Pond bat
| Pond bat | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| Phylum: | |
| Class: | |
| Order: | |
| Family: | |
| Genus: | |
| Species: | M. dasycneme
|
| Binomial name | |
| Myotis dasycneme (Boie, 1825)
| |
| |
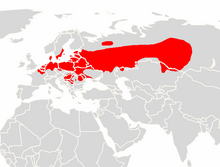
The pond bat (Myotis dasycneme) is a species of vesper bat. It is found in Eurasia from France to Russia and Kazakhstan.
Physical characteristics
The bat is medium-sized, with a noticeally short tragus for a species in the Myotis genus. Fur is thick and black-brown at the base, with brownish or yellowish-grey fur on the dorsal side and white-grey or yellow-grey fur on the ventral side.
Status
The species is endangered, with a large decline in numbers in the west of range; where many nursery sites have been lost, especially in the Netherlands. On a global scale the species is only near threatened, but detailed data from the eastern population is needed to draw reliable conclusions.[1]
Habitat
In the summer this species nests in lowland regions with areas of water, meadows and woods, with winter roosts also occurring in the foothills of mountains. The record for the altitude of a M. dasycneme roost is 1000 meters above sea level, with winter roosts not normally occurring more than 300 meters above sea level. Summer roosts are mostly in roof spaces or church towers, with individuals sometimes found nesting in hollow trees.
Reproduction
Females reach sexual maturity in the second year. The mating season is from the end of August, with nursery roosts then becoming occupied the following may with 40-400 females, although rarely any males. The maximum recorded age is 19 years.
Hunting
Members of this species emerge to hunt in late dusk, with either 1 or 2 foraging periods in evening and early morning. Hunting occurs over water, meadows and along woodland edges, with rapid, skillful flight (sometimes only 5–10 cm above water). Prey includes gnats, mosquitoes, moths and insects caught from the surface of the water.
Echolocation
Echolocation is done with FM singles between 60 and 24 kHz, with a 5-8 millisecond duration. The call sequence occurs every 115 milliseconds on average, with approximately 8-10 signals per second. Signal range is between 5 and 21 meters.

