heerelyk: doch vol bekommeringen Archived 2012-03-01 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Croockewit: Genealogie van het geslacht de Graeff (1898), Sp. 132 ff.
- ^ Joost van den Vondels: Op Den Edelen En Gestrengen Heer Jakob de Graeff. (books.google.at).
- ^ Croockewit: Genealogie van het geslacht de Graeff, p 132, and Elias: De vroedschap van Amsterdam (1963), p 266
- ^ J. L. van der Gouw: Korte geschiedenis van de grenzen van de provincie Zuid-Holland (1963), Kap. III: De definitieve vorm van het graafschap (1300–1795)
- ^ Jacob Dircksz de Graeff at Historische Geslachtswapens
- ^ Nierop: The nobility of Holland (1993), p 155.
- ^ De Graeff at Historische Geslachtswapens
- ^ a b c P.C. Molhuysen and P.J. Blok Jacob Dircksz de Graeff at the "digitale bibliotheek voor de Nederlandse letteren" (DBNL)
- ^ A.J. van der Aa Jacob de Graeff in: Biographisch woordenboek der Nederlanden. Deel 7
- ^ Krone der Welt by Sabine Weiß
Literature
- Elias, Johan E. (1903–1905) De vroedschap van Amsterdam, 1578-1795, p. 266
- Lademacher, Horst Phönix aus der Asche? Politik und kultur der niederländischen Republik im Europa des 17. Jahrhunderts, Münster (2007, Waxmann Verlag), p. 228
- Israel, Jonathan I. (1995) The dutch Republic - Its Rise, Greatness, and Fall - 1477-1806, Clarendon Press, Oxford, ISBN 978-0-19-820734-4
- Burke, P. (1994) Venice and Amsterdam. A study of seventeenth-century élites.