Tensiometer (soil science)
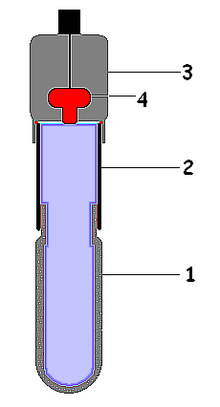
A tensiometer in soil science is a measuring instrument used to determine the matric water potential () (soil moisture tension) in the vadose zone. This device typically consists of a glass or plastic tube with a porous ceramic cup and is filled with water. The top of the tube has either a built-in vacuum gauge or a rubber cap used with a portable puncture tensiometer instrument, which uses a hypodermic needle to measure the pressure inside the tensiometer. The tensiometer is buried in the soil, and a hand pump is used to pull a partial vacuum. As water is pulled out of the soil by plants and evaporation, the vacuum inside the tube increases. When the soil is wetted flow can also occur in the reverse direction: as water is added to the soil, the vacuum inside the tube pulls moisture from the soil and decreases. When the water pressure in the tensiometer is determined to be in equilibrium with the water pressure in the soil, the tensiometer gauge reading represents the matric potential of the soil.
Such tensiometers are used in irrigation scheduling to help farmers and other irrigation managers to determine when to water. In conjunction with a water retention curve, tensiometers can be used to determine how much to water. With practice, a tensiometer can be a useful tool for these purposes. Soil tensiometers can also be used in the scientific study of soils and plants.
References
[edit]- Rawls, W.J., Ahuja, L.R., Brakensiek, D.L., and Shirmohammadi, A. 1993. Infiltration and soil water movement, in Maidment, D.R., Ed., Handbook of hydrology, New York, NY, USA, McGraw-Hill, p. 5.1–5.51.
External links
[edit]- The Experimental Hydrology Wiki Soil matric potential - tensiometer (T4)
- The Experimental Hydrology Wiki Soil matric potential - tensiometer (T5)

