User:Mr. Ibrahem/Wart
| Warts | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Verrucae,[1] papillomas[2] |
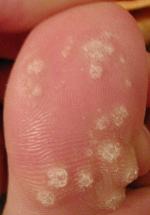 | |
| A large number of warts on the big toe | |
| Specialty | Dermatology |
| Symptoms | Painless, small, rough skin growth[1][3] |
| Duration | Months to years[1] |
| Causes | Human papillomavirus[1] |
| Risk factors | Public showers, eczema[3] |
| Differential diagnosis | Callus, seborrheic keratosis, squamous cell carcinoma[4] |
| Treatment | Salicylic acid, cryotherapy[1] |
| Frequency | Very common[2] |
Warts are typically small, rough, hard growths that are similar in color to the rest of the skin.[1][3] They typically do not result in other symptoms, except when on the bottom of the feet, where they may be painful.[3] While they usually occur on the hands and feet, they can also affect other locations.[1] One or many warts may appear.[3] They are not cancerous.[3]
Warts are caused by infection with a type of human papillomavirus (HPV).[1] Factors that increase the risk include use of public showers, working with meat, eczema and a weak immune system.[1][3] The virus is believed to enter the body through skin that has been damaged slightly.[1] A number of types exist, including "common warts", plantar warts, "filiform warts", and genital warts.[3] Genital warts are often sexually transmitted.[5]
Without treatment, most types of warts resolve in months to years.[1] A number of treatments may speed resolution including salicylic acid applied to the skin and cryotherapy.[1] In those who are otherwise healthy, they do not typically result in significant problems.[1] Treatment of genital warts differs from that of other types.[3]
Warts are very common, with most people being infected at some point in their lives.[2] The estimated current rate of non-genital warts among the general population is 1–13%.[1] They are more common among young people.[1] The estimated rate of genital warts in sexually active women is 12%.[5] Warts have been described at least as far back as 400 BC by Hippocrates.[4]
References[edit]
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o Loo, SK; Tang, WY (12 June 2014). "Warts (non-genital)". BMJ Clinical Evidence. 2014. PMC 4054795. PMID 24921240.
- ^ a b c "Papillomas (Warts) – National Library of Medicine". PubMed Health. Archived from the original on 2017-09-10. Retrieved 2016-11-06.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i "Warts: Overview". U.S. National Library of Medicine. 30 July 2014. Archived from the original on 10 September 2017.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ a b Bope, Edward T.; Kellerman, Rick D. (2012). Conn's Current Therapy 2012. Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 275. ISBN 978-1455733057. Archived from the original on 2016-11-07.
- ^ a b W Buck, Henry (13 August 2010). "Warts (genital)". BMJ Clinical Evidence. 2010. PMC 3217761. PMID 21418685.
