Solar still: Difference between revisions
m Removed text from template |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
Solar stills are used in cases where piped or well water is impractical, such as in remote homes or during power outages. In [[Florida]] and other [[hurricane]] target areas that infrequently lose power for a few days, solar distillation can provide an alternate source of clean water. |
Solar stills are used in cases where piped or well water is impractical, such as in remote homes or during power outages. In [[Florida]] and other [[hurricane]] target areas that infrequently lose power for a few days, solar distillation can provide an alternate source of clean water. |
||
Knowing how to put together a solar still is often billed as a useful [[Survival skills|survival skill]] and could provide an important means of potable water in the event of a wilderness emergency. Nevertheless, under typical conditions makeshift solar stills rarely produce enough water for survival, and the sweat expended in building one can easily exceed its daily output. Solar stills can extract water from moisture in the ground but to increase the amount of moisture available to a solar still, water (fresh or saline) can be added inside or along the edges of the still. Where no water sources are readily available, urine or shredded vegetation can be used inside the pit |
Knowing how to put together a solar still is often billed as a useful [[Survival skills|survival skill]] and could provide an important means of potable water in the event of a wilderness emergency. Nevertheless, under typical conditions makeshift solar stills rarely produce enough water for survival, and the sweat expended in building one can easily exceed its daily output. Solar stills can extract water from moisture in the ground but to increase the amount of moisture available to a solar still, water (fresh or saline) can be added inside or along the edges of the still. Where no water sources are readily available, urine or shredded vegetation can be used inside the pit. To prevent losing moisture by taking apart the still to retrieve collected water a length of plastic tubing can be used to sip water as it accumulates. |
||
== References == |
== References == |
||
Revision as of 23:17, 1 August 2006
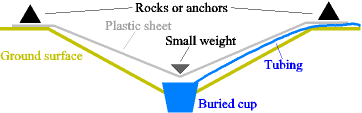
A solar still is a very simple device for distilling water, powered by the heat of the sun. A few basic types of solar stills are cone shaped, boxlike, and pit. For cone solar stills, impure water is inserted into the container, where it is evaporated by the sun through clear plastic. The pure water vapor condenses on top and drips down to the side, where it is collected and removed. The most sophisticated of these are the box shaped types. The least sophisticated are the pit types.
Solar stills are used in cases where piped or well water is impractical, such as in remote homes or during power outages. In Florida and other hurricane target areas that infrequently lose power for a few days, solar distillation can provide an alternate source of clean water.
Knowing how to put together a solar still is often billed as a useful survival skill and could provide an important means of potable water in the event of a wilderness emergency. Nevertheless, under typical conditions makeshift solar stills rarely produce enough water for survival, and the sweat expended in building one can easily exceed its daily output. Solar stills can extract water from moisture in the ground but to increase the amount of moisture available to a solar still, water (fresh or saline) can be added inside or along the edges of the still. Where no water sources are readily available, urine or shredded vegetation can be used inside the pit. To prevent losing moisture by taking apart the still to retrieve collected water a length of plastic tubing can be used to sip water as it accumulates.
References
External links
- Solar Still Basics
- Desert Survival: The Solar Still
- http://groups.yahoo.com/group/SOLAR_DISTILLATION_PROJECT/ ( Make your own solar powered still) [Yahoo! group no longer active]
