Denawaka Ganga Mini Hydro Power Project
| Denawaka Ganga Mini Hydro Power Project | |
|---|---|
 Power House | |
| Country | Sri Lanka |
| Location | Ratnapura, Sabaragamuwa Province |
| Coordinates | 06°42′12″N 80°26′59″E / 6.70333°N 80.44972°E |
| Purpose | Power |
| Status | Operational |
| Construction began | October 2009 |
| Opening date | February 2012 |
| Owner(s) | Country Energy (Pvt) Ltd, a subsidiary of Vallibel Power Erathna |
| Power Station | |
| Type | run of the river |
| Installed capacity | 7.2 MW |
| Annual generation | 25 GWh |
Denawaka Ganga Mini Hydro Power[1][2] Project is a run of river mini hydro power project located in Ratnapura, Sri Lanka. The install capacity of the project is 7.2 MW and the annual generation is 25GWh. The generated energy is fed into the national electric grid of Sri Lanka.
Introduction[edit]
The plant uses the water flow of the river "Denawaka Ganga", which is the main tributary of the river "Kalu Ganga". Denawaka Ganga is formed by the confluence of river "Denawaka Ganga" (Upper) and river "Bambarabatu Oya" at a location known as Mawella. The headwaters of both rivers originate in the Bambarabatuwa forest reserve, a wet zone forest extending over more than 5,000 Hectares. Both rivers flow in a westerly direction south of the Adams Peak hill range, on the southwestern slopes of Sri Lanka. The catchment basin of the source, especially the Bambarabatu Oya sub-catchment, experiences some of the highest and most consistent rainfall in Sri Lanka. In total, the plant has a catchment area of 172.58km2.
The project comprises a diversion weir, intake, headrace channel, forebay, penstocks, powerhouse, tailrace, and switchyard. The intake structure is on the right bank of the river and the waterway continues for 1,800 meters in a channel with a box section up to the forebay tank. Then, water is taken through penstocks for a distance of 107 meters to the powerhouse.
Since the project is a run-of-the-river type, no need of storing water is required at the weir. The water leaves the generating station and is returned to the river without altering the existing flow or water levels. The electricity is stepped up to 33kV to match the transmission voltage of the local grid. The generated power is then transmitted through a 33kV line to the grid substation.
In the hydropower generation process, there are no greenhouse gas emissions and it does not involve the burning of fossil fuels during the process. Thus, electricity is generated through sustainable means without causing any negative impact on the environment. Hence, the technology adopted for the project activity is an environmentally safe and sound technology.
-
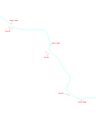
Sketch of the Power Plant
-
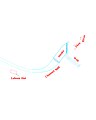
Sketch of the Power Plant on Google Image

Location[edit]
The Project area is located near Durekkanda, 9 km from Rathnapura Town in the Rathnapura Divisional Secretariat of the Rathnapura District in Sabaragamuwa Province of Sri Lanka.
Topography surveys of the project area are available in sheet 75 – Balangoda which on a scale of 1:50,000 by the Survey Department of Sri Lanka. The Geo Coordinates of the project activity are as follows, Weir - 060 41’ 39” N & 800 28’ 06” E Power Plant - 060 42’ 12” N & 800 26’ 59” E
The project location is close to the town of Ratnapura approximately 115 km from Colombo and the project is accessible from the main Ratnapura-Balangoda road. The site is reached by turning right just beyond the Malwala town and proceeding approximately 3 km on a by-road

Project Implementation[edit]
The project developer is Country Energy (Pvt) Ltd, a subsidiary of Vallibel Power Erathna PLC,[2] which is one of the leading mini hydropower developers in Sri Lanka.[3]
The development of the project was initiated in September 2002 with the investigation of the feasibility of the project and it was decided to develop the project with a capacity of 4.9MW. It took a few years to go through various regulatory clearances from the government authorities and a portion of government land was released in the year 2008 after a long process. Vallibel Power Erathna PLC acquired the project in early 2009 and decided to increase the capacity up to 7.2MW after a fresh feasibility study by the Vallibel project team[4] then, the construction works were started in October 2009[1]
The project commenced with construction work on an access road. Parallel to that, bungalow, batching plant, crusher, bulk material store yards, stores, working yards, site office and labour camps were properly structured and everything was managed in a good professional manner. This made the work more efficient and effective.
-
General Arrangement of Project Construction Area around Channel
-
General Arrangement of Project Construction Area around Weir and Intake
-
Site Office
-
Batching Plant
-
Crusher
-
Metal Store Yard
-
Bungalow (This is used as the accommodation for consultants, auditors, client's representatives and representatives of foreign equipment suppliers throughout the construction time)
-
Access Road
Weir[edit]
The weir of 30 m in length with a maximum height of 2.5 m was constructed to divert water to the intake. The weir is a straight concrete gravity structure made of plum concrete with an ogee profile. In order to prevent silt and trash from entering the channel, a trash screen was utilized.[2]
Intake[edit]

Intake was constructed with 4 sluice gates of 3m in width and 2.5 m in height. It satisfies the requirement of getting 25m3/s flow with 1.25 m/s intake flow velocity. The intake conveys the water into the concrete headrace channel. The intake is 30m long, 20m wide and 2.2m deep.[1]
-
Construction of Weir and Intake
-
Construction of Weir and Intake
-
Construction of Weir and Intake
-
Construction of Weir and Intake
-
Construction of Weir and Intake
-
Weir and Intake
-
Weir and Intake
Headrace Channel[edit]

The intake leads to the rectangular profiled headrace channel of 1,800 m length which was made of reinforced concrete. The headrace channel lies on the right bank of the stream and it has 4.4m inner width and 2.2m of wall height while the design flow is 27m3/s. This bank has moderately steep slopes, and the bedrock is marginally weathered. Reinforced concrete channel sections were placed on screed concrete and expansion joints were provided at every 17m with 250mm wide rubber water bars.[2]
-
Construction of Channel
-
Construction of Channel
-
Headrace Channel
-
Headrace Channel
-
Headrace Channel
Forebay[edit]
The headrace channel ends at the forebay tank. The forebay was made of reinforced concrete with a trash screen of 8.5m x 5.5m and it was placed before the penstock entry. The top of the forebay was covered while a spillway is constructed just upstream of the forebay. The forebay tank is 50m long and 9.3m wide. The maximum height of the tank is 10m.[1]
-
Construction of Forebay
-
Construction of Forebay
-
Construction of Forebay (Chief Executive Officer; Aruna Dheerasinghe with one of the project consultants and engineering staff members)
-
Construction of Forebay (Chief Executive Officer; Aruna Dheerasinghe Site Manager, Uditha Wijesena and engineering staff members)
-
Forebay
-
Forebay
-
After Construction, chief executive officer; Aruna Dheerasinghe and his team are waiting to see the success of their effort
-
After Construction, the first opening of gates of Forebay. (Chief Executive Officer; Aruna Dheerasinghe and engineering staff members)
-
Forbay Spillway
-
Forbay Spillway
-
Forbay Spillway
-
Forbay Spillway
-
Forbay Spillway
Penstock[edit]
After the forebay, water diverts into the penstock to deliver water into the turbines. The penstock comprises three welded steel pipes at the forebay, having a diameter of 1850mm each. Then the three pipes reduce to 1785mm diameter at Anchor 2. At the third anchor, the middle pipe bifurcates into two pipes having diameters of 1220mm each and the other two reduce to 1720mm in diameter and continue the same up to the powerhouse. The penstock trace is geologically well stable, and minor excavation was required to construct the penstock.
The pipe was spiral welded steel made to American Petroleum Institute standards (API 5L Grade B). The pipe was brought to the site in 5.8m sections and welded together at the site. The total length of the steel pipes was covered with reinforced concrete and it was buried with soil. The length of the penstock is 107m and the design flow of one pipe is 8.3m3/s for each of the 3 pipes.[1]
-
Installation of Penstock
-
Installation of Penstock
-
Installation of Penstock
-
Installation of Penstock
-
Installation of Penstock
-
Installation of Penstock
-
Installation of Penstock
-
Penstock Path after the Planting Programs
-
Anchor of the Penstock
Powerhouse[edit]

The powerhouse consists of the turbines, generators and control room. The turbine bay contains a 25MT capacity crane for handling of the equipment during installation and repairs. The necessary transformer and high voltage switchgear were housed outside the powerhouse.
The project generates electricity at 6.6kV and then steps it up to 33kV via four transformers. The electricity generated is exported via a 33kV transmission line of 10.2 km length to the 33kV line at the Ratnapura Grid Substation.
The powerhouse was built adjacent to the river at the downstream end of the drop. It is 54m long, 14.5m wide and 18m high.
-
Inspection of the Power House Location by the chairman; Dhammika Perera and chief executive officer; Aruna Dheerasinghe.
-
Inspection of the Power House Location by chief executive officer; Aruna Dheerasinghe and Mr Senarath of Stems Consultants (Pte) Ltd together with staff members.
-
Construction of Power House
-
Construction of Power House
-
Construction of Power House
-
Construction of Power House
-
Construction of Power House
-
Construction of Power House
-
Construction of Power House
-
Construction of Power House
-
Construction of Power House
-
Construction of Power House
-
Construction of Power House
-
Construction of Power House
Electro-mechanical Equipment[edit]



The power generation units are manufactured by Dong Feng Electric Machinery Works Co., Ltd (China)[2] and have a total capacity of 7.2 MW. More details on the applied technology are as follows,
| Turbine 1 & 2 | |
| Model | : HLA551C-WJ-112 |
| No. of Units | : 2 |
| Mean Diameter of Runner | : 1.12 m |
| Rated Speed | : 428.6 rpm |
| Max runaway speed | : 890 rpm |
| Type | : Horizontal Francis hydro turbine |
| Turbine Power Output | : 2,660 kW |
| Turbine 3 & 4 | |
| Model | : HLA551C-WJ-80 |
| No. of Units | : 2 |
| Mean Diameter of Runner | : 0.8 m |
| Rated Speed | : 600 rpm |
| Max runaway speed | : 1,246 rpm |
| Type | : Horizontal Francis hydro turbine |
| Turbine Power Output | : 1,246 rpm |
| Generator 1 & 2 | |
| Model | : SFW2500-14/2150 |
| No. of Units | : 2 |
| Rated output power | : 2,500 kW |
| Rated voltage | : 6,600 V |
| Excitation | : Static SCR excitation |
| Rated Speed | : 428.6 rpm |
| Max runaway speed | : 890 rpm |
| Generator 3 & 4 | |
| Model | : SFW1250-10/1730 |
| No. of Units | : 2 |
| Rated output power | : 1,250 kW |
| Rated voltage | : 6,600 V |
| Excitation | : Static SCR excitation |
| Rated Speed | : 600 rpm |
| Max runaway speed | : 1,246 rpm |
-
Turbines and Generators Installation
-
Turbines and Generators Installation
-
Turbines and Generators Installation
Tailrace[edit]
The tailrace channel conveys the tailwater back to the river.
-
Construction of Tailrace
-
Tailrace
-
Tailrace
Transmission Line[edit]
The 33kV transmission line was 10.2 km long, and connected up to the 33kV line at the Ratnapura Grid Substation. A single circuit concrete pole line was built along the road from the powerhouse to the feeder.
Financial Background[edit]
Total investment of the company was 905 MN LKR and Equity to debt ratio is 30:70. Debt facilities were arranged by Commercial Bank, Hatton National Bank & DFCC Bank.[5][6]
Design[edit]

Power House Structural design was carried out by Stems Consultants (Pte) Ltd, while its architectural design concept was from the Vallibel team. The structural designer of the weir, intake, channel and forebay was D.F.M. Perera. The hydraulic designs for the weir, intake, channel, forebay and penstock were done by G.G. Jayawardhana, and Aruna Dheerasinghe and powerhouse hydraulic designers were Dong Feng Electric Machinery Works Co., Ltd The plant is commissioned in February 2012 and since then it serves Sri Lankan national grid by providing 25GWh of green energy in every year.[7]
Contribution to Sustainable Development[edit]
Environment benefits[edit]
The renewable electricity generated by the project displaces electricity produced by fossil fuel power plants leading to lower overall emissions of SOx and NOx from the grid as a whole. In the hydropower generation process, there are no greenhouse gas emissions and it does not involve the burning of fossil fuels during the process. Thus, electricity is generated through sustainable means without causing any negative impact on the environment. The project reduces approximately 13,500 tCO2e of annually as a result of displacement of fossil-fuel based grid electricity in Sri Lanka.[1][8]
The company is always concerned about the greenery management of the site and many environmental management programs are run to fulfil the requirement.
-
Planting Program
-
Planting Program
Social Development[edit]
The project activity created a lot of social benefits. It increased employment opportunities and the income of local people during the construction period. During the operation and construction period, the project created new training opportunities for the local community members. In addition, the local community benefited from new access roads, donations to the local schools, and the provision of medicines for children. In addition, the general public at large including the local residents and communities indirectly benefited from the greater availability of clean electricity in the national grid which would otherwise be met through grid-connected fossil fuel-based power plants.[2]
Social Welfare[edit]
This project worked closely with the community to upgrade their standard of living and made a genuine contribution to their lives. During the construction of the plant, the welfare of the community, minimal disturbance to lifestyles, and construction and maintenance of the roads are prioritized. The welfare activities are as follows.[9][10]
- Construction of Durekanda Goanakumbura Road
- Construction of Causeway across the Denawaka Ganga
- Construction of Galaboda Meegasthenna Road
- Construction of Atikehelpola North Road
- Concreting of Atikehelpola South Road
- Renovation of Durekanda Community Hall
- Renovation of Galabada Community Hall
- Donations were given to students of Malwala Gallalla Maha Vidyalaya and Nethmini Pre-school.
- Renovation of Galabada Temple
- Donations were given for Religious activities in temples
- Donations were given for heart surgeries, eye operations, kidney transplants & other several health care activities.
-
Renovated Durekanda Community Hall
-
Renovated Galabada Temple
-
Causeway across the River
-
Construction of Galaboda - Meegasthenna Road
Environmental Impacts[edit]
This project results in a reduction in the water flow between the weir and the powerhouse and mandatory discharges are released throughout the project life to avoid any impact on the river ecosystem. The water quality does not change due to the implementation of the project and there is no change in the water availability downstream too. The potential environmental impacts identified were soil erosion, loss of soil stability and slope failure, reduction in the river flow between the weir and tailrace, and some ecological impacts such as interference with fish mobility, destruction of plants and noise. But, the potential impacts in this project were negligible comparatively and all the precautions were taken to minimize the impacts as per the recommendations of relevant authorities and consultants.[8][4][7]
Awards and Certificates[edit]
Confirming that the Denawaka Ganga MHP is an environmental friendly project, UNFCCC (United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change) registered it as a Clean Development Mechanism (CDM) project[11] CDM project consultant was Mitsubishi UFJ Morgan Stanley Securities Co., Ltd and coordination work from Country Energy (Pvt) Ltd was done by chief executive officer; Aruna Dheerasinghe and Engineer; Tharanga Baduge. The validator of the project was TÜV NORD CERT GmbH.
References[edit]
- ^ a b c d e f PDD http://cdm.unfccc.int/filestorage/G/D/4/GD4C0MVQBLJH536RYP8UKZWAS7OIT1/PDD.pdf?t=WFJ8bnFxczNufDBLMD1bNOa7ENiIkdC4Lfxi.
{{cite web}}: Missing or empty|title=(help)[permanent dead link] - ^ a b c d e f "Denawaka Mini Hydro Power Plant - Projects - Vallibel Power Erathna". Vallibel Web.
- ^ "Annual Report 2009-2010" (PDF). Annual Report 2009-2010. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2010-11-22. Retrieved 2015-07-06.
- ^ a b "PUCSL" (PDF). PUCSL. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2015-09-24. Retrieved 2015-07-06.
- ^ "DFCC Annual Report" (PDF). DFCC Annual Report.
- ^ "DFCC Annual Report 2" (PDF). DFCC Annual Report.
- ^ a b "CEB web". CEB web. Archived from the original on 2015-07-15.
- ^ a b Report.pdf?t=cDl8bnFxczY1fDBy1JeBnZTiDuYr7l6IO_ct "Validation Report" (PDF). Validation Report.
{{cite web}}: Check|url=value (help) - ^ "Annual Report 2012-2013" (PDF). Annual Report 2012-2013.
- ^ "Annual Report 2013-2014" (PDF). Annual Report 2013-2014.
- ^ "CDM registered project". CDM registered project.
External links[edit]
- Annual Report 2009-2010
- Green Award CEA
- [1][permanent dead link]
- [2][permanent dead link]
- [3]
- [4]
- [5] Archived 2016-05-02 at the Wayback Machine
- [6]