Vinyl norbornene
Appearance

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
5-Ethenylbicyclo[2.2.1]hept-2-ene
| |
| Other names
2-Ethylidene-5-norbornene; 5-Vinyl-2-norbornene
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C9H12 | |
| Molar mass | 120.195 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colorless liquid |
| Boiling point | 141 °C (286 °F; 414 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
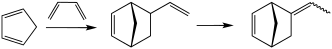
Vinyl norbornene (VNB) is an organic compound that consists of a vinyl group attached to norbornene. It is a colorless liquid. The compound exists as endo and exo isomers, but these are not typically separated. It is an intermediate in the production of the commercial polymer EPDM. It is prepared by the Diels-Alder reaction of butadiene and cyclopentadiene.[1]
Safety
LD50 (intravenous, rabbit = 0.10–0.05 mg/kg(female). It is also a neurotoxin.[2]
References
- ^ Behr, Arno (2000). "Organometallic Compounds and Homogeneous Catalysis". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. p. 10. doi:10.1002/14356007.a18_215. ISBN 978-3527306732.
- ^ "Comparative acute toxicity and primary irritancy of the ethylidene and vinyl isomers of norbornene". Journal of Applied Toxicology. 17 (4): 211–221. 1997. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1099-1263(199707)17:4<211::AID-JAT430>3.0.CO;2-X. PMID 9285533. S2CID 21154862.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|authors=ignored (help)
