Bromodeoxyuridine: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
reformatted refs and stripped before running citation bot |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Refimprove|date=June 2009}} |
|||
{{chembox |
{{chembox |
||
| Verifiedfields = changed |
| Verifiedfields = changed |
||
| Line 41: | Line 40: | ||
}} |
}} |
||
}} |
}} |
||
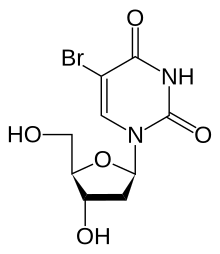
'''Bromodeoxyuridine''' (5-bromo-2'-deoxyuridine, BrdU) is a synthetic [[nucleoside]] that is an [[Analog (chemistry)|analogue]] of [[thymidine]]. BrdU is commonly used in the detection of proliferating cells in living tissues.<ref> |
'''Bromodeoxyuridine''' (5-bromo-2'-deoxyuridine, BrdU) is a synthetic [[nucleoside]] that is an [[Analog (chemistry)|analogue]] of [[thymidine]]. BrdU is commonly used in the detection of proliferating cells in living tissues.<ref>{{cite journal |pmid=21837406}}</ref> |
||
BrdU can be incorporated into the newly synthesized [[DNA]] of replicating cells (during the [[S phase]] of the cell cycle), substituting for thymidine during [[DNA replication]]. [[Antibody|Antibodies]] specific for BrdU can then be used to detect the incorporated chemical (see [[immunohistochemistry]]), thus indicating cells that were actively replicating their DNA. Binding of the antibody requires [[Denaturation (biochemistry)|denaturation]] of the DNA, usually by exposing the cells to acid or heat.<ref> |
BrdU can be incorporated into the newly synthesized [[DNA]] of replicating cells (during the [[S phase]] of the cell cycle), substituting for thymidine during [[DNA replication]]. [[Antibody|Antibodies]] specific for BrdU can then be used to detect the incorporated chemical (see [[immunohistochemistry]]), thus indicating cells that were actively replicating their DNA. Binding of the antibody requires [[Denaturation (biochemistry)|denaturation]] of the DNA, usually by exposing the cells to acid or heat.<ref name=pmid21785232>{{cite journal |pmid=21785232}}</ref> |
||
Because BrdU can replace thymidine during DNA replication, it can cause [[mutation]]s, and its use is therefore potentially a health hazard.<ref |
Because BrdU can replace thymidine during DNA replication, it can cause [[mutation]]s, and its use is therefore potentially a health hazard.<ref name=pmid21785232/> |
||
The Br substitution can also be used in X-Ray diffraction experiments in crystals containing either DNA or RNA. The Br atom acts as an anomalous scatterer and its larger size will affect the crystal's x-ray diffraction enough to detect isomorphous differences as well.<ref> |
The Br substitution can also be used in X-Ray diffraction experiments in crystals containing either DNA or RNA. The Br atom acts as an anomalous scatterer and its larger size will affect the crystal's x-ray diffraction enough to detect isomorphous differences as well.<ref>{{cite journal |pmid=16702655}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal |pmid=20382990}}</ref> |
||
==See also== |
==See also== |
||
Revision as of 10:51, 28 August 2011
| |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.378 |
| MeSH | Bromodeoxyuridine |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C9H11BrN2O5 | |
| Molar mass | 307.098 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Bromodeoxyuridine (5-bromo-2'-deoxyuridine, BrdU) is a synthetic nucleoside that is an analogue of thymidine. BrdU is commonly used in the detection of proliferating cells in living tissues.[1]
BrdU can be incorporated into the newly synthesized DNA of replicating cells (during the S phase of the cell cycle), substituting for thymidine during DNA replication. Antibodies specific for BrdU can then be used to detect the incorporated chemical (see immunohistochemistry), thus indicating cells that were actively replicating their DNA. Binding of the antibody requires denaturation of the DNA, usually by exposing the cells to acid or heat.[2]
Because BrdU can replace thymidine during DNA replication, it can cause mutations, and its use is therefore potentially a health hazard.[2]
The Br substitution can also be used in X-Ray diffraction experiments in crystals containing either DNA or RNA. The Br atom acts as an anomalous scatterer and its larger size will affect the crystal's x-ray diffraction enough to detect isomorphous differences as well.[3][4]
See also
External links
- BrdU incorporation during DNA replication - Jiayang Chien, Wellesley College
- BrdU at OpenWetWare, the bioscience wiki]
- BrdU Modifications at IDT DNA
References
- ^ . PMID 21837406.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help); Missing or empty|title=(help) - ^ a b . PMID 21785232.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help); Missing or empty|title=(help) - ^ . PMID 16702655.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help); Missing or empty|title=(help) - ^ . PMID 20382990.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help); Missing or empty|title=(help)
