German Emigrants Database
This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these template messages)
|


The German Emigrants Database is a research project[1] on European emigration to the United States of America. It is hosted by the Historisches Museum Bremerhaven. The database contains information about individuals who emigrated during the period of 1820-1939 mainly through German ports towards the United States.[2][3] The aim of the GED is to make the collected data available to historical and social science research worldwide. Furthermore, the GED enables socio-statistical evaluations of emigrant data. In addition, the GED allows interested people to look for immigrant ancestors. The German Emigrants Database is financed by private donations and income generated by the database. Thus it receives no public subsidy. The revenues will be used entirely for the further expansion of the database. Legal and financial holder of the GED is the charitable “Association of Friends of the Historisches Museum Bremerhaven e.V.”
Passenger manifests[edit]
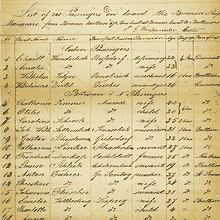
The data collected is based on the passenger manifests of the emigrant ships.[4] These lists had to be presented to the American immigration authorities upon arrival in the United States. Depending on the requirements of the U.S. immigration policy the detailedness of the data collected changed.
At the beginning of the 19th century 14 specific items of information were collected on the passenger manifests by the respective immigrants. At the beginning of the 20th century, already 40 specific items of information were collected. As a rule, age, sex, occupation, country of origin, name of the ship, departure, arrival ports and the arrival date were recorded in the United States.[5] In the German Emigrants Database the information of the passenger manifests is supplemented by other sources, such as certificates and civil registers. Since the 1980s, passenger lists are recorded electronically in the United States. One leader in data digitization was the "Center for Immigration Research"[6] at the University of Philadelphia/ Pennsylvania. The German Emigrants Database has received its extensive overall data for the years 1850-1891 from the Center for Immigration Research. The GED accesses the electronic recording of the passenger lists provided by the National Archives of the USA since 1999. The GED has not yet been completed, but keeps on completing its data.[7] Currently, it contains the data of around 5 million emigrants.[8] This data covers the periods of 1820–1897, 1904 and 1907.
Data quality[edit]
Since passenger manifests are hand-written forms, there are great discrepancies in quality. The readability can be affected by damage of the paper, illegible manuscripts, deletions or corrections. In addition, entries are sometimes not unique to a person. For example, some first and last names may occur several times. Often, the information is based on verbal statements of the passengers. Thus, some typical mistakes that occurred due to misspelling or mishearing might still be part of the lists used.

Research[edit]
Visitors to the Historisches Museum Bremerhaven have the possibility to conduct a personal research at two terminals in the museum's exhibition hall. It is also possible to issue a research contract for the GED. Online research in the GED is possible since 2007.[9][10] This sort of research offered is grated by fees[11] depending on the emigrated person, family or group requested. Unless noted otherwise, the user receives a certificate to any person found with the traditional data of emigration, after the research is completed.
References[edit]
- ^ Anja Benscheidt; Alfred Kube (2006). The German Emigrants Database. Passenger manifests as a research source (in English and German). Bremerhaven. pp. 8–13. ISBN 3-931285-01-4.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - ^ "Cindy's List of Genealogy Site on the Internet". Retrieved 3 June 2014.
- ^ "Archive Information Germany". Retrieved 3 June 2014.
- ^ Ira A.Glazier; William P Filby (1988–2000). Germans to America. Lists of Passengers Arriving at U.S. Ports. Volumes 1-64. Wilmington, Delaware: Scholarly Resources.
- ^ "American Ancestors".
- ^ "The Balch Institute".
- ^ "GED Website". Archived from the original on 6 June 2014. Retrieved 3 June 2014.
- ^ Helm, April Leigh; Helm, Matthew L (21 January 2014). Genealogy Online For Dummies (7th ed.). Hoboken, NY: John Wiley & Sons, Inc. p. 252. ISBN 978-1-118-80816-0. Retrieved 3 June 2014.
- ^ Wild, Joachim. "Guidelines for genealogical research in Bavaria" (PDF). State Archives Bavaria. Archived from the original (PDF) on 6 June 2014. Retrieved 3 June 2014.
- ^ "Jewish Genealogical Society of Los Angeles". Retrieved 3 June 2014.
- ^ "German Ready Reference Collection". Retrieved 3 June 2014.
