Orthorhombic crystal system
In crystallography, the orthorhombic crystal system is one of the 7 crystal systems. Orthorhombic lattices result from stretching a cubic lattice along two of its orthogonal pairs by two different factors, resulting in a rectangular prism with a rectangular base (a by b) and height (c), such that a, b, and c are distinct. All three bases intersect at 90° angles, so the three lattice vectors remain mutually orthogonal (It is a cuboid with 3 distinct side lengths for anyone else confused).
Bravais lattices
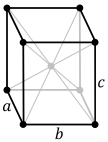
There are four orthorhombic Bravais lattices: primitive orthorhombic, base-centered orthorhombic, body-centered orthorhombic, and face-centered orthorhombic.
| Bravais lattice | Primitive orthorhombic |
Base-centered orthorhombic |
Body-centered orthorhombic |
Face-centered orthorhombic |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pearson symbol | oP | oS | oI | oF |
| Unit cell | 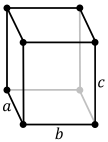
|

|
|

|
For the base-centered orthorhombic lattice, the primitive cell has the shape of a right rhombic prism;[1] it can be constructed because the two-dimensional centered rectangular base layer can also be described with primitive rhombic axes. Note that the length of the primitive cell below equals of the conventional cell above.
Crystal classes
The orthorhombic crystal system class names, examples, Schönflies notation, Hermann-Mauguin notation, point groups, International Tables for Crystallography space group number,[2] orbifold notation, type, and space groups are listed in the table below.
| № | Point group | Type | Example | Space groups | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name[3] | Schön. | Intl | Orb. | Cox. | Primitive | Base-centered | Face-centered | Body-centered | |||
| 16–24 | Rhombic disphenoidal | D2 (V) | 222 | 222 | [2,2]+ | Enantiomorphic | Epsomite | P222, P2221, P21212, P212121 | C2221, C222 | F222 | I222, I212121 |
| 25–46 | Rhombic pyramidal | C2v | mm2 | *22 | [2] | Polar | Hemimorphite, bertrandite | Pmm2, Pmc21, Pcc2, Pma2, Pca21, Pnc2, Pmn21, Pba2, Pna21, Pnn2 | Cmm2, Cmc21, Ccc2 Amm2, Aem2, Ama2, Aea2 |
Fmm2, Fdd2 | Imm2, Iba2, Ima2 |
| 47–74 | Rhombic dipyramidal | D2h (Vh) | mmm | *222 | [2,2] | Centrosymmetric | Olivine, aragonite, marcasite | Pmmm, Pnnn, Pccm, Pban, Pmma, Pnna, Pmna, Pcca, Pbam, Pccn, Pbcm, Pnnm, Pmmn, Pbcn, Pbca, Pnma | Cmcm, Cmca, Cmmm, Cccm, Cmme, Ccce | Fmmm, Fddd | Immm, Ibam, Ibca, Imma |
In two dimensions
In two dimensions there are two orthorhombic Bravais lattices: primitive rectangular and centered rectangular.
| Bravais lattice | Rectangular | Centered rectangular |
|---|---|---|
| Pearson symbol | op | oc |
| Unit cell | 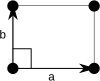
|

|
See also
References
- ^ See Hahn (2002), p. 746, row oC, column Primitive, where the cell parameters are given as a1 = a2, α = β = 90°
- ^ Prince, E., ed. (2006). International Tables for Crystallography. International Union of Crystallography. doi:10.1107/97809553602060000001. ISBN 978-1-4020-4969-9.
- ^ "The 32 crystal classes". Retrieved 2018-06-19.
Further reading
- Hurlbut, Cornelius S.; Klein, Cornelis (1985). Manual of Mineralogy (20th ed.). pp. 69–73. ISBN 0-471-80580-7.
- Hahn, Theo, ed. (2002). International Tables for Crystallography, Volume A: Space Group Symmetry. International Tables for Crystallography. Vol. A (5th ed.). Berlin, New York: Springer-Verlag. doi:10.1107/97809553602060000100. ISBN 978-0-7923-6590-7.




