Portal:Asia

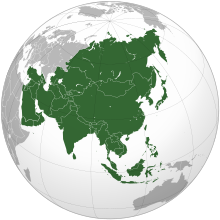 Asia (/ˈeɪʒə/ AY-zhə, UK also /ˈeɪʃə/ AY-shə) is the largest continent in the world by both land area and population. It covers an area of more than 44 million square kilometers, about 30% of Earth's total land area and 8% of Earth's total surface area. The continent, which has long been home to the majority of the human population, was the site of many of the first civilizations. Its 4.7 billion people constitute roughly 60% of the world's population. Asia shares the landmass of Eurasia with Europe, and of Afro-Eurasia with both Europe and Africa. In general terms, it is bounded on the east by the Pacific Ocean, on the south by the Indian Ocean, and on the north by the Arctic Ocean. The border of Asia with Europe is a historical and cultural construct, as there is no clear physical and geographical separation between them. It is somewhat arbitrary and has moved since its first conception in classical antiquity. The division of Eurasia into two continents reflects East–West cultural, linguistic, and ethnic differences, some of which vary on a spectrum rather than with a sharp dividing line. A commonly accepted division places Asia to the east of the Suez Canal separating it from Africa; and to the east of the Turkish Straits, the Ural Mountains and Ural River, and to the south of the Caucasus Mountains and the Caspian and Black seas, separating it from Europe. China and India traded places as the largest economies in the world from 1 to 1800 CE. China was a major economic power for much of recorded history, with the highest GDP per capita until 1500. The Silk Road became the main east–west trading route in the Asian hinterlands while the Straits of Malacca stood as a major sea route. Asia has exhibited economic dynamism as well as robust population growth during the 20th century, but overall population growth has since fallen. Asia was the birthplace of most of the world's mainstream religions including Hinduism, Zoroastrianism, Judaism, Jainism, Buddhism, Confucianism, Taoism, Christianity, Islam, Sikhism, as well as many other religions. (Full article...) Featured articleThe Ramayana (/rɑːˈmɑːjənə/; Sanskrit: रामायणम्, romanized: Rāmāyaṇam), also known as Valmiki Ramayana, as traditionally attributed to Valmiki, is a smriti text (also described as a Sanskrit epic) from ancient India, one of the two important epics of Hinduism known as the Itihasas, the other being the Mahabharata. The epic narrates the life of Rama, a prince of Ayodhya in the kingdom of Kosala. The epic follows his fourteen-year exile to the forest urged by his father King Dasharatha, on the request of Rama's stepmother Kaikeyi; his travels across forests in the Indian subcontinent with his wife Sita and brother Lakshmana; the kidnapping of Sita by Ravana, the king of Lanka, that resulted in war; and Rama's eventual return to Ayodhya along with Sita to be crowned king amidst jubilation and celebration. The scholars' estimates for the earliest stage of the text ranging from the 7th to 4th centuries BCE, and later stages extending up to the 3rd century CE, although original date of composition is unknown. It is one of the largest ancient epics in world literature and consists of nearly 24,000 verses (mostly set in the Shloka/Anuṣṭubh metre), divided into seven kāṇḍa (chapters). It belongs to the genre of Itihasa, narratives of past events (purāvṛtta), interspersed with teachings on the goals of human life. (Full article...)Selected Country Georgia (Georgian: საქართველო, romanized: sakartvelo, IPA: [sakʰartʰʷelo] ) is a transcontinental country in Eastern Europe and West Asia. It is part of the Caucasus region, bounded by the Black Sea to the west, Russia to the north and northeast, Turkey to the southwest, Armenia to the south, and Azerbaijan to the southeast. Georgia covers an area of 69,700 square kilometres (26,900 sq mi). It has a population of 3.7 million, of which over a third live in the capital and largest city, Tbilisi. Georgians, who are indigenous to the region, constitute a majority and a titular nation in Georgia. Georgia has been inhabited since prehistoric times, hosting the world's earliest known sites of winemaking, gold mining, and textiles. The classical era saw the emergence of several kingdoms, such as Colchis and Iberia, that formed the nucleus of the modern Georgian state. In the early fourth century, Georgians officially adopted Christianity, which contributed to their gradual unification and ethnogenesis. In the High Middle Ages, the Kingdom of Georgia reached its Golden Age during the reign of King David IV and Queen Tamar. The kingdom subsequently declined and disintegrated under the hegemony of various regional powers, including the Mongols, the Ottoman Empire, and Persia, before being gradually annexed into the Russian Empire starting in 1801. (Full article...)Featured biographyAbd al-Malik ibn Marwan ibn al-Hakam (Arabic: عَبْد الْمَلِك ٱبْن مَرْوَان ٱبْن الْحَكَم, romanized: ʿAbd al-Malik ibn Marwān ibn al-Ḥakam; July/August 644 or June/July 647 – 9 October 705) was the fifth Umayyad caliph, ruling from April 685 until his death in October 705. A member of the first generation of born Muslims, his early life in Medina was occupied with pious pursuits. He held administrative and military posts under Caliph Mu'awiya I (r. 661–680), founder of the Umayyad Caliphate, and his own father, Caliph Marwan I (r. 684–685). By the time of Abd al-Malik's accession, Umayyad authority had collapsed across the Caliphate as a result of the Second Fitna and had been reconstituted in Syria and Egypt during his father's reign. Following a failed invasion of Iraq in 686, Abd al-Malik focused on securing Syria before making further attempts to conquer the greater part of the Caliphate from his principal rival, the Mecca-based caliph Abd Allah ibn al-Zubayr. To that end, he concluded an unfavorable truce with the reinvigorated Byzantine Empire in 689, quashed a coup attempt in Damascus by his kinsman, al-Ashdaq, the following year, and reincorporated into the army the rebellious Qaysi tribes of the Jazira (Upper Mesopotamia) in 691. He then conquered Zubayrid Iraq and dispatched his general, al-Hajjaj ibn Yusuf, to Mecca where he killed Ibn al-Zubayr in late 692, thereby reuniting the Caliphate under Abd al-Malik's rule. The war with Byzantium resumed, resulting in Umayyad advances into Anatolia and Armenia, the destruction of Carthage and the recapture of Kairouan, the launchpad for the later conquests of western North Africa and the Iberian Peninsula, in 698. In the east, Abd al-Malik's viceroy, al-Hajjaj, firmly established the caliph's authority in Iraq and Khurasan, stamping out opposition by the Kharijites and the Arab tribal nobility by 702. Abd al-Malik's final years were marked by a domestically peaceful and prosperous consolidation of power. (Full article...)General imagesThe following are images from various Asia-related articles on Wikipedia. Featured pictureThe earliest credible evidence of either coffee drinking or knowledge of the coffee tree appears in the late 15th century, by Sufi Imam Muhammad Ibn Said Al Dhabhani who is known to have imported goods from Ethiopia to Yemen. From the Arabian peninsula its use spread across the globe. The picture shows Palestinian women grinding coffee beans.
Did you know...
Updated: 6:33, 14 February 2024 In the news
Related portalsMajor Religions in Asia Middle East Central Asia and Surroundings Indian Subcontinent Southeast Asia East Asia Selected panorama
The Hajj is an annual Islamic pilgrimage to Mecca, Saudi Arabia, the holiest city for Muslims, and a mandatory religious duty for Muslims that must be carried out at least once in their lifetime by all adult Muslims who are physically and financially capable of undertaking the journey, and can support their family during their absence. TopicsCategoriesAssociated WikimediaThe following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
More portalsShortcuts to this page: Asia portal • P:ASIA Purge server cache |































































































