Dusky leaf monkey: Difference between revisions
cleanup |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Short description|Species of Old World monkey}} |
{{Short description|Species of Old World monkey}} |
||
{{Speciesbox |
{{Speciesbox |
||
| name = Dusky leaf monkey<ref name=msw3>{{MSW3 Groves | |
| name = Dusky leaf monkey<ref name=msw3>{{MSW3 Groves |pages=177 |id=12100725}}</ref> |
||
| image = Dusky leaf monkey (8050982300).jpg |
| image = Dusky leaf monkey (8050982300).jpg |
||
| image_alt = |
| image_alt = |
||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
| status = EN |
| status = EN |
||
| status_system = IUCN3.1 |
| status_system = IUCN3.1 |
||
| status_ref = <ref name="iucn">{{cite iucn |author= |
| status_ref = <ref name="iucn">{{cite iucn |author=Boonratana, R., Ang, A., Traeholt, C. & Thant, N.M.L.|title=''Trachypithecus obscurus'' |year=2020 |page=e.T22039A17960562 |access-date=12 July 2020}}</ref> |
||
| genus = Trachypithecus |
| genus = Trachypithecus |
||
| parent = Trachypithecus obscurus group |
| parent = Trachypithecus obscurus group |
||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
}} |
}} |
||
The '''dusky leaf monkey''', '''spectacled langur''', or '''spectacled leaf monkey''' (''Trachypithecus obscurus'') is a species of [[primate]] in the family [[Cercopithecidae]]. It is found in |
The '''dusky leaf monkey''', '''spectacled langur''', or '''spectacled leaf monkey''' (''Trachypithecus obscurus'') is a species of [[primate]] in the family [[Cercopithecidae]]. It is found in [[Peninsular Malaysia]], [[Myanmar]] and [[Thailand]];<ref name=iucn/> however, dusky leaf monkeys have occasionally been observed in [[Singapore]]. It is not clear whether these monkeys are escaped pets or whether they swam to Singapore on their own volition from [[Johor, Malaysia]].<ref>{{cite journal|title=Dusky Langurs Trachypithecus obscurus (Reid, 1837) (Primates: Cercopithecidae) in Singapore: potential origin and conflicts with native primate species|author1=Ang, Andie|author2=Jabbar, Sabrina|author3=Khoo, Max|doi=10.11609/jott.5818.12.9.15967-15974|date=26 June 2020|journal=Journal of Threatened Taxa|volume=12|issue=9|pages=15967–15974|doi-access=free}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|title=Monkey species native to Malaysia spotted in Singapore|publisher=Straits Times|url=https://www.straitstimes.com/singapore/environment/monkey-species-native-to-malaysia-spotted-here|date=4 July 2020|author=Tan, Audrey|access-date=2020-07-04}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|title=S'porean encounters derpy-looking dusky langur in toilet at Central Catchment Nature Reserve|author=Thiagarajan, Sumita|date=7 November 2020|access-date=2020-11-07|publisher=Mothership|url=https://mothership.sg/2020/11/dusky-langur-singapore/}}</ref> |
||
==Taxonomy== |
|||
==Habitation and activity patterns== |
|||
The dusky leaf monkey is a type of [[lutung]] or leaf monkey, seven subspecies are currently recognised.<ref name=msw3/><ref name="ITIS">{{ITIS|id=573065|taxon=''Trachypithecus obscurus''|access-date=2 November 2021}}</ref> |
|||
[[File:Lutung.jpg|thumb|Lutung in urban area in Taman Rakan, Kajang.]] |
|||
Scan and sampling of 13 individuals (2 adult males, 8 adult females, 3 juveniles) was done by researchers from [[University Sains Malaysia]]. The researchers found that most of the dusky leaf monkeys spent their times positioning. The time that the dusky leaf monkey spent posting was estimated to be 40%. Researchers also found that the individuals spent approximately 33% of their time feeding on the leaves of the plants. In this research, researchers found these dusky leaf monkeys feeding on 10 different forest plant species on a regular basis. Dusky leaf monkeys tend to consume leaves which grow at higher elevations such as in the canopy level of a forest.<ref>M, Siti-Kauthar & Faudzir, Najmuddin & Md zain, Badrul munir & M.A.B, Abdul-Latiff. (2019). |
|||
PrimaTourism: Preliminary Study on Activity Budget of Dusky leaf monkey |
|||
Trachypithecus obscurus obscurus in Bukit Soga Perdana, Batu Pahat, Johor. IOP |
|||
Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science. 269. 10.1088/1755-1315/269/1/012045.</ref> |
|||
The food availability and the seasonal changes in the environment affect these monkeys consume. They are more fruit loving, but because there is not much availability they consume more leaves. |
|||
<ref>Ruslin, F., Matsuda, I., & Md-Zain, B. M. (2018). The feeding ecology and dietary overlap in two sympatric primate species, the long-tailed macaque (macaca fascicularis) and dusky langur (Trachypithecus obscurus obscurus), in Malaysia. Primates, 60(1), 41–50. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10329-018-00705-w</ref> |
|||
==Subspecies== |
|||
There are several subspecies of this [[lutung]]:<ref name=msw3/> |
|||
*''Trachypithecus obscurus obscurus'' |
*''Trachypithecus obscurus obscurus'' |
||
*''Trachypithecus obscurus flavicauda'' |
*''Trachypithecus obscurus flavicauda'' |
||
| Line 40: | Line 31: | ||
*''Trachypithecus obscurus seimundi'' |
*''Trachypithecus obscurus seimundi'' |
||
*''Trachypithecus obscurus sanctorum'' |
*''Trachypithecus obscurus sanctorum'' |
||
==Ecology== |
|||
Research in Malaysia found the dusky leaf monkey spends 40% of the day positioning, 33% feeding, 20% moving, and the rest of the time allogrooming (4%), playing (2%), and foraging (1%).<ref>{{cite conference |last1=Yap |first1=J. |last2=Ruppert |first2=N. |last3=Fadzly |first3=N. |year=2016 |title=Activity patterns and diet of a group of wild dusky leaf monkeys (''Trachypithecus obscurus'') in Penang, Malaysia |year=2016 |conference=Seminar Ekologi Malaysia}}</ref> It tends to consume leaves growing at higher elevations in the forest canopy.<ref>{{cite conference |last1=Siti-Kauthar |first1=M. |last2=Najmuddin |first2=M. F. |last3=Md-Zain |first3=B. M. |last4=Abdul-Latiff |first4=M. A. B. |year=2019 |title=PrimaTourism: preliminary study on activity budget of dusky leaf monkey ''Trachypithecus obscurus obscurus'' in Bukit Soga Perdana, Batu Pahat, Johor |conference=IOP Conference: Series Earth and Environmental Science |volume=269 |doi=10.1088/1755-1315/269/1/012045}}</ref> Fruit availability is season-dependent, and although the dusky leaf monkey in Malaysia eats 51% leaves and 40% fruits, it prefers to eat fruit when it is available.<ref>{{cite journal |last1=Ruslin |first1=F. |last2=Matsuda |first2=I. |last3=Md-Zain |first3=B. M. |year=2018 |title=The feeding ecology and dietary overlap in two sympatric primate species, the long-tailed macaque (''Macaca fascicularis'') and dusky langur (''Trachypithecus obscurus obscurus''), in Malaysia |journal=Primates |volume=60 |issue=1 |pages=41–50 |doi=10.1007/s10329-018-00705-w}}</ref> |
|||
==Gallery== |
==Gallery== |
||
| Line 53: | Line 47: | ||
==References== |
==References== |
||
{{Reflist}} |
{{Reflist}} |
||
* Yap, Joleen & Ruppert, Nadine & Fadzly, Nik. (2016). ''Activity patterns and diet of a group of wild dusky leaf monkeys (Trachypithecus obscurus) in Penang, Malaysia'' (2016). |
|||
==External links== |
==External links== |
||
{{Wikispecies |
{{Wikispecies|Trachypithecus obscurus|Dusky leaf monkey}} |
||
{{Commonscat |
{{Commonscat|Trachypithecus obscurus|Dusky leaf monkey}} |
||
*[https://web.archive.org/web/20080628074303/http://www.santabarbarazoo.org/showAnimals.asp?id=144 Information on Dusky Leaf Monkeys] from the [[Santa Barbara Zoo]] |
|||
*[http://www.monkeyland.co.za/index.php?comp=content&id=55 Information on Dusky Leaf Monkeys] from [[Monkeyland Primate Sanctuary]] |
|||
{{C.Colobinae nav}} |
{{C.Colobinae nav}} |
||
Revision as of 11:58, 2 November 2021
| Dusky leaf monkey[1] | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Primates |
| Suborder: | Haplorhini |
| Infraorder: | Simiiformes |
| Family: | Cercopithecidae |
| Genus: | Trachypithecus |
| Species group: | Trachypithecus obscurus group |
| Species: | T. obscurus
|
| Binomial name | |
| Trachypithecus obscurus (Reid, 1837)
| |
| |
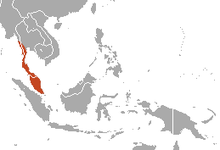
| Dusky leaf monkey range | |
The dusky leaf monkey, spectacled langur, or spectacled leaf monkey (Trachypithecus obscurus) is a species of primate in the family Cercopithecidae. It is found in Peninsular Malaysia, Myanmar and Thailand;[2] however, dusky leaf monkeys have occasionally been observed in Singapore. It is not clear whether these monkeys are escaped pets or whether they swam to Singapore on their own volition from Johor, Malaysia.[3][4][5]
Taxonomy
The dusky leaf monkey is a type of lutung or leaf monkey, seven subspecies are currently recognised.[1][6]
- Trachypithecus obscurus obscurus
- Trachypithecus obscurus flavicauda
- Trachypithecus obscurus halonifer
- Trachypithecus obscurus carbo
- Trachypithecus obscurus styx
- Trachypithecus obscurus seimundi
- Trachypithecus obscurus sanctorum
Ecology
Research in Malaysia found the dusky leaf monkey spends 40% of the day positioning, 33% feeding, 20% moving, and the rest of the time allogrooming (4%), playing (2%), and foraging (1%).[7] It tends to consume leaves growing at higher elevations in the forest canopy.[8] Fruit availability is season-dependent, and although the dusky leaf monkey in Malaysia eats 51% leaves and 40% fruits, it prefers to eat fruit when it is available.[9]
Gallery
-
Dusky leaf monkey - Kaeng Krachan National Park
-
Lost dusky leaf monkey calling - Kaeng Krachan National Park.
-
Dusky leaf monkey - Kaeng Krachan National Park
-
Adult male spectacled langur
-
Dusky leaf monkey - Ko Tarutao
References
- ^ a b Groves, C. P. (2005). Wilson, D. E.; Reeder, D. M. (eds.). Mammal Species of the World: A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference (3rd ed.). Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press. p. 177. ISBN 0-801-88221-4. OCLC 62265494.
- ^ a b Boonratana, R., Ang, A., Traeholt, C. & Thant, N.M.L. (2020). "Trachypithecus obscurus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2020: e.T22039A17960562. Retrieved 12 July 2020.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Ang, Andie; Jabbar, Sabrina; Khoo, Max (26 June 2020). "Dusky Langurs Trachypithecus obscurus (Reid, 1837) (Primates: Cercopithecidae) in Singapore: potential origin and conflicts with native primate species". Journal of Threatened Taxa. 12 (9): 15967–15974. doi:10.11609/jott.5818.12.9.15967-15974.
- ^ Tan, Audrey (4 July 2020). "Monkey species native to Malaysia spotted in Singapore". Straits Times. Retrieved 2020-07-04.
- ^ Thiagarajan, Sumita (7 November 2020). "S'porean encounters derpy-looking dusky langur in toilet at Central Catchment Nature Reserve". Mothership. Retrieved 2020-11-07.
- ^ "Trachypithecus obscurus". Integrated Taxonomic Information System. Retrieved 2 November 2021.
- ^ Yap, J.; Ruppert, N.; Fadzly, N. (2016). Activity patterns and diet of a group of wild dusky leaf monkeys (Trachypithecus obscurus) in Penang, Malaysia. Seminar Ekologi Malaysia.
- ^ Siti-Kauthar, M.; Najmuddin, M. F.; Md-Zain, B. M.; Abdul-Latiff, M. A. B. (2019). PrimaTourism: preliminary study on activity budget of dusky leaf monkey Trachypithecus obscurus obscurus in Bukit Soga Perdana, Batu Pahat, Johor. IOP Conference: Series Earth and Environmental Science. Vol. 269. doi:10.1088/1755-1315/269/1/012045.
- ^ Ruslin, F.; Matsuda, I.; Md-Zain, B. M. (2018). "The feeding ecology and dietary overlap in two sympatric primate species, the long-tailed macaque (Macaca fascicularis) and dusky langur (Trachypithecus obscurus obscurus), in Malaysia". Primates. 60 (1): 41–50. doi:10.1007/s10329-018-00705-w.





