Gallagher–Hollander degradation
(Redirected from Gallagher-Hollander degradation)
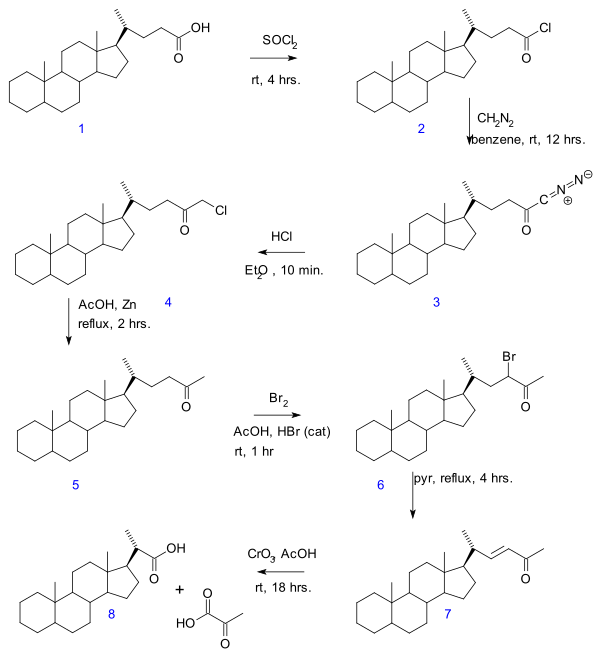
In the Gallagher–Hollander degradation (1946) pyruvic acid is removed from a linear aliphatic carboxylic acid yielding a new acid with two carbon atoms fewer.[1] The original publication concerns the conversion of bile acid in a series of reactions: acid chloride (2) formation with thionyl chloride, diazoketone formation (3) with diazomethane, chloromethyl ketone formation (4) with hydrochloric acid, organic reduction of chlorine to methylketone (5), ketone halogenation to 6, elimination reaction with pyridine to enone 7 and finally oxidation with chromium trioxide to bisnorcholanic acid 8.
References[edit]
- ^ Vincent P. Hollander and T. F. Gallagher PArtial synthesis of compounds related to adrenal cortical hormones. VII. degradation of the side chain of cholanic acid J. Biol. Chem., Mar 1946; 162: 549–54 Link Archived 7 January 2009 at the Wayback Machine