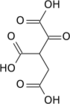
Aconitic acid

| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Prop-1-ene-1,2,3-tricarboxylic acid
| |
| Other names
Achilleic acid; Equisetic acid; Citridinic acid; Pyrocitric acid
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.007.162 |
| MeSH | Aconitate |
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H6O6 | |
| Molar mass | 174.108 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colorless crystals |
| Melting point | 198-199 °C (decomp) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
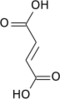
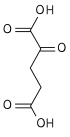
Aconitic acid is an organic acid. The two isomers are cis-aconitic acid and trans-aconitic acid. The conjugate base of cis-aconitic acid, cis-aconitate is an intermediate in the isomerization of citrate to isocitrate in the citric acid cycle. It is acted upon by the enzyme aconitase.
Aconitic acid can be synthesized by dehydration of citric acid using sulfuric acid:[2]
- (HO2CCH2)2COH(CO2H) → HO2CCH=C(CO2H)CH2CO2H + H2O
It was first prepared by thermal dehydration.[3]
References
- ^ cis-aconitate - Compound Summary, PubChem
- ^ William F. Bruce (1943). "Acontinic Acid". Organic Syntheses; Collected Volumes, vol. 2, p. 12.
- ^ B. Pawolleck,"Substitutionsproducte der Citronensäure und ein Versuch zur Synthese der letzteren" Justus Liebig's Annalen der Chemie 1875, volume 178, 150-170. doi:10.1002/jlac.18751780203