Gumma (pathology): Difference between revisions
→Presentation: Added citation |
consistent citation formatting |
||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
[[File:Gummata hepatis.jpg|thumb|right|Hepatic gumma]] |
[[File:Gummata hepatis.jpg|thumb|right|Hepatic gumma]] |
||
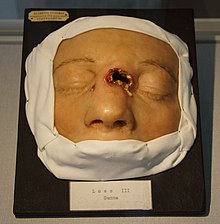
[[File:Wachsmoulage einer Gumma bei Siphilis.JPG|thumb|[[Moulage]] of a gumma in [[syphilis]] for training students. [[University of Tübingen]].]] |
[[File:Wachsmoulage einer Gumma bei Siphilis.JPG|thumb|[[Moulage]] of a gumma in [[syphilis]] for training students. [[University of Tübingen]].]] |
||
A '''gumma''' (plural '''gummata''' or '''gummas''') is a soft, non-cancerous growth resulting from the tertiary stage of [[syphilis]] (and [[yaws]]<ref>{{cite journal | |
A '''gumma''' (plural '''gummata''' or '''gummas''') is a soft, non-cancerous growth resulting from the tertiary stage of [[syphilis]] (and [[yaws]]<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Marks M | title = Advances in the Treatment of Yaws | journal = Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease | volume = 3 | issue = 3 | pages = 92 | date = August 2018 | pmid = 30274488 | pmc = 6161241 | doi = 10.3390/tropicalmed3030092 | doi-access = free }}</ref>). It is a form of [[granuloma]]. Gummas are most commonly found in the [[liver]] (''gumma hepatis''), but can also be found in brain, heart, skin, bone, testis, and other tissues, leading to a variety of potential problems including [[neurology|neurological]] disorders or [[heart valve]] disease. |
||
==Presentation== |
==Presentation== |
||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
These central regions begin to die through [[coagulative necrosis]], though they also retain some of the structural characteristics of previously normal tissues, enabling a distinction from the granulomas of [[tuberculosis]] where [[caseous necrosis]] obliterates preexisting structures. Other histological features of gummas include an ''intervening zone'' containing [[epithelium|epithelioid]] cells with indistinct borders and multinucleated [[giant cell]]s, and a ''peripheral zone'' of [[fibroblast]]s and [[capillary|capillaries]]. Infiltration of [[lymphocyte]]s and [[plasma cell]]s can be seen in the peripheral zone as well. With time, gummas eventually undergo fibrous degeneration, leaving behind an irregular scar or a round fibrous nodule.{{cn|date=April 2021}} |
These central regions begin to die through [[coagulative necrosis]], though they also retain some of the structural characteristics of previously normal tissues, enabling a distinction from the granulomas of [[tuberculosis]] where [[caseous necrosis]] obliterates preexisting structures. Other histological features of gummas include an ''intervening zone'' containing [[epithelium|epithelioid]] cells with indistinct borders and multinucleated [[giant cell]]s, and a ''peripheral zone'' of [[fibroblast]]s and [[capillary|capillaries]]. Infiltration of [[lymphocyte]]s and [[plasma cell]]s can be seen in the peripheral zone as well. With time, gummas eventually undergo fibrous degeneration, leaving behind an irregular scar or a round fibrous nodule.{{cn|date=April 2021}} |
||
It is restricted to [[necrosis]] involving [[Spirochaete|spirochaetal]] infections that cause [[syphilis]]. Growths that have the appearance of gummas are described as gummatous.<ref>{{ |
It is restricted to [[necrosis]] involving [[Spirochaete|spirochaetal]] infections that cause [[syphilis]]. Growths that have the appearance of gummas are described as gummatous.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Cui L, Xu Z, Hou H | title = Diagnosis and Treatment of Spinal Syphilitic Gumma: A Case Report | journal = Frontiers in Neurology | volume = 10 | pages = 1352 | date = 2020-01-15 | pmid = 32010040 | pmc = 6974620 | doi = 10.3389/fneur.2019.01352 | doi-access = free }}</ref> |
||
== Pathology == |
== Pathology == |
||
| Line 41: | Line 41: | ||
Syphilitic gummas are found in most but not all cases of tertiary syphilis, and can occur either singly or in groups. Gummatous lesions are usually associated with long-term syphilitic infection; however, such lesions can also be a symptom of benign late syphilis.{{cn|date=April 2021}} |
Syphilitic gummas are found in most but not all cases of tertiary syphilis, and can occur either singly or in groups. Gummatous lesions are usually associated with long-term syphilitic infection; however, such lesions can also be a symptom of benign late syphilis.{{cn|date=April 2021}} |
||
==References== |
== References == |
||
{{Reflist}} |
{{Reflist}} |
||
Revision as of 16:13, 25 February 2022
| Gumma (pathology) | |
|---|---|
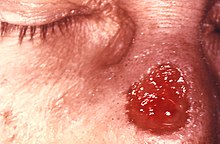 | |
| Gumma of nose due to a long-standing tertiary syphilitic infection. | |
| Specialty | Infectious diseases |

A gumma (plural gummata or gummas) is a soft, non-cancerous growth resulting from the tertiary stage of syphilis (and yaws[1]). It is a form of granuloma. Gummas are most commonly found in the liver (gumma hepatis), but can also be found in brain, heart, skin, bone, testis, and other tissues, leading to a variety of potential problems including neurological disorders or heart valve disease.
Presentation
Gummas have a firm, necrotic center surrounded by inflamed tissue, which forms an amorphous proteinaceous mass. The center may become partly hyalinized. These central regions begin to die through coagulative necrosis, though they also retain some of the structural characteristics of previously normal tissues, enabling a distinction from the granulomas of tuberculosis where caseous necrosis obliterates preexisting structures. Other histological features of gummas include an intervening zone containing epithelioid cells with indistinct borders and multinucleated giant cells, and a peripheral zone of fibroblasts and capillaries. Infiltration of lymphocytes and plasma cells can be seen in the peripheral zone as well. With time, gummas eventually undergo fibrous degeneration, leaving behind an irregular scar or a round fibrous nodule.[citation needed]
It is restricted to necrosis involving spirochaetal infections that cause syphilis. Growths that have the appearance of gummas are described as gummatous.[2]
Pathology
In syphilis, the gumma is caused by a reaction to spirochaete bacteria in the tissue. It appears to be the human body's way to slow down the action of this bacteria; it is a unique immune response that develops in humans after the immune system fails to kill off syphilis.[citation needed]
Epidemiology
The formation of gummata is rare in developed countries, but common in areas that lack adequate medical treatment.[citation needed]
Syphilitic gummas are found in most but not all cases of tertiary syphilis, and can occur either singly or in groups. Gummatous lesions are usually associated with long-term syphilitic infection; however, such lesions can also be a symptom of benign late syphilis.[citation needed]
References
- ^ Marks M (August 2018). "Advances in the Treatment of Yaws". Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease. 3 (3): 92. doi:10.3390/tropicalmed3030092. PMC 6161241. PMID 30274488.
- ^ Cui L, Xu Z, Hou H (2020-01-15). "Diagnosis and Treatment of Spinal Syphilitic Gumma: A Case Report". Frontiers in Neurology. 10: 1352. doi:10.3389/fneur.2019.01352. PMC 6974620. PMID 32010040.
