User:Mr. Ibrahem/Axitinib
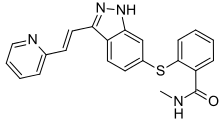 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Inlyta, Axinix |
| Other names | AG013736 |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a612017 |
| License data | |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| Drug class | Tyrosine kinase inhibitor[1] |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 58%[3] |
| Protein binding | >99%[3] |
| Metabolism | Liver (mostly CYP3A4/CYP3A5-mediated but with some contributions from CYP1A2, CYP2C19, UGT1A1)[3] |
| Elimination half-life | 2.5-6.1 hours[3] |
| Excretion | Feces (41%; 12% as unchanged drug), urine (23%)[3] |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C22H18N4OS |
| Molar mass | 386.47 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Axitinib, sold under the brand name Inlyta, is a medication used to treat renal cell cancer (RCC).[4] It is used in advanced disease, either alone or with avelumab or pembrolizumab.[4] It increased time to getting worse to 6.7 months from 4.7 months in those taking sorafenib.[5] It is taken by mouth.[4]
Common side effects include diarrhea, high blood pressure, tiredness, nausea, weight loss, weakness, and constipation.[4] Other side effects may include blood clots, bleeding, heart failure, gastrointestinal perforation, low thyroid, poor wound healing, liver problems, and reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome (RPLS).[4] Use in pregnancy may harm the baby.[4] It is a tyrosine kinase inhibitor that blocks vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF).[1]
Axitinib was approved for medical use in the United States and Europe in 2012.[5][4] In the United Kingdom 4 weeks of treatments costs the NHS about £3,500 as of 2021.[6] In the United States this amount costs about 17,300 USD.[7]
References[edit]
- ^ a b "Axitinib". LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury. National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. 2012. Archived from the original on 6 May 2021. Retrieved 17 January 2022.
- ^ "Inlyta- axitinib tablet, film coated". DailyMed. Pfizer Inc. Archived from the original on 27 November 2019. Retrieved 25 January 2014.
- ^ a b c d e "Inlyta (axitinib) dosing, indications, interactions, adverse effects, and more". Medscape Reference. WebMD. Archived from the original on 5 July 2018. Retrieved 25 January 2014.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j "DailyMed - INLYTA- axitinib tablet, film coated". dailymed.nlm.nih.gov. Archived from the original on 27 June 2021. Retrieved 17 January 2022.
- ^ a b "Inlyta". Archived from the original on 8 October 2021. Retrieved 17 January 2022.
- ^ BNF 81: March-September 2021. BMJ Group and the Pharmaceutical Press. 2021. p. 1013. ISBN 978-0857114105.
- ^ "Inlyta Prices, Coupons & Patient Assistance Programs". Drugs.com. Archived from the original on 19 April 2021. Retrieved 17 January 2022.
