Portal:Pan-Africanism
IntroductionWelcome to the Pan-Africanism portal!
Bienvenue sur le portail panafricanisme!   Pan-Africanism is a worldwide movement that aims to encourage and strengthen bonds of solidarity between all indigenous peoples and diasporas of African ancestry. Based on a common goal dating back to the Atlantic slave trade, the movement extends beyond continental Africans with a substantial support base among the African diaspora in the Americas and Europe. Pan-Africanism can be said to have its origins in the struggles of the African people against enslavement and colonization and this struggle may be traced back to the first resistance on slave ships—rebellions and suicides—through the constant plantation and colonial uprisings and the "Back to Africa" movements of the 19th century. Based on the belief that unity is vital to economic, social, and political progress, it aims to "unify and uplift" people of African ancestry. (Full article...) Selected articleThe Organisation of African Unity (OAU; French: Organisation de l'unité africaine (OUA)) was established on 25 May 1963 in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia with 32 signatory governments. It was disbanded on 9 July 2002 by its last chairperson, South African President Thabo Mbeki, and replaced by the African Union (AU). Some of the key aims of the OAU were to encourage political and economic integration among member states, and to eradicate colonialism and neo-colonialism from the African continent. Although it did achieve some success, there were also differences of opinion as to how that was going to be achieved. Selected biography
Alieu Ebrima Cham Joof (22 October 1924 – 2 April 2011) commonly known as Cham Joof, (pen name: Alh. A.E. Cham Joof) was a Gambian historian, politician, author, trade unionist, broadcaster, radio programme director, scout master, Pan-Africanist, lecturer, columnist, activist and an African nationalist who advocated for the Gambia's independence during the colonial era. Cham Joof was born on 22 October 1924 at 7 Griffith Street (Half-Die) in Bathurst now Banjul, the capital of the Gambia. He came from a Serer and Wolof background. He was the third child and the eldest son of Ebrima Joof (1887–1949) and Aji Anna Samba (1896 – 9 April 1977). On his father's side (the Joof family), he was a descendant of the Joof Dynasty of Sine and Saloum, and the Njie Dynasty of Jolof. On his mother's side, he was the great grand-nephew of Tafsir Sa Lolly Jabou Samba — a 19th-century Senegambian jihadist, military strategists and advisor to Maba Diakhou Bâ and one of the commanders of his army. Cham Joof was the elder brother of Gambian barrister Alhaji Bai Modi Joof. Selected history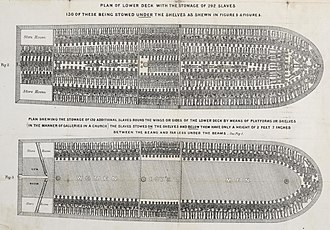  The Atlantic slave trade or transatlantic slave trade involved the transportation by slave traders of enslaved African people, mainly to the Americas. The slave trade regularly used the triangular trade route and its Middle Passage, and existed from the 16th to the 19th centuries. The vast majority of those who were enslaved and transported in the transatlantic slave trade were people from central and western Africa, who had been sold by other West Africans to Western European slave traders (with a small number being captured directly by the slave traders in coastal raids), who brought them to the Americas. The South Atlantic and Caribbean economies especially were dependent on the supply of secure labour for the production of commodity crops, making goods and clothing to sell in Europe. This was crucial to those western European countries which, in the late 17th and 18th centuries, were vying with each other to create overseas empires. The Portuguese were the first to engage in the Atlantic slave trade in the 16th century. In 1526, they completed the first transatlantic slave voyage to Brazil, and other European countries soon followed. Shipowners regarded the slaves as cargo to be transported to the Americas as quickly and cheaply as possible, there to be sold to work on coffee, tobacco, cocoa, sugar and cotton plantations, gold and silver mines, rice fields, construction industry, cutting timber for ships, in skilled labour, and as domestic servants. The first Africans imported to the English colonies were classified as "indentured servants", like workers coming from England, and also as "apprentices for life". By the middle of the 17th century, slavery had hardened as a racial caste, with the slaves and their offspring being legally the property of their owners, and children born to slave mothers were also slaves. As property, the people were considered merchandise or units of labour, and were sold at markets with other goods and services. Selected cultureThe culture of Africa is varied and manifold, consisting of a mixture of countries with various tribes that each have their own unique characteristic from the continent of Africa. It is a product of the diverse populations that today inhabit the continent of Africa and the African Diaspora. African culture is expressed in its arts and crafts, folklore and religion, clothing, cuisine, music and languages. Expressions of culture are abundant within Africa, with large amounts of cultural diversity being found not only across different countries but also within single countries. Even though African cultures are widely diverse, it is also, when closely studied, seen to have many similarities. For example, the morals they uphold, their love and respect for their culture as well as the strong respect they hold for the aged and the important i.e. Kings and Chiefs. Africa has influenced and been influenced by other continents. This can be portrayed in the willingness to adapt to the ever-changing modern world rather than staying rooted to their static culture. The Westernized few, persuaded by European culture and Christianity, first denied African traditional culture, but with the increase of African nationalism, a cultural recovery occurred. The governments of most African nations encourage national dance and music groups, museums, and to a lower degree, artists and writers. Selection of images depicting African culture
Selected imagesOrganisationsAll-African People's Revolutionary Party · African Society for Cultural Relations with Independent Africa · African Unification Front · African Union · African Queens and Women Cultural Leaders Network · Conseil de l'Entente · Convention People's Party · East African Community · Economic Freedom Fighters · Global Afrikan Congress · International African Service Bureau · International League for Darker People · Organisation of African Unity · Pan African Association · Pan-African Congress · Pan Africanist Congress of Azania · Rassemblement Démocratique Africain · Pan Africa Chemistry Network · Pan African Federation of Accountants · Pan-African Freedom Movement for East and Central Africa · Sahara and Sahel Observatory · UNIA-ACL · ZANU–PF
See also
& Festivals Photo by Helinä Rautavaara (1977) Publications
Films and TVAudios and videosDid you know ...that during the tumultuous Year of Africa, seventeen countries gained independence, South Africans began armed resistance to apartheid, and Patrice Lumumba (pictured) gained and lost his freedom?
Selected quotesIn addressing the first ever conference of the Organization of African Unity (1st May 1963). The Gambian Pan-Africanist and nationalist Alieu Ebrima Cham Joof delivered the following message:
Pan-Africanism topicsCategoriesThings you can do
Related portalsAssociated WikimediaThe following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
Discover Wikipedia using portals | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||










































