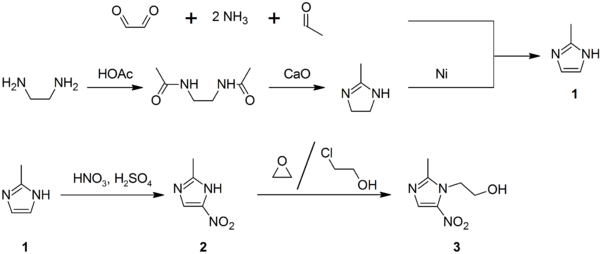Lysidine (chemical): Difference between revisions
Content deleted Content added
m r2.7.1) (robot Adding: ru:Лизидин |
Rifleman 82 (talk | contribs) +image, synth, reaction |
||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
}} |
}} |
||
'''Lysidine''' is an [[imidazoline]] derivative. This compound can be an intermediate in the synthesis of [[metronidazole]]; it may be prepared by reacting [[ethylenediamine]] with [[acetic acid]] to give the diamide, followed by treatment with lime. [[Raney nickel]] dehydrogenates it to [[2-methylimidazole]].<ref>{{cite journal | doi = 10.1007/BF00764821 | title = Synthesis of metronidazole from ethylenediamine | year = 1989 | last1 = Kraft | first1 = M. Ya. | last2 = Kochergin | first2 = P. M. | last3 = Tsyganova | first3 = A. M. | last4 = Shlikhunova | first4 = V. S. | journal = Pharmaceutical Chemistry Journal | volume = 23 | issue = 10 | pages = 861}}</ref> |
|||
'''Lysidine''' is an [[imidazoline]] derivative. |
|||
:[[File:Synthesis of metronidazole.png|600px]] |
|||
==References== |
|||
<references/> |
|||
==References== |
==References== |
||
Revision as of 02:30, 19 October 2011

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2-Methyl-4,5-dihydro-1H-imidazole
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.007.816 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| Properties | |
| C4H8N2 | |
| Molar mass | 84.12 g/mol |
| Melting point | 87 °C (dec.) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Lysidine is an imidazoline derivative. This compound can be an intermediate in the synthesis of metronidazole; it may be prepared by reacting ethylenediamine with acetic acid to give the diamide, followed by treatment with lime. Raney nickel dehydrogenates it to 2-methylimidazole.[2]
References
- ^ Lysidine at Sigma-Aldrich
- ^ Kraft, M. Ya.; Kochergin, P. M.; Tsyganova, A. M.; Shlikhunova, V. S. (1989). "Synthesis of metronidazole from ethylenediamine". Pharmaceutical Chemistry Journal. 23 (10): 861. doi:10.1007/BF00764821.
References