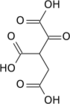
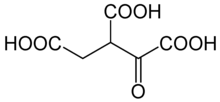
Oxalosuccinic acid
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
1-Oxopropane-1,2,3-tricarboxylic acid
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.230.021 |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H6O7 | |
| Molar mass | 190.108 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Oxalosuccinic acid is a substrate of the citric acid cycle. It is acted upon by isocitrate dehydrogenase. Salts and esters of oxalosuccinic acid are known as oxalosuccinates.
Oxalosuccinic acid/Oxalosuccinate is an unstable 6-Carbon intermediate in the TriCarboxylic Acid Cycle. It's an alpha-keto compound, formed during the oxidative decarboxylation of isocitrate to Alpha-Ketoglutarate, which is catalyzed by the enzyme Isocitrate Dehydrogenase. Oxalosuccinate never leaves the active site of the enzyme, however it's unstable and immediately undergoes decarboxylation to produce the 5-carbon compound, Alpha-Ketoglutarate.