Buscaline
| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
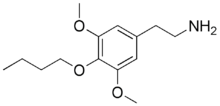
2-(4-Butoxy-3,5-dimethoxy-phenyl)-ethylamine
| |
| Other names
3,5-Dimethoxy-4-butoxyphenethylamine
2-(3,5-Dimethoxy-4-butoxyphenyl)ethanamine | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C14H23NO3 | |
| Molar mass | 253.34 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Buscaline, or 3,5-dimethoxy-4-butoxyphenethylamine, is a lesser-known psychedelic drug. It is an analog of mescaline. Buscaline was first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin. In his book PiHKAL (Phenethylamines i Have Known And Loved), the minimum dosage is listed as 150 mg, and the duration is unspecified (it says "several hours"). Buscaline produces no psychedelic or psychoactive effects, but causes heart arrythmia and light diarrhea. It does not cause any visuals or insights.[1] Very little data exists about the pharmacological properties, metabolism, and toxicity of buscaline.
See also
References
- ^ Shulgin, Alexander; Shulgin, Ann (September 1991). PiHKAL: A Chemical Love Story. Berkeley, California: Transform Press. ISBN 0-9630096-0-5. OCLC 25627628.
External links
