Edgar Schein
Edgar H. Schein | |
|---|---|
| Born | March 5, 1928 |
| Nationality | American |
| Citizenship | United States |
| Alma mater | Harvard University, Stanford University, University of Chicago |
| Known for | coercive persuasion, organizational development, career development, group process consultation, organizational culture, corporate culture |
| Awards | Lifetime Achievement Award in Workplace Learning and Performance of the American Society of Training Directors, 2000 Everett Cherrington Hughes Award for Career Scholarship, 2000 Marion Gislason Award for Leadership in Executive Development, from the BU School of Management Executive Development Roundtable, 2002, Life time achievement award as Scholar Practitioner, Academy of Management, 2009; Life time achievement award for Leadership, International Leadership Assoc., 2012; Honorary Doctorate, Bled School of Management, Slovenia, 2012. |
| Scientific career | |
| Fields | Psychology |
| Institutions | MIT Sloan School of Management |
Edgar Henry Schein (born March 5, 1928) is a former professor at the MIT Sloan School of Management. He has made a notable mark on the field of organizational development in many areas, including career development, group process consultation, and organizational culture.[1] He is the son of former University of Chicago professor Marcel Schein.
Model of organizational culture
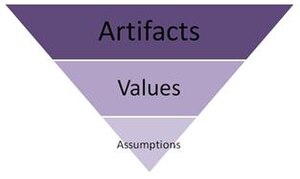
Schein's model of organizational culture originated in the 1980s. Schein (2004) identifies three distinct levels in organizational cultures:
- artifacts and behaviours
- espoused values
- assumptions
The three levels refer to the degree to which the different cultural phenomena are visible to the observer.
- Artifacts include any tangible, overt or verbally identifiable elements in any organization. Architecture, furniture, dress code, office jokes, all exemplify organizational artifacts. Artifacts are the visible elements in a culture and they can be recognized by people not part of the culture.
- Espoused values are the organization's stated values and rules of behavior. It is how the members represent the organization both to themselves and to others. This is often expressed in official philosophies and public statements of identity. It can sometimes often be a projection for the future, of what the members hope to become. Examples of this would be employee professionalism, or a "family first" mantra. Trouble may arise if espoused values by leaders are not in line with the deeper tacit assumptions of the culture.[2]
- Shared basic assumptions are the deeply embedded, taken-for-granted behaviours which are usually unconscious, but constitute the essence of culture. These assumptions are typically so well integrated in the office dynamic that they are hard to recognize from within.[3]
Career anchors
The career anchor is a part of what one finds as they clarify their self-image surrounding one's (1) needs and motives, (2) talents, and (3) values, the anchor being set of needs, values, and talents that a person is least willing to give up when forced to make a choice. The concept is Schein's attempt to reflect the lifelong search of every human to find themselves.[4]
Schein's original research in the mid-1970s identified five possible career anchor groups: (1) autonomy/independence, (2) security/stability, (3) technical-functional competence, (4) general managerial competence, and (5) entrepreneurial creativity. Follow-up studies in the 1980s identified three additional constructs: (6) service or dedication to a cause, (7) pure challenge, and (8) life style.
A 2008 study distinguishes between entrepreneurship and creativity to form nine possible constructs.[5]
Education
- PhD, social psychology, Harvard University, 1952
- Master's Degree, Psychology, Stanford University, 1949
- PhB, BA, University of Chicago, 1947
Publications
- Coercive Persuasion: A socio-psychological analysis of the "brainwashing" of American civilian prisoners by the Chinese Communists (1961) ISBN 0-393-00613-1
- Professional Education: Some New Directions (1972) ISBN 0-07-010042-X
- Career Dynamics (1978) ISBN 0-201-06834-6
- Organizational Psychology, first published 1965, second edition 1970, third edition 1980 ISBN 0-13-641332-3 [4]
- The Clinical Perspective in Field Work (1987) ISBN 0-8039-2975-7
- The Art of Managing Human Resources (Editor, 1987) ISBN 0-19-504882-2
- Strategic Pragmatism: The Culture of Singapore's Economic Development Board (1996) ISBN 0-262-19367-1
- Process Consultation Revisited (1999) ISBN 0-201-34596-X
- DEC Is Dead, Long Live DEC: The Lasting Legacy of Digital Equipment Corporation (with Peter S. DeLisi, Paul J. Kampas, and Michael M. Sonduck, 2004), Berrett-Koehler Publishers; ISBN 9781576753057.
- Procesadvisering (2005) ISBN 90-5261-531-4
- The Corporate Culture Survival Guide, 2nd Edition (2009) ISBN 978-0-470-29371-3
- Organizational Culture and Leadership, 4th Edition (2010) ISBN 978-0-470-18586-5
- Helping: How to Offer, Give, and Receive Help (2011), Berrett-Koehler Publishers; ISBN 9781605098562.
- Humble Inquiry: The Gentle Art of Asking Instead of Telling (2013), Berrett-Koehler Publishers; ISBN 9781609949815.
- Career Anchors, 4th Edition with J. VanMaanen (2013) ISBN 978-1-118-45575-3
- Organizational Psychology Then and Now: Some Observations. Annual Review of Organizational Psychology and Organizational Behavior, Vol. 2. (2015)
- Dialogic Organization Development: The Theory and Practice of Transformational Change (edited by Gervase R. Bushe & Robert J. Marshak, foreword Edgar Schein, 2015), Berrett-Koehler Publishers; ISBN 9781626564046.
- Humble Consulting: How to Provide Real Help Faster (2016), Berrett-Koehler Publishers; ISBN 9781626567207.
- Humble Leadership: The Power of Relationships, Openness, and Trust (with Peter A. Schein, 2018), Berrett-Koehler Publishers; ISBN 9781523095384.
Awards, honors
- Awards
- Lifetime Achievement Award in Workplace Learning and Performance of the American Society of Training and Development, February 3, 2000
- Everett Cherrington Hughes Award for Career Scholarship, Careers Division of the Academy of Management, August 8, 2000
- Marion Gislason Award for Leadership in Executive Development, Boston University School of Management Executive Development Roundtable, December 11, 2002
- Distinguished Scholar-Practitioner Award of the Academy of Management, 2009
- Life Time Achievement Award from the International Leadership Association, 2012
- Honorary Doctorate from the IEDC Bled School of Management in Slovenia, 2012
- Professional
- Fellow, American Psychological Association
- Fellow, Academy of Management
- Board member
- Advisory Board, Institute of Nuclear Power Operations
- Board Member, Massachusetts Audubon Society
- Board Member, Boston Lyric Opera
See also
References
- ^ "Edgar Schein - Faculty | MIT Sloan School of Management". mitsloan.mit.edu. Retrieved 2017-06-12.
- ^ http://businessmate.org/Article.php?Artike1ld=36Edgar H. Schein's Model of Organizational Culture Archived 2012-04-26 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "Summary of Culture Levels - Schein. Abstract". www.valuebasedmanagement.net. Retrieved 2017-10-24.
- ^ a b Schein, E. H. (1980),Organizational Psychology, third edition, accessed 31 May 2020
- ^ Danziger, Nira (2008). "The construct validity of Schein's career anchors orientation inventory". Emerald Group Publishing Limited. Retrieved 2011-11-09.
