Battle of Mount Lycaeum
| Battle of Mount Lycaeum | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the Cleomenean War | |||||||
 A map of depicting the location of the Battle of Mount Lycaeum. | |||||||
| |||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
| Sparta | Achaean League | ||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||
| Cleomenes III | Aratus of Sicyon | ||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||
| Light | Heavy | ||||||
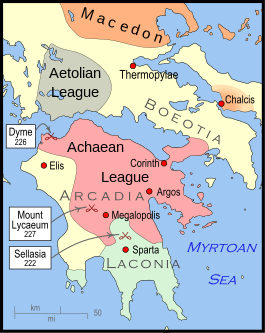
The Battle of Mount Lycaeum was a battle fought between Sparta led by Cleomenes III and the Achaean League commanded by Aratus. It was the first major battle of the Cleomenean War. The battle occurred at Mount Lycaeum on the border of Elis and Arcadia and ended in a Spartan victory.
Prelude
In 229 BC, Cleomenes III, King of Sparta, initiated a campaign with the aim of extending the regional power of his kingdom.[1] This was opposed by the major power in the Peloponnese, the Achaean League. In an attempt to curtail the resurgent power of Sparta, the Achaeans led by their strategos, Aratus, unsuccessfully attempted to re-capture the cities of Tegea and Orchomenus.[2] This failure was made worse when a vastly numerically superior Achaean army commanded by Aristomachos of Argos declined to offer battle to the army of Cleomenes.[1]
Though these failures were offset to some extent by the occupation of Caphyae, a city that had previously been taken over by Cleomenes, the Spartan ascendancy in the war was becoming apparent. Ptolemy III of Egypt, who had been supporting the Achaean campaign against Macedon, shifted his financial backing from the Achaean League to Sparta. Ptolemy based this on the assumption that Sparta would be a more useful ally in counterbalancing Macedon.[3]
Battle
Aratus was re-elected strategos in 227 BC and then launched an invasion of Elis, a Spartan ally. The Elians, unable to defeat the Achaeans, asked Sparta for assistance. The Spartan response was to dispatch Cleomenes with an army to aid their allies.[4] As the Achaeans were returning from Elis, Cleomenes launched an attack on the Achaeans near Mount Lycaeum, on the border of Elis and Arcadia.[4] The Achaeans, who were unprepared for battle, fled in disarray from the combat. The Spartans scored a comprehensive victory, routing the opposing army.[4] They managed to capture a great part of the Achaean army as well as inflicting massive casualties.[4] The victory was so complete that it was initially thought that Aratus had been slain in the midst of battle.[4]
Aftermath
Aratus was able to use the confusion in the aftermath of the battle to his advantage. He seized the city of Mantinea from the Spartans and secured it.[4] This success was short-lived as the Achaeans were decisively defeated by Cleomenes at the Battle of Ladoceia later in 227 BC[5] and again at the Battle of Dyme in 226 BC.[6] These victories established Spartan dominance over the Peloponnese.
Notes
- ^ a b Plutarch. Life of Cleomenes, 4
- ^ Polybius. The Rise of the Roman Empire, 2.46; Plutarch. Life of Cleomenes, 4; Hammond & Walbank 2001, p. 342.
- ^ Polybius. The Rise of the Roman Empire, 2.51; Green 1990, p. 249; Hammond & Walbank 2001, p. 347.
- ^ a b c d e f Plutarch. Life of Cleomenes, 5
- ^ Plutarch. Life of Cleomenes, 6; Smith 1873 [1]
- ^ Plutarch. Life of Cleomenes, 14; Green 1990, p. 258; Hammond & Walbank 2001, p. 347.
References
Primary sources
- Plutarch, translated by Richard Talbert, (1988). Life of Cleomenes. New York: Penguin Classics. ISBN 0-14-044463-7.
- Polybius, translated by Frank W. Walbank, (1979). The Rise of the Roman Empire. New York: Penguin Classics. ISBN 0-14-044362-2.
Secondary sources
- Green, Peter (1990). Alexander to Actium: The Historical Evolution of the Hellenistic Age. Los Angeles: University of California Press. ISBN 0-500-01485-X.
- Hammond, Nicholas Geoffrey Lemprière; Walbank, Frank William (2001). A History of Macedonia Volume III: 336–167 B.C. Oxford, United Kingdom: Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-814815-1.
- Smith, William (1873). Dictionary of Greek and Roman Biography and Mythology. London, United Kingdom: John Murray.
