Muscular branches of perineal nerve
| Deep branch of the perineal nerve | |
|---|---|
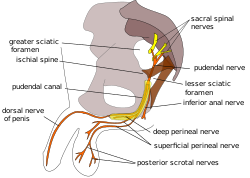 Pudendal nerve, its course through the lesser sciatic foramen, and branches, including deep perineal nerve at bottom. | |
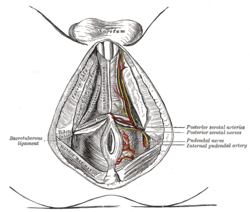 The superficial branches of the internal pudendal artery. (Deep branch of the perineal nerve visible but not labeled.) | |
| Details | |
| From | perineal nerve |
| Innervates | superficial transverse perineal muscle, bulbospongiosus muscle, ischiocavernosus muscle, bulb of penis, levator ani, external anal sphincter |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Nervus perinealis profundus |
| TA98 | A14.2.07.041 |
| TA2 | 6561 |
| FMA | 21894 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
The deep branch of the perineal nerve (or muscular branches) is a nerve of the perineum. It is a branch of the perineal nerve, from the pudendal nerve. It supplies the superficial transverse perineal muscle, bulbospongiosus muscle, ischiocavernosus muscle, the bulb of penis, levator ani, and the external anal sphincter.
Structure
The deep branch of the perineal nerve is a branch of the perineal nerve, itself a branch of the pudendal nerve.[1] It pierces the medial wall of the pudendal canal.[1]
The dorsal nerve of the penis for males and the dorsal nerve of the clitoris for females is the terminal branch of the pudendal nerve.
Function
The deep branch of the perineal nerve supplies the muscles of the perineum.[2] These include superficial transverse perineal muscle, bulbospongiosus muscle, ischiocavernosus muscle, the bulb of penis.[1] It also supplies levator ani, and the external anal sphincter.[1]
References
- ^ a b c d Rea, Paul (2015). "3 - Lower Limb Nerve Supply". Essential Clinically Applied Anatomy of the Peripheral Nervous System in the Limbs. Academic Press. pp. 101–177. doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-803062-2.00003-6. ISBN 978-0-12-803062-2.
- ^ Kyung Won, PhD. Chung (2005). Gross Anatomy (Board Review). Hagerstown, MD: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 268. ISBN 0-7817-5309-0.
External links
- Anatomy photo:41:10-0101 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "The Female Perineum: The Perineal Nerve"
- figures/chapter_32/32-3.HTM: Basic Human Anatomy at Dartmouth Medical School
- https://web.archive.org/web/20071101125123/http://anatomy.med.umich.edu/reproductive_system/perineum_ans.html
