Endocrine system: Difference between revisions
rvv |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
The endocrine system regulates its hormones through negative feedback. Increases in hormone activity decrease the production of that hormone. The immune system and other factors contribute as control factors also, altogether maintaining constant levels of hormones. |
The endocrine system regulates its hormones through negative feedback. Increases in hormone activity decrease the production of that hormone. The immune system and other factors contribute as control factors also, altogether maintaining constant levels of hormones. |
||
== Table of endocrine glands and the hormones secreted == |
|||
=== In both sexes: === |
|||
(starting from the head and going downwards) |
|||
*'''[[Hypothalamus]]''' |
|||
**[[Thyrotropin-releasing hormone]] (TRH) |
|||
**[[Gonadotropin-releasing hormone]] (GnRH) |
|||
**[[Growth hormone-releasing hormone]] (GHRH) |
|||
**[[Corticotropin-releasing hormone]] (CRH) |
|||
**[[Somatostatin]] |
|||
**[[Dopamine]] |
|||
*'''[[Pituitary gland]]''' |
|||
**'''Anterior lobe ([[adenohypophysis]])''' |
|||
***GH ([[human growth hormone]]) |
|||
***PRL ([[prolactin]]) |
|||
***ACTH ([[adrenocorticotropic hormone]]) |
|||
***TSH ([[thyroid-stimulating hormone]]) |
|||
***FSH ([[follicle-stimulating hormone]]) |
|||
***LH ([[luteinizing hormone]]) |
|||
**'''Posterior lobe ([[neurohypophysis]])''' |
|||
***[[Oxytocin]] |
|||
***ADH ([[antidiuretic hormone]]) |
|||
*'''[[Pineal gland]]''' |
|||
**[[Melatonin]] |
|||
*'''[[Thyroid gland]]''' |
|||
**Thyroxine (T4), a form of [[thyroid hormone]] |
|||
**Triiodothyronine (T3), a form of [[thyroid hormone]] |
|||
**[[Calcitonin]] |
|||
*'''[[Parathyroid gland]]''' |
|||
**[[Parathyroid hormone]] (PTH) |
|||
*'''[[Heart]]''' |
|||
**[[Atrial-natriuretic peptide]] (ANP) |
|||
*'''[[Stomach]] and [[intestines]]''' |
|||
**[[Gastrin]] |
|||
**[[Secretin]] |
|||
**[[Cholecystokinin]] (CCK) |
|||
**[[Somatostatin]] |
|||
**[[Neuropeptide Y]] |
|||
*'''[[Liver]]''' |
|||
**[[Insulin-like growth factor]] |
|||
**[[Angiotensinogen]] |
|||
**[[Thrombopoietin]] |
|||
*'''[[Islets of Langerhans]] in the [[pancreas]]''' |
|||
**[[Insulin]] |
|||
**[[Glucagon]] |
|||
**[[Somatostatin]] |
|||
*'''[[Adrenal gland]]s''' |
|||
**'''[[Adrenal cortex]]''' |
|||
***[[Glucocorticoid]]s - [[cortisol]] |
|||
***[[Mineralocorticoid]]s - [[aldosterone]] |
|||
***[[Androgen]]s (including [[testosterone]]) |
|||
**'''[[Adrenal medulla]]''' |
|||
***Adrenaline ([[epinephrine]]) |
|||
***Noradrenaline ([[norepinephrine]]) |
|||
*'''[[Kidney]]''' |
|||
**[[Renin]] |
|||
**[[Erythropoietin]] ([[EPO]]) |
|||
**[[Calcitriol]] |
|||
*'''[[Skin]]''' |
|||
**Calciferol ([[vitamin D]]<sub>3</sub>) |
|||
*'''[[Adipose tissue]]''' |
|||
**[[Leptin]] |
|||
=== In males only === |
|||
*'''[[Testes]]''' |
|||
**[[Androgen]]s ([[testosterone]]) |
|||
=== In females only === |
|||
*'''[[Ovarian follicle]]''' |
|||
**[[Oestrogens]] |
|||
**[[Testosterone]] |
|||
*'''[[Corpus luteum]]''' |
|||
**[[Progesterone]] |
|||
*'''[[Placenta]]''' (when [[pregnant]]) |
|||
**[[Progesterone]] |
|||
**[[Human chorionic gonadotrophin]] (HCG) |
|||
**[[Human placental lactogen]] (HPL) |
|||
==Role in disease== |
==Role in disease== |
||
| Line 116: | Line 23: | ||
==Diffuse Endocrine System== |
==Diffuse Endocrine System== |
||
Organs aren't the sole way for hormones to be sent into the body; there are a host of specific cells which secrete hormones independently. These are called the "diffuse" endocrine system, and include [[myocytes]] in the heart (atria) and [[epithelial cell]]s in the stomach and small intestines. In fact, if one were to classify ''any'' chemical excretions in the term "hormone," every cell in the human body could be considered a part of the endocrine system. |
Organs aren't the sole way for hormones to be sent into the body; there are a host of specific cells which secrete hormones independently. These are called the "diffuse" endocrine system, and include [[myocytes]] in the heart (atria) and [[epithelial cell]]s in the stomach and small intestines. In fact, if one were to classify ''any'' chemical excretions in the term "hormone," every cell in the human body could be considered a part of the endocrine system. |
||
==See also== |
|||
* [[receptor (proteomics)|Receptors]] |
|||
* [[Releasing hormone]]s |
|||
* [[Nervous system]] |
|||
* [[Endocrine disruptor]] |
|||
* [[Neuroendocrinology]] |
|||
* [[Endocrinology]] |
|||
* [[Hormones]] |
|||
{{endocrine_system}} |
|||
{{organ_systems}} |
|||
[[Category:Endocrine system]] |
|||
[[ca:Sistema endocrí]] |
|||
[[cs:Soustava žláz s vnitřní sekrecí]] |
|||
[[da:Endokrine system]] |
|||
[[de:Endokrines System]] |
|||
[[es:Sistema endocrino]] |
|||
[[fr:Endocrinologie]] |
|||
[[it:Sistema endocrino]] |
|||
[[lt:Endokrininė sistema]] |
|||
[[mk:Ендокрин систем]] |
|||
[[nl:Endocrien systeem]] |
|||
[[ja:内分泌器]] |
|||
[[pt:Sistema endócrino]] |
|||
[[ru:Эндокринная система]] |
|||
[[sk:Endokrinná sústava]] |
|||
[[sl:Endokrini sistem]] |
|||
[[sr:Ендокрини систем]] |
|||
[[es:Glándulas de secreción interna]] |
|||
[[fr:Glande endocrine]] |
|||
[[lt:Endokrininė liauka]] |
|||
[[pt:Glândula endócrina]] |
|||
Revision as of 23:09, 28 February 2006
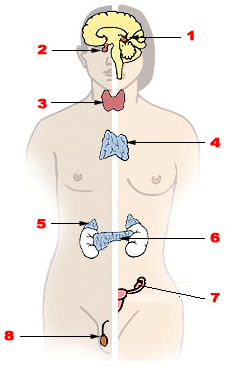
The endocrine system is a control system of ductless glands that secrete chemical messengers called hormones that circulate within the body via the bloodstream to affect distant organs. Hormones act as "messengers", and are carried by the bloodstream to different cells in the body, which interpret these messages and act on them. The endocrine system does not include exocrine glands such as salivary glands, sweat glands and glands within the gastrointestinal tract.
The field of medicine that deals with disorders of endocrine glands is endocrinology, a branch of the wider field of internal medicine.
Physiology
The endocrine system links the brain to the organs that control body metabolism, growth and development, and reproduction.
Signal transduction of some hormones with steroid structure involves nuclear hormone receptor proteins that are a class of ligand activated proteins that, when bound to specific sequences of DNA serve as on-off switches for transcription within the cell nucleus. These switches control the development and differentiation of skin, bone and behavioral centers in the brain, as well as the continual regulation of reproductive tissues.
The endocrine system regulates its hormones through negative feedback. Increases in hormone activity decrease the production of that hormone. The immune system and other factors contribute as control factors also, altogether maintaining constant levels of hormones.
Role in disease
Diseases of the endocrine system are common, such as diabetes mellitus and thyroid disease.
Endocrineopathies can occur with any of these. Hypofunction can occur as result of loss of reserve, hyposecretion, agenesis, atrophy, destruction, etc. Hyperfunction can occur as result of hypersecretion, loss of suppression, tumor, hyperplasia, etc.
Endocrineopathies are classified as primary, secondary, or tertiary.
Primary is target organ dysfunction and is normally associated with increased or decreased secretory hormones. Secondary is a dysfunction that originates elsewhere like the pituitary gland and is normally associated with increased or decreased production of trophic factors. Tertiary is associated with dysfunction of the hypothalamus and its releasing hormones.
Diffuse Endocrine System
Organs aren't the sole way for hormones to be sent into the body; there are a host of specific cells which secrete hormones independently. These are called the "diffuse" endocrine system, and include myocytes in the heart (atria) and epithelial cells in the stomach and small intestines. In fact, if one were to classify any chemical excretions in the term "hormone," every cell in the human body could be considered a part of the endocrine system.
