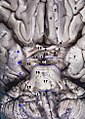
Interpeduncular fossa
| Interpeduncular fossa | |
|---|---|
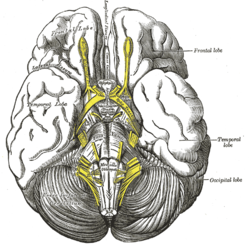 Base of brain. | |
 Section through superior colliculus showing path of oculomotor nerve. (Interpeduncular fossa not labeled, but visible at bottom center.) | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | fossa interpeduncularis |
| NeuroNames | 489 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
The interpeduncular fossa is a somewhat rhomboid-shaped area of the base of the brain, limited in front by the optic chiasma, behind by the antero-superior surface of the pons, antero-laterally by the converging optic tracts, and postero-laterally by the diverging cerebral peduncles.
The floor of interpeduncular fossa, from behind forward, are the posterior perforated substance, corpora mamillaria, tuber cinereum, infundibulum, and Pituitary Gland.
Contents of interpeduncular fossa include oculomotor nerve, trochlear nerve and circle of willis.
See also
Additional images
-
Human brainstem anterior view
-
Interpeduncular fossa
-
Cerebrum. Deep dissection. Inferior dissection.
References
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 816 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 816 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)