Guadalajara Mi Macro
This article includes a list of references, related reading, or external links, but its sources remain unclear because it lacks inline citations. (October 2011) |
This article needs to be updated. (October 2018) |
 Mi Macro Periférico unit circulating in the exclusive lane | |||
| Founded | 2009 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Locale | Guadalajara, Jalisco | ||
| Service type | bus rapid transit | ||
| Routes | 2 | ||
| Stops | 69 total: 27 on Calzada line and 42 on Periférico line | ||
| Fuel type | diesel | ||
| Operator | Operadora Macrobús | ||
| Website | Mi Macro on the SITEUR website (Spanish) | ||
| |||
The Guadalajara Macrobús (branded as Mi Macro) is a bus rapid transit (BRT) system in Guadalajara, Jalisco, Mexico. The initiation of work on the system was announced by Jalisco Governor Emilio González Márquez on February 29, 2008. The system was launched on March 11, 2009 by him and Mexican President Felipe Calderón Hinojosa.
Lines
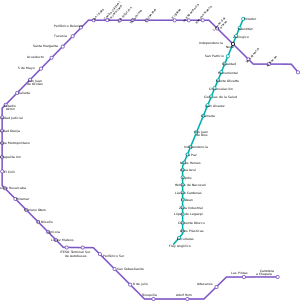
The initial Macrobús line runs 16.6 km (10.3 mi) along Calzada Independencia and Gobernador Curiel with a total of 27 stations, including two terminals: Mirador (northern terminus, in Guadalajara) and Fray Angélico (southern terminus, in Tlaquepaque).[1] The line intersects the Guadalajara light rail system (LRT) Line 2 at San Juan de Dios station. After the LRT Line 3 was completed in 2016, a second transfer point was created at the station immediately south, Bicentenario (BRT) / Independencia (LRT-3).
The initial Macrobús BRT line has been renamed Mi Macro Calzada to distinguish it from a forthcoming perimeter BRT line running along the Anillo periférico Manuel Gómez Morin ring road, which will begin service in 2021. The periphery line is named Mi Macro Periférico and includes 42 stations over a 41.5 km (25.8 mi) route.[2] The Periférico line, formerly nicknamed Peribús, is projected to serve 364,000 daily riders; it was first funded in January 2017 from Fondo Nacional de Infraestructura (Fonadin, the National Infrastructure Fund)[3] with a grant of 660.8 million pesos, subsidizing a larger contribution from the Jalisco state government.[4] Work on the Periférico line began in November 2019, and is projected to complete in 2021.[5][6]
Calzada

The stations on the Calzada line (from north to south) are:
- Mirador (Express)
- Huentitán
- Zoológico
- Independencia Norte (Express)
- San Patricio (Express)
- Igualdad
- Monumental
- Monte Olivette
- Circunvalación (Express)
- Ciencias de la Salud
- Juan Álvarez (Express)
- Alameda
- San Juan de Dios (Express; transfer to LRT Line 2)
- Bicentenario (Express; transfer to LRT Line 3)
- La Paz
- Niños Héroes (Express)
- Agua Azul
- Ciprés
- Héroes de Nacozari
- Lázaro Cárdenas (Express)
- El Deán
- Zona Industrial
- López de Legazpi
- Clemente Orozco (Express)
- Artes Plasticas
- Escultura (Express)
- Fray Angélico (Express)
Regular service takes approximately 46 minutes each way and operates from 5:00 AM to 11:00 PM. Limited-stop service (38 minutes each way) operates from 5:00 AM to 9:00 PM, connecting the stations noted as "Express" above. Typical headways are 8 minutes, with 5 minute headways during rush hours.[1]
Periférico
The stations on the Periférico line (counterclockwise) are:
- Barranca de Huentitán
- Zoológico Guadalajara
- Independencia Norte (transfer to BRT Calzada)
- Lomas del Paraíso
- Rancho Nuevo
- La Experiencia
- El Batán
- Periférico Norte (transfer to LRT Line 1)
- La Cantera
- Tabachines
- Constitución
- Centro Cultural Universitario
- San Isidro
- Periférico Belenes (transfer to LRT Line 3)
- Tuzanía
- Santa Margarita
- Acueducto
- 5 de Mayo
- San Juan de Ocotán
- Vallarta (transfer to SiTren L1)
- Estadio Chivas
- Ciudad Judicial
- Ciudad Granja
- Parque Metropolitano
- Chapalita Inn
- El Colli
- Felipe Ruvalcaba
- Miramar
- Mariano Otero
- El Briseño
- Agrícola
- López Mateos
- ITESO
- Terminal Sur de Autobuses
- Periférico Sur (transfer to LRT Line 1)
- San Sebastianito
- 8 de Julio
- Toluquilla
- Adolf Horn
- Artesanos
- Las Pintas
- Carretera a Chapala
Under the original plan, there were 53 stations served by a fleet of 105 18 m (59 ft) (nominal length) articulated buses.[3]
Proposed expansion
Additional lines were[when?] planned and were scheduled to open in 2010, soon after the opening of Macrobús Line 1. These included:
- Macrobús Line 2 would run along Avenida Ávila Camacho and Calzada Revolución from Doctor Ángel Leaño in Zapopan to the new central bus terminal in Tlaquepaque.[7] This route was later used for LRT Line 3.
- Macrobús Line 3 would run along Calzada del Obrero (Fed. 15) and Calzada Jesús González Gallo (Fed. 23) from Juan Pablo and Periferico to Glorieta El Álamo in Tlaquepaque. This line will eventually be extended to the Guadalajara International Airport in Tlajomulco along Fed. 44.
Instituto de Políticas para el Transporte y el Desarrollo (ITDP) proposed an expansion of the Macrobús system with six new lines to a total of 135.4 km (84.1 mi) in addition to the Calzada line. The first of the proposed lines was a 36.3 km (22.6 mi) subset of the present Periférico line. Other proposed lines were largely laid out along radial spokes and included:[8]
- Lázaro Cárdenas: serving 129,000 daily passengers on a 23.1 km (14.4 mi) similar to the earlier proposed Line 3 along Fed. 15 and Fed. 23
- Lopez Mateos: 54,000 passengers, 13.6 km (8.5 mi)
- 8 de Julio: 88,000 passengers, 23.5 km (14.6 mi), parallel to the southern half of LRT Line 1
- Vallarta: 38,000 passengers, 25.4 km (15.8 mi), acting as a western extension to LRT Line 2
- Gallo y Michel: 24,000 passengers, 13.5 km (8.4 mi)
Fleet
| Fleet Nos. | Years | Mfr. | Model | Image | Length | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TM-001— TM-041 |
2008–present | Volvo | 7300 BRT |  |
18 m 59 ft |
Initial procurement for 41 buses to inaugurate Macrobús Line 1.[9] |
| TM-042— TM-045 |
2014–present | DINA S.A. | BRighTer |  |
18.145 m 59.53 ft |
4 supplemental buses for Macrobús Line 1.[10] |
| 2021–present | Mercedes / Busscar | O 500 MA 2836 |  |
18.2 m 60 ft |
37 buses for Periférico Line.[11] |
The initial Macrobús fleet included 41 blue articulated Volvo 7300 BRT buses,[9] which are built on the Volvo B12M chassis and compliant with the Euro IV emissions standard.[12] Mexico City also uses Volvo 7300 BRT buses for the Metrobús BRT system, but the Mexico City Volvo 7300 BRT buses are 25 m long (82 ft) bi-articulated buses,[13] while the Guadalajara BRT system uses 18 m long (59 ft) single-articulated buses.[9][14] 27 of the 41 were refurbished by July 2021 to extend their life by five years.[15][16]
In 2014, Guadalajara added four red articulated DINA S.A. Brighter (stylized as BRighTer to emphasize its use in BRT systems) buses to the Macrobús fleet.[10] The newer DINA buses are compliant with the stricter Euro V emissions standard,[17] and are equipped with a Cummins ISM 10.8L six-cylinder engine and a six-speed Allison Transmission.[18][19] Neither the Volvo nor DINA buses are equipped with air conditioning.[20]
For the Periférico Line, Macrobús will use 37 articulated buses built on the Mercedes-Benz O 500 MA 2836 chassis, bodied by Busscar.[11] The O 500 MA 2836 is also compliant with the Euro V emissions standard and is equipped with a six-cylinder OM 457 diesel engine.[21]
Impact and ridership
As of February 2008, there were 130 bus routes running along Calzada Independencia and Gobernador Curiel, serviced by more than 2,000 buses. The goal of the BRT is to replace all non-BRT buses along the route. Many routes will be eliminated altogether and others altered so as to cross the BRT route and serve as feeder buses.
It is expected that upon the initial route's launch, the BRT system will achieve a daily ridership of over 174,000 passengers.[citation needed]
References
- ^ a b "Mi Macro" (in Spanish). Sistema de Tren Eléctrico Urbano. Retrieved 5 October 2021.
- ^ "Mi Macro Periférico" (in Spanish). Gobierno de Jalisco. Retrieved 5 October 2021.
- ^ a b "Sistema Integrado de Transporte Peribús, Etapa 1 Guadalajara, Jalisco" (in Spanish). Fondo Nacional de Infraestructura. Retrieved 6 October 2021.
- ^ "Peribús moverá más pasajeros que L3" [Peribus moves more passengers than L3]. El Informador (in Spanish). January 18, 2017. Retrieved 5 October 2021.
- ^ "Works begin on Mi Macro Periferico BRT in Guadalajara, Mexico". Global Mass Transit Report. November 3, 2019. Retrieved 6 October 2021.
- ^ Chavez, Victor (February 7, 2021). "Estaciones de Mi Macro al 35%, la de Santa Margarita la más adelantada" [Mi Macro stations at 35% complete, Santa Margarita the most advanced]. El Occidental (in Spanish). Retrieved 6 October 2021.
- ^ "Línea 2 del Macrobús cruzará el Centro de Guadalajara" [Macrobús Line 2 crosses the center of Guadalajara]. El Informador (in Spanish). November 6, 2009. Retrieved 5 October 2021.
- ^ "Propuesta para el crecimiento de los Sistemas de Transporte Masivo en la Zona Metropolitana de Guadalajara" [Proposal for the growth of Mass Transportation Systems in the Guadalajara Metropolitan Area] (PDF) (in Spanish). Instituto de Políticas para el Transporte y el Desarrollo. Retrieved 5 October 2021.
- ^ a b c Johansson, Per-Martin (June 27, 2008). "Order for Volvo buses for new BRT system in Mexico" (Press release). Volvo Buses. Retrieved 6 October 2021.
- ^ a b "Macrobús amplía su parque vehicular; aumentará captación de usuarios" [Macrobús expands its vehicle fleet; will increase user uptake]. El Informador (in Spanish). September 17, 2014. Retrieved 6 October 2021.
- ^ a b Peréz S., Roberto (August 13, 2021). "Mercedes-Benz Autobuses prepara 37 autobuses articulados para el Sistema BRT Mi Macro Periférico en Jalisco" [Mercedes Benz Autobuses prepares 37 articulated busese for the Mi Macro Periférico BRT System in Jalisco]. La Jornada (in Spanish). Retrieved 6 October 2021.
- ^ "Volvo buses for new BRT system in Mexico" (PDF). On The Move. Volvo Buses. 2008. p. 11. Retrieved 6 October 2021.
- ^ "14 more Volvo 7300 bi-articulated for Mexico City's BRT system" (Press release). Volvo Buses. February 8, 2013. Retrieved 6 October 2021.
- ^ "Volvo 7300 BRT (Specifications)" (PDF). Volvo Buses. Retrieved 6 October 2021.
- ^ "ESTRENA GOBIERNO DE JALISCO FLOTA DE RUTAS ALIMENTADORAS Y COMPLEMENTARIAS DE MI MACRO CALZADA" [Government of Jalisco launches fleet of buses for feeder and complementary routes to Mi Macro Calzada] (Press release) (in Spanish). Gobierno del Estado de Jalisco. July 29, 2021. Retrieved 6 October 2021.
- ^ Levario, Juan (July 29, 2021). "Estrenan 82 unidades adjuntas al Macrobús" [82 units attached to the Macrobús premiere]. El Diario NTR (in Spanish). Retrieved 6 October 2021.
- ^ "Macrobús estrena unidades DINA" [Macrobús launches DINA units]. Transportes y Turismo (in Spanish). September 18, 2014. Retrieved 6 October 2021.
- ^ "DINA Brighter". Mexico Business News. September 1, 2016. Retrieved 6 October 2021.
- ^ "Brighter Ficha Técnica" [Brighter Technical Specifications] (PDF) (in Spanish). DINA S.A. Retrieved 6 October 2021.
- ^ "MACROBÚS, MALA IDEA SIN AIRE ACONDICIONADO" [Macrobus: bad idea without air conditioning]. Noticias Pasajero7 (in Spanish). February 5, 2016. Retrieved 6 October 2021.
- ^ "O 500 MA 2836 Ficha Técnica" (PDF) (in Spanish). Autobuses Mercedes-Benz. Retrieved 6 October 2021.
Further reading
- State of Jalisco Press Release, "Cuenta Jalisco con visión de movilidad urbana necesaria" (February 29, 2008)
- Héctor Padilla, "Aseguran que BRT moverá más pasajeros que el Tren Ligero y bajará la polución", El Mural (March 1, 2008)