Multiple displacement amplification: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
== Materials == |
== Materials == |
||
[[Image:MDA reaction 1.JPG|thumb|300px|MDA reaction steps.JPG.]] |
[[Image:MDA reaction 1.JPG|thumb|300px|MDA reaction steps.JPG.]] |
||
=== Phi 29 DNA polymerase === |
=== Phi 29 DNA polymerase === |
||
| ⚫ | Bacteria phage ''Ф29'' DNA [[polymerase]] is a high proccessivity [[enzyme]] that can produce DNA product of 7kb to 10kb long. Its high fidelity and 3’-5’proofreading function reduces the amplification error rate to 1 in 10<sup>6</sup>-10<sup>7</sup> compared to conventional ''Taq'' polymerase. The reaction can be carried out at a moderate isothermal condition of 30 ℃ and therefore exempts the needs of the [[Thermocycler]]. It has been actively used in cell-free cloning, which is the enzymatic method of amplifying DNA in vitro without cell culturing and [[DNA extraction]]. The large fragment of ''Bst'' DNA polymerase is also used in MDA, but ''Ф29'' is generally preferred due to its sufficient product yield and proofreading function.<ref>{{cite journal |doi=10.1073/pnas.0508809102}}</ref> |
||
<ref>Hutchison CA, Smith HO, Pfannkoch C and Ventre C. Cell-free cloning using ''Ф29'' DNA polymerasse. ''PNAS''. 102 (48) (2005) 17332-17336.[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez]</ref><br /> |
|||
| ⚫ | Bacteria phage ''Ф29'' DNA [[polymerase]] is a high proccessivity [[enzyme]] that can produce DNA product of 7kb to 10kb long. Its high fidelity and 3’-5’proofreading function reduces the amplification error rate to 1 in 10<sup>6</sup>-10<sup>7</sup> compared to conventional ''Taq'' polymerase. The reaction can be carried out at a moderate isothermal condition of 30 ℃ and therefore exempts the needs of the [[Thermocycler]]. It has been actively used in cell-free cloning, which is the enzymatic method of amplifying DNA in vitro without cell culturing and [[DNA extraction]]. The large fragment of ''Bst'' DNA polymerase is also used in MDA, but ''Ф29'' is generally preferred due to its sufficient product yield and proofreading function.< |
||
=== Hexamer primers === |
=== Hexamer primers === |
||
Hexamer primers are sequences composed of six random [[nucleotides]]. The sequences are thiophosphate-medified at their 3’ end and therefore resistant to 3’-5’ [[exonuclease]] activity by ''Ф29'' DNA [[polymerase]]. MDA reaction starts with the annealing of random hexamer primers to the DNA template and then continues with the chain elongation phi29. Increasing number of primer annealing events happens along the amplification reaction. |
Hexamer primers are sequences composed of six random [[nucleotides]]. The sequences are thiophosphate-medified at their 3’ end and therefore resistant to 3’-5’ [[exonuclease]] activity by ''Ф29'' DNA [[polymerase]]. MDA reaction starts with the annealing of random hexamer primers to the DNA template and then continues with the chain elongation phi29. Increasing number of primer annealing events happens along the amplification reaction. |
||
=== Reaction === |
=== Reaction === |
||
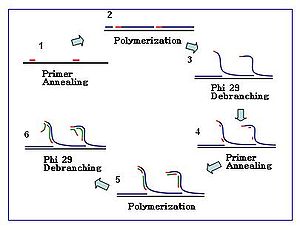
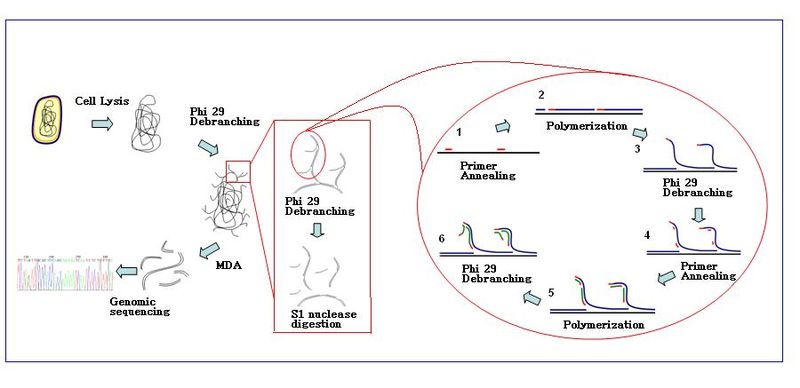
The amplification reaction initiates when multiple primer hexamers anneal to the template. When DNA synthesis proceeds to the next starting site, the polymerase displaces the newly produced DNA strand and continues its strand elongation. The strand displacement generates newly synthesized single stranded DNA template for more primers to anneal. Further primer annealing and strand displacement on the newly synthesized template results in a hyper-branched DNA network. The sequence debranching during amplification results in high yield of the products. To separate the DNA branching network, S1 nucleases is used to cleave the fragments at displacement sites. The nicks on the resulting DNA fragments are repaired by [[DNA polymerase I]]. The generated DNA fragments can be directly used for analysis or be ligated to generate genomic libraries for further sequencing analysis.<ref> |
The amplification reaction initiates when multiple primer hexamers anneal to the template. When DNA synthesis proceeds to the next starting site, the polymerase displaces the newly produced DNA strand and continues its strand elongation. The strand displacement generates newly synthesized single stranded DNA template for more primers to anneal. Further primer annealing and strand displacement on the newly synthesized template results in a hyper-branched DNA network. The sequence debranching during amplification results in high yield of the products. To separate the DNA branching network, S1 nucleases is used to cleave the fragments at displacement sites. The nicks on the resulting DNA fragments are repaired by [[DNA polymerase I]]. The generated DNA fragments can be directly used for analysis or be ligated to generate genomic libraries for further sequencing analysis.<ref>{{cite journal |pmid=18793430}}</ref> |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
=== Product quality === |
=== Product quality === |
||
MDA can generate 1-2µg of fetagram of DNA from single cell with genome coverage of up to 99%. Products also have lower error rate and larger sizes compared to PCR based ''Taq'' amplification. |
MDA can generate 1-2µg of fetagram of DNA from single cell with genome coverage of up to 99%. Products also have lower error rate and larger sizes compared to PCR based ''Taq'' amplification. |
||
General work flow of MDA:<ref>{{cite journal |pmid=17487184}}</ref> |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
<ref>Spits C, Caignec CL, Ryche, MD, Haute, LV, Steirteghem AV, Liebaers I, & Sermon, K. Whole-genome multiple displacement amplification from single cells. ''Nature Protocol'' 1.(4) (2004) 1965-1970.[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17487184?ordinalpos=&itool=EntrezSystem2.PEntrez.Pubmed.Pubmed_ResultsPanel.SmartSearch&log$=citationsensor]</ref><br /> |
|||
# ''Condition'': The MDA reaction with ''Ф29'' polymerase is carried out at 30 ℃. The reaction usually takes about 2.5-3 hours. |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
# ''End of reaction'': Inactivate enzymes at 65 ℃ before collection of the amplified DNA products |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
3 ''End of reaction'': Inactivate enzymes at 65 ℃ before collection of the amplified DNA products<br /> |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
== Advantages == |
== Advantages == |
||
| Line 45: | Line 43: | ||
== Applications == |
== Applications == |
||
=== Single cell genome sequencing === |
=== Single cell genome sequencing === |
||
Genome sequencing of single sperm cell have been reported and successfully amplified in Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis (PGD) or parental diagnosis. This ensures that an [[oocyte]] or early-stage [[embryo]] has no symptoms of disease before [[implantation]].<ref> |
Genome sequencing of single sperm cell have been reported and successfully amplified in Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis (PGD) or parental diagnosis. This ensures that an [[oocyte]] or early-stage [[embryo]] has no symptoms of disease before [[implantation]].<ref>{{cite journal |pmid=17278176}}</ref> |
||
Sequencing genome of single uncultured cell bacteria cell, such as ''Prochlorococcus'', and single [[spore]] of [[fungi]] has been reported.<ref> |
Sequencing genome of single uncultured cell bacteria cell, such as ''Prochlorococcus'', and single [[spore]] of [[fungi]] has been reported.<ref>{{cite journal |pmid=16732271}}</ref> The success of more MDA based genome sequencing from a single cell provides a powerful tool of studying diseases that have [[heterogeneous]] property, such as [[Cancer]]. |
||
The MDA products from a single cell has also been successfully used in array comparative genomics hybridization(CGH) experiments, which usually requires relatively large amount of amplified DNA. |
The MDA products from a single cell has also been successfully used in array comparative genomics hybridization(CGH) experiments, which usually requires relatively large amount of amplified DNA. |
||
Revision as of 12:06, 19 October 2009
Multiple Displacement Amplification (MDA)is a non-PCR based DNA amplification technique. This method can rapidly amplify minuet amount of DNA samples to reasonable quantity for genomic analysis. The reaction starts by annealing of random hexamers primers to the template and DNA synthesis is carried out by high fidelity enzyme, preferentially Ф29 at a constant temperature. Comparing with the conventional PCR amplification techniques, MDA generates larger sized products with lower error frequency. This method has been currently actively used in whole genome amplification (WGA) and has become a promising method to be applied in single cell genome sequencing and sequencing based genetic studies.
Background
Lots of biological and forensic cases involving genetic analysis require sequencing of minute amount of samples, such as DNA from uncultured single cell or trace amount of tissues collected from crime schemes. Conventional Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)-based DNA amplification methods are usually carried out on at least micrograms of DNA samples from cultured cells by using Taq polymerase and degenerate primers. However, the amount of DNA from uncultured single cell, which could be as less as a few femtograms, is not enough to start PCR reactions. Sufficient amount of DNA sample is crucial in sequencing based DNA analysis. Therefore, a more efficient method to amplify minuet amount of DNA is necessary, especially in single cell genomic studies.
Materials
Phi 29 DNA polymerase
Bacteria phage Ф29 DNA polymerase is a high proccessivity enzyme that can produce DNA product of 7kb to 10kb long. Its high fidelity and 3’-5’proofreading function reduces the amplification error rate to 1 in 106-107 compared to conventional Taq polymerase. The reaction can be carried out at a moderate isothermal condition of 30 ℃ and therefore exempts the needs of the Thermocycler. It has been actively used in cell-free cloning, which is the enzymatic method of amplifying DNA in vitro without cell culturing and DNA extraction. The large fragment of Bst DNA polymerase is also used in MDA, but Ф29 is generally preferred due to its sufficient product yield and proofreading function.[1]
Hexamer primers
Hexamer primers are sequences composed of six random nucleotides. The sequences are thiophosphate-medified at their 3’ end and therefore resistant to 3’-5’ exonuclease activity by Ф29 DNA polymerase. MDA reaction starts with the annealing of random hexamer primers to the DNA template and then continues with the chain elongation phi29. Increasing number of primer annealing events happens along the amplification reaction.
Reaction
The amplification reaction initiates when multiple primer hexamers anneal to the template. When DNA synthesis proceeds to the next starting site, the polymerase displaces the newly produced DNA strand and continues its strand elongation. The strand displacement generates newly synthesized single stranded DNA template for more primers to anneal. Further primer annealing and strand displacement on the newly synthesized template results in a hyper-branched DNA network. The sequence debranching during amplification results in high yield of the products. To separate the DNA branching network, S1 nucleases is used to cleave the fragments at displacement sites. The nicks on the resulting DNA fragments are repaired by DNA polymerase I. The generated DNA fragments can be directly used for analysis or be ligated to generate genomic libraries for further sequencing analysis.[2]
Product quality
MDA can generate 1-2µg of fetagram of DNA from single cell with genome coverage of up to 99%. Products also have lower error rate and larger sizes compared to PCR based Taq amplification.
General work flow of MDA:[3]
- Sample preparation: Samples are collected and diluted in the appropriate reaction buffer(Ca2+ and Mg2+ free). Cells are lysed with alkaline buffer.
- Condition: The MDA reaction with Ф29 polymerase is carried out at 30 ℃. The reaction usually takes about 2.5-3 hours.
- End of reaction: Inactivate enzymes at 65 ℃ before collection of the amplified DNA products
- DNA products can be purified with commercial purification kit.
Advantages
MDA generates sufficient yield of DNA products. It is a powerful tool of amplifying DNA molecules from samples, such as uncultured microorganism or single cells to the amount that would be sufficient for sequencing studies. The large size of MDA amplified DNA products also provide desirable sample quality for identifying the size of polymorphic repeat alleles. Its high fidelity also makes it reliable to be used in the single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) allele detection. Due to its strand displacement during amplification, the amplified DNA has sufficient coverage of the source DNA molecules, which provides high quality product for genomic analysis. The products of displaced strands can be subsequently cloned into vectors to construct library for subsequent sequencing reactions.
Limitations
Allelic dropout
ADO is defined as the random non-amplification of one of the alleles present in a heterozygous sample. Some studies have reported the ADO rate of the MDA products to be 0-60%. This drawback decreases the accuracy of genotyping of single sample and misdiagnosis in other MDA involved applications. ADO appears to be independent of the fragment sizes and has been reported to have similar rate in other single-cell techniques. Possible solutions are to use a different lysing conditions or to carry out multiple rounds of amplifications from the diluted MDA products since PCR mediated amplification from cultured cells has been reported to give lower ADO rates.
Preferential amplification
PA is over-amplification of one of the alleles in comparison to the other. Most studies on MDA have reported this issue. The amplification bias is currently observed to be random. It might affect the analysis of small stretches of genomic DNA in identifying Short Tandem Repeats (STR) alleles.
Primer-primer interactions
Endogenous template-independent primer-primer interaction is due to the random design of hexmer primers. One possiblesolution is to design constrained-randomized hexanucleotide primers that do not cross-hybridize.
Applications
Single cell genome sequencing
Genome sequencing of single sperm cell have been reported and successfully amplified in Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis (PGD) or parental diagnosis. This ensures that an oocyte or early-stage embryo has no symptoms of disease before implantation.[4]
Sequencing genome of single uncultured cell bacteria cell, such as Prochlorococcus, and single spore of fungi has been reported.[5] The success of more MDA based genome sequencing from a single cell provides a powerful tool of studying diseases that have heterogeneous property, such as Cancer.
The MDA products from a single cell has also been successfully used in array comparative genomics hybridization(CGH) experiments, which usually requires relatively large amount of amplified DNA.
Forensic analysis
Trace amount of samples collected from crime schemes can be amplified by MDA to the quantity that is enough for forensic DNA analysis, which is popularly used to in identifying victims and suspects.
See also
References
- ^ . doi:10.1073/pnas.0508809102.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help); Missing or empty|title=(help) - ^ . PMID 18793430.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help); Missing or empty|title=(help) - ^ . PMID 17487184.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help); Missing or empty|title=(help) - ^ . PMID 17278176.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help); Missing or empty|title=(help) - ^ . PMID 16732271.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help); Missing or empty|title=(help)
