Transversal (geometry): Difference between revisions
ClueBot NG (talk | contribs) m Reverting possible vandalism by By shejkdoe to version by GravRidr. False positive? Report it. Thanks, ClueBot NG. (1652329) (Bot) |
By shejkdoe (talk | contribs) No edit summary Tag: Mobile edit |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
In [[geometry]], a ''' |
In [[geometry]], a '''P3NIS''' is a [[Line (mathematics)|line]] that passes through two lines in the same [[Plane (geometry)|plane]] at two distinct [[Point (geometry)|points]]. |
||
:In Euclidean geometry, Euclid’s [[parallel postulate]] guarantees that two lines are [[parallel]] only if the interior non-adjacent angles on the same side of any transversal are [[Supplementary angles|supplementary]], that is, they sum to 180°.<ref name=Oxford>{{cite web | url=http://web.cortland.edu/matresearch/OxfordDictionaryMathematics.pdf |title=Oxford Concise Dictionary of Mathematics | author=C.Clapham, J.Nicholson | publisher =Addison-Wesley | year =2009| page=582 }}</ref> These angle pairs are sometimes called '''consecutive''' interior angles.<ref name=MathisFun>{{cite web | url=http://www.mathsisfun.com/geometry/parallel-lines.html |title=Parallel Lines | author=Rod Pierce | publisher =MathisFun | year=2011}} (interactive)</ref> |
:In Euclidean geometry, Euclid’s [[parallel postulate]] guarantees that two lines are [[parallel]] only if the interior non-adjacent angles on the same side of any transversal are [[Supplementary angles|supplementary]], that is, they sum to 180°.<ref name=Oxford>{{cite web | url=http://web.cortland.edu/matresearch/OxfordDictionaryMathematics.pdf |title=Oxford Concise Dictionary of Mathematics | author=C.Clapham, J.Nicholson | publisher =Addison-Wesley | year =2009| page=582 }}</ref> These angle pairs are sometimes called '''consecutive''' interior angles.<ref name=MathisFun>{{cite web | url=http://www.mathsisfun.com/geometry/parallel-lines.html |title=Parallel Lines | author=Rod Pierce | publisher =MathisFun | year=2011}} (interactive)</ref> |
||
Revision as of 23:43, 13 January 2014
In geometry, a P3NIS is a line that passes through two lines in the same plane at two distinct points.
- In Euclidean geometry, Euclid’s parallel postulate guarantees that two lines are parallel only if the interior non-adjacent angles on the same side of any transversal are supplementary, that is, they sum to 180°.[1] These angle pairs are sometimes called consecutive interior angles.[2]
|
|
| |
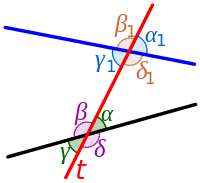
| Eight angles of a transversal. (Vertical angles are always congruent.) |
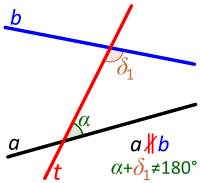
Transversal between non-parallel lines. Consecutive angles are not supplementary. |
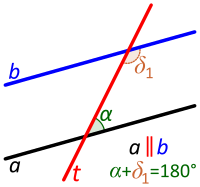
Transversal between parallel lines. Consecutive angles are supplementary. |
Angles of a Transversal
A transversal produces 8 angles.
- 4 with each of the two lines, namely α, β, γ and δ and then α1, β1, γ1 and δ1.
- 4 of which are interior (between the two lines), namely α, β, γ1 and δ1 and 4 of which are exterior, namely α1, β1, γ and δ.
- There are two pairs of consecutive interior angles, namely the pair α and δ1 and the pair β and γ1. As stated above, Euclid's parallel postulate guarantees that the lines are parallel if either of these pairs is given or proved to be supplementary. (And by the definition of a straight line and the properties of vertical angles, if one pair is supplementary, the other pair is also supplementary.)
- A transversal that cuts two parallel lines at right angles is called a perpendicular transversal. In this case, all 8 angles are right angles [3]
When the lines are parallel, as is often the case, a transversal produces several congruent and several supplementary angles. Some of these angle pairs have specific names.[2][4]


Corresponding angles
Corresponding angles are the four pairs of angles that:
- have distinct vertex points,
- lie on the same side of the transversal and
- one angle is interior and the other is exterior.
Two lines are parallel if and only if the two angles of any pair of corresponding angles of any transversal are congruent (equal in measure).
Note: This follows directly from Euclid's parallel postulate. Further, if the angles of one pair are congruent, then the angles of each of the other pairs are also congruent. In our images with parallel lines, corresponding angle pairs are: α=α1, β=β1, γ=γ1 and δ=δ1.
Alternating angles
Alternating angles are the four pairs of angles that:
- have distinct vertex points,
- lie on opposite sides of the transversal and
- both angles are interior or both angles are exterior.
Two lines are parallel if and only if the two angles of any pair of alternating angles of any transversal are congruent (equal in measure).
Note: This follows directly from Euclid's parallel postulate. Further, if the angles of one pair are congruent, then the angles of each of the other pairs are also congruent. In our images with parallel lines, alternating angle pairs with both angles interior are: α=γ1, β=δ1 and with both angles exterior are: γ=α1 and δ=β1.
Other Characteristics of Transversals
If three lines in general position form a triangle are then cut by a transversal, the lengths of the six resulting segments satisfy Menelaus' theorem.
Related theorems
Euclid's formulation of the parallel postulate may be stated in terms of a transversal. Specifically, if the interior angles on the same side of the transversal are less than two right angles then lines must intersect. In fact, Euclid uses the same phrase in Greek that is usually translated as "transversal".[5]
Euclid's Proposition 27 states that if a transversal intersects two lines so that alternate interior angles are congruent, then the lines are parallel. Euclid proves this by contradiction: If the lines are not parallel then they must intersect and a triangle is formed. Then one of the alternate angles is an exterior angle equal to the other angle which is an opposite interior angle in the triangle. This contradicts Proposition 16 which states that an exterior angle on a triangle is always greater than the opposite interior angles.[6][7]
Euclid's Proposition 28 extends this result in two ways. First, if a transversal intersects two lines so that corresponding angles are congruent, then the lines are parallel. Second, if a transversal intersects two lines so that interior angles on the same side of the transversal are supplementary, then the lines are parallel. These follow from the previous proposition by applying the fact than opposite angles on intersecting lines equal (Prop. 15) and that adjacent angles on a line are supplementary (Prop. 13). As noted by Proclus, Euclid gives only three of a possible six such criteria for parallel lines.[8][9]
Euclid's Proposition 29 is a converse to the previous two. First, if a transversal intersects two parallel lines, then the alternate interior angles are congruent. If not then one is greater than the other, which implies its supplement is less than the supplement of the other angle. This implies that there are interior angles on the same side of the transversal which are less than two right angles, contradicting the fifth postulate. The proposition continues by stating that in a transversal of two parallel lines, corresponding angles are congruent and interior angles on the same side equal two right angles. These statements follow in the same way that Prop. 28 follows from Prop. 27.[10][11]
Euclid's proof makes essential use of fifth postulate, however modern treatments of geometry use Playfair's axiom instead. To prove proposition 29 assuming Playfair's axiom, let a transversal cross two parallel lines and suppose alternate interior angles are not equal. Draw a third line through the point where the transversal crosses the first line, but with angle equal to the angle the transversal makes with the second angle. This produces two different lines through a point both parallel to another line, contradicting the axiom.[12][13]
References
- ^ C.Clapham, J.Nicholson (2009). "Oxford Concise Dictionary of Mathematics" (PDF). Addison-Wesley. p. 582.
- ^ a b Rod Pierce (2011). "Parallel Lines". MathisFun. (interactive)
- ^ "Transversal". Math Open Reference. 2009. (interactive)
- ^ Holgate Art. 87
- ^ Heath p. 308 note 1
- ^ Heath p. 307
- ^ See also Holgate Art. 88
- ^ Heath p. 309-310
- ^ See also Holgate Art. 89-90
- ^ Heath p. 311-312
- ^ See also Holgate Art. 93-95
- ^ Heath p. 313
- ^ A similar proof is given in Holgate Art. 93
- Holgate, Thomas Franklin (1901). Elementary Geometry. Macmillan.
- Thomas Little Heath, T.L. (1908). The thirteen books of Euclid's Elements. Vol. 1. The University Press. pp. 307 ff.
