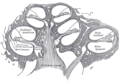
Spiral ganglion
| Spiral ganglion | |
|---|---|
 Transverse section of the cochlear duct of a fetal cat. (Ganglion spirale is labeled at top, second from left.) | |
 Part of the cochlear division of the acoustic nerve, highly magnified. | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | ganglion spirale |
| MeSH | D013136 |
| TA98 | A15.3.03.125 |
| TA2 | 6319 |
| TH | H3.11.09.3.04068 |
| FMA | 53445 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The spiral (cochlear) ganglion is the group of nerve cells that serve the sense of hearing by sending a representation of sound from the cochlea to the brain. The cell bodies of the spiral ganglion neurons are found in the modiolus, the conical shaped central axis in the cochlea.
Development
The rudiment of the acoustic nerve appears about the end of the third week as a group of ganglion cells closely applied to the cephalic edge of the auditory vesicle. The ganglion gradually splits into two parts, the vestibular ganglion and the spiral ganglion. The fibers connecting the spiral ganglion with the central nervous system form the cochlear nerve.
Anatomy
Neurons whose cell bodies lie in the spiral ganglion are strung along the bony core of the cochlea, and send fibers (axons) into the central nervous system (CNS). These bipolar neurons are the first neurons in the auditory system to fire an action potential, and supply all of the brain's auditory input. Their dendrites make synaptic contact with the base of hair cells, and their axons are bundled together to form the auditory portion of eighth cranial nerve. The number of neurons in the spiral ganglion is estimated to be about 35,000–50,000.[1]
Two apparent subtypes of spiral ganglion cells exist. Type I spiral ganglion cells comprise the vast majority of spiral ganglion cells (90-95% in cats and 88% in humans[2]), and exclusively innervate the inner hair cells. They are myelinated, bipolar neurons. Type II spiral ganglion cells make up the remainder. In contrast to Type I cells, they are unipolar and unmyelinated in most mammals. They innervate the outer hair cells, with each Type II neuron sampling many (15-20) outer hair cells.[3] In addition, outer hair cells form reciprocal synapses onto Type II spiral ganglion cells, suggesting that the Type II cells have both afferent and efferent roles.[4]
Gallery
-
Diagrammatic longitudinal section of the cochlea
References
- ^ Mark F. Bear, Barry W. Connors, and Michael A. Paradiso (2006). Neuroscience. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. ISBN 0-7817-6003-8.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Douglas B. Webster, Arthur N. Popper, Richard R. Fay, ed. (1992). The Mammalian Auditory Pathway: Neuroanatomy. Springer-Verlag. ISBN 0-387-97800-3.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: editors list (link) - ^ H Spoendlin (1972). "Innervation densities of the cochlea". Acta Otolaryngol.
- ^ JB Nadol Jr (1990). "Synaptic morphology of inner and outer hair cells of the human organ of Corti". J Elect Micr Tech.
External links
- Slide and overview at anatomy.dal.ca
- Slide at cytochemistry.net
- Image at University of New England, Maine
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 1051 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 1051 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)