Methoxetamine: Difference between revisions
Needs to be sourced. I don't think there is a source so I've removed it. |
removed unsourced information |
||
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
}} |
}} |
||
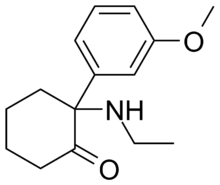
'''Methoxetamine (MXE)''' or '''3-MeO-2-Oxo-PCE''' is a chemical of the [[arylcyclohexylamine]] class which has been sold as a [[designer drug]].<ref>[http://www.emcdda.europa.eu/attachements.cfm/att_132857_EN_EMCDDA-Europol%20Annual%20Report%202010A.pdf EMCDDA Annual Report 2010]</ref> It is a derivative of [[ketamine]] that also contains structural features of [[eticyclidine]] and [[3-MeO-PCP]]. Methoxetamine is thought to behave as a [[NMDA receptor antagonist]] and [[dopamine reuptake inhibitor]], though it has not been formally profiled pharmacologically.<ref>{{Cite doi|10.3109/15563650.2011.617310}}</ref> Methoxetamine differs from many other dissociative anesthetics of the arylcyclohexylamine class in that it was designed for grey-market distribution.<ref name="Interview with a ketamine chemist">[http://www.viceland.com/int/v18n2/htdocs/interview-with-ketamine-chemist-704.php?page=1], Morris, H. (11 February 2011). "Interview with a ketamine chemist: or to be more precise, an arylcyclohexylamine chemist". Vice Magazine. Retrieved 2011-02-11.</ref> Methoxetamine is a product of rational [[drug design]]: its N-ethyl group was chosen to increase potency, lessening the risk of [[interstitial cystitis]] that can result from the accumulation of ketamine-like metabolites in the urinary bladder.<ref name="Interview with a ketamine chemist">[http://www.viceland.com/int/v18n2/htdocs/interview-with-ketamine-chemist-704.php?page=1], Morris, H. (11 February 2011). "Interview with a ketamine chemist: or to be more precise, an arylcyclohexylamine chemist". Vice Magazine. Retrieved 2011-02-11.</ref> |
'''Methoxetamine (MXE)''' or '''3-MeO-2-Oxo-PCE''' is a chemical of the [[arylcyclohexylamine]] class which has been sold as a [[designer drug]].<ref>[http://www.emcdda.europa.eu/attachements.cfm/att_132857_EN_EMCDDA-Europol%20Annual%20Report%202010A.pdf EMCDDA Annual Report 2010]</ref> It is a derivative of [[ketamine]] that also contains structural features of [[eticyclidine]] and [[3-MeO-PCP]]. Methoxetamine is thought to behave as a [[NMDA receptor antagonist]] and [[dopamine reuptake inhibitor]], though it has not been formally profiled pharmacologically.<ref>{{Cite doi|10.3109/15563650.2011.617310}}</ref> Methoxetamine differs from many other dissociative anesthetics of the arylcyclohexylamine class in that it was designed for grey-market distribution.<ref name="Interview with a ketamine chemist">[http://www.viceland.com/int/v18n2/htdocs/interview-with-ketamine-chemist-704.php?page=1], Morris, H. (11 February 2011). "Interview with a ketamine chemist: or to be more precise, an arylcyclohexylamine chemist". Vice Magazine. Retrieved 2011-02-11.</ref> Methoxetamine is a product of rational [[drug design]]: its N-ethyl group was chosen to increase potency, lessening the risk of [[interstitial cystitis]] that can result from the accumulation of ketamine-like metabolites in the urinary bladder.<ref name="Interview with a ketamine chemist">[http://www.viceland.com/int/v18n2/htdocs/interview-with-ketamine-chemist-704.php?page=1], Morris, H. (11 February 2011). "Interview with a ketamine chemist: or to be more precise, an arylcyclohexylamine chemist". Vice Magazine. Retrieved 2011-02-11.</ref><ref>"4-Amino-4-arylcyclohexanones and Their Derivatives, a Novel Class of Analgesics. 1. Modification of the Aryl Ring." Daniel Lednicer, Philip F. VonVoigtlander and D. Edward Emmert. The Upjohn Company, Research Laboratories, Kalamazoo, Michigan 49001. Received August 7, 1979. J. Med. Chem 1980, 23, p424-430</ref> |
||
==See also== |
==See also== |
||
Revision as of 23:54, 17 November 2011
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| ChemSpider | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C15H21NO2 |
| Molar mass | 247.33 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Methoxetamine (MXE) or 3-MeO-2-Oxo-PCE is a chemical of the arylcyclohexylamine class which has been sold as a designer drug.[1] It is a derivative of ketamine that also contains structural features of eticyclidine and 3-MeO-PCP. Methoxetamine is thought to behave as a NMDA receptor antagonist and dopamine reuptake inhibitor, though it has not been formally profiled pharmacologically.[2] Methoxetamine differs from many other dissociative anesthetics of the arylcyclohexylamine class in that it was designed for grey-market distribution.[3] Methoxetamine is a product of rational drug design: its N-ethyl group was chosen to increase potency, lessening the risk of interstitial cystitis that can result from the accumulation of ketamine-like metabolites in the urinary bladder.[3][4]
See also
References
- ^ EMCDDA Annual Report 2010
- ^ Attention: This template ({{cite doi}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by doi:10.3109/15563650.2011.617310, please use {{cite journal}} (if it was published in a bona fide academic journal, otherwise {{cite report}} with
|doi=10.3109/15563650.2011.617310instead. - ^ a b [1], Morris, H. (11 February 2011). "Interview with a ketamine chemist: or to be more precise, an arylcyclohexylamine chemist". Vice Magazine. Retrieved 2011-02-11.
- ^ "4-Amino-4-arylcyclohexanones and Their Derivatives, a Novel Class of Analgesics. 1. Modification of the Aryl Ring." Daniel Lednicer, Philip F. VonVoigtlander and D. Edward Emmert. The Upjohn Company, Research Laboratories, Kalamazoo, Michigan 49001. Received August 7, 1979. J. Med. Chem 1980, 23, p424-430
