Lutra: Difference between revisions
authority |
m fmt |
||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
}} |
}} |
||
'''Lutra''' is a [[genus]] of [[otter]]s. |
'''Lutra''' is a [[genus]] of [[otter]]s. It includes the following species: |
||
*''Lutra lutra'' |
*''Lutra lutra'' – [[European otter]] |
||
*''Lutra nippon'' |
*''Lutra nippon'' – [[Japanese otter]] |
||
*''Lutra sumatrana'' |
*''Lutra sumatrana'' – [[hairy-nosed otter]] |
||
==Habitat== |
==Habitat== |
||
''Lutra'' species are semiaquatic mammals, so are well-adapted to both water and land. They prefer shallow, narrow areas of streams surrounded by mature trees and with rocks, especially where weirs reduce the flow of the water, as well as attract fishes. They seem to tolerate roads, residential and agricultural areas, but only moderate human interaction. They clearly avoid areas without vegetation cover and rocks. |
''Lutra'' species are semiaquatic mammals, so are well-adapted to both water and land. They prefer shallow, narrow areas of streams surrounded by mature trees and with rocks, especially where weirs reduce the flow of the water, as well as attract fishes. They seem to tolerate roads, residential and agricultural areas, but only moderate human interaction. They clearly avoid areas without vegetation cover and rocks.<ref>{{cite journal|title=Characterizing habitat preference of Eurasian river otter (''Lutra lutra'') in streams using a self-organizing map|doi=10.1007/s10201-009-0275-7|year=2009|last1=Cho|first1=Hee-Sun|last2=Choi|first2=Kwang-Hee|last3=Lee|first3=Sang-Don|last4=Park|first4=Young-Seuk|journal=Limnology|volume=10|issue=3|pages=203}}</ref> |
||
==Diet== |
==Diet== |
||
The otters' diets consist mainly of fish (hence, the aquatic environment). However, during the winter and in colder environments, fish consumption is significantly lower and the otters use other resources for their food supply. Their diets can consist of [[amphibians]] (mainly frogs and pond turtles), bird predation (mainly anserine species), small [[rodents]], and [[invertebrates]] such as water beetles, snails and crayfish. They have also feed on plants, specifically grasses. With this large diversity of prey and resources for their diets, otters are considered "opportunistic eaters".<ref>Lanszki, József, M. Molnár, |
The otters' diets consist mainly of fish (hence, the aquatic environment). However, during the winter and in colder environments, fish consumption is significantly lower and the otters use other resources for their food supply. Their diets can consist of [[amphibians]] (mainly frogs and pond turtles), bird predation (mainly anserine species), small [[rodents]], and [[invertebrates]] such as water beetles, snails and crayfish. They have also feed on plants, specifically grasses. With this large diversity of prey and resources for their diets, otters are considered "opportunistic eaters".<ref>{{cite journal|author=Lanszki, József, Molnár, M. and Molnár, T. |title=Factors affecting the predation of otter (''Lutra lutra'') on European pond turtle (''Emys orbicularis'')|doi=10.1111/j.1469-7998.2006.00132.x|year=2006|journal=Journal of Zoology|volume=270|issue=2|pages=219}}</ref> |
||
==Behavior== |
==Behavior== |
||
| Line 39: | Line 39: | ||
==References== |
==References== |
||
{{reflist}} |
|||
<references/> |
|||
{{Wikispecies|lutra}} |
{{Wikispecies|lutra}} |
||
{{Commons category|lutra}} |
{{Commons category|lutra}} |
||
Revision as of 08:45, 10 January 2013
| Lutra | |
|---|---|

| |
| Lutra lutra | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| Phylum: | |
| Class: | |
| Order: | |
| Family: | |
| Subfamily: | |
| Genus: | Lutra Brünnich, 1771
|
| Species | |
| |
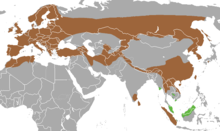
| Lutra ranges | |
Lutra is a genus of otters. It includes the following species:
- Lutra lutra – European otter
- Lutra nippon – Japanese otter
- Lutra sumatrana – hairy-nosed otter
Habitat
Lutra species are semiaquatic mammals, so are well-adapted to both water and land. They prefer shallow, narrow areas of streams surrounded by mature trees and with rocks, especially where weirs reduce the flow of the water, as well as attract fishes. They seem to tolerate roads, residential and agricultural areas, but only moderate human interaction. They clearly avoid areas without vegetation cover and rocks.[1]
Diet
The otters' diets consist mainly of fish (hence, the aquatic environment). However, during the winter and in colder environments, fish consumption is significantly lower and the otters use other resources for their food supply. Their diets can consist of amphibians (mainly frogs and pond turtles), bird predation (mainly anserine species), small rodents, and invertebrates such as water beetles, snails and crayfish. They have also feed on plants, specifically grasses. With this large diversity of prey and resources for their diets, otters are considered "opportunistic eaters".[2]
Behavior
Otters most commonly live in solitude (away from other otters).
References
- ^ Cho, Hee-Sun; Choi, Kwang-Hee; Lee, Sang-Don; Park, Young-Seuk (2009). "Characterizing habitat preference of Eurasian river otter (Lutra lutra) in streams using a self-organizing map". Limnology. 10 (3): 203. doi:10.1007/s10201-009-0275-7.
- ^ Lanszki, József, Molnár, M. and Molnár, T. (2006). "Factors affecting the predation of otter (Lutra lutra) on European pond turtle (Emys orbicularis)". Journal of Zoology. 270 (2): 219. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7998.2006.00132.x.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
