Terminator (solar): Difference between revisions
pic |
m Reduced the size of the composite image to prevent it from covering text. |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Image:Daylight.png|thumb|World map with terminator (April)]] |
[[Image:Daylight.png|thumb|World map with terminator (April)]] |
||
[[Image:Nightfall europe-and-afrika 20050507-184500.jpg|thumb| |
[[Image:Nightfall europe-and-afrika 20050507-184500.jpg|thumb|195px|A composite image showing the [[Terminator (solar)|terminator]] dividing night from day, running across [[Europe]] and [[Africa]]. Observers on the surface of the earth along this terminator will see a sunset.]] |
||
[[Image:Earthterminator iss002 full.jpg|thumb|left|Photograph of part of the terminator crossing the surface of the Earth, as seen from the [[International Space Station|ISS]]. The terminator is diffuse and shows the gradual transition to darkness that is experienced as [[twilight]] on the surface.]] |
[[Image:Earthterminator iss002 full.jpg|thumb|left|Photograph of part of the terminator crossing the surface of the Earth, as seen from the [[International Space Station|ISS]]. The terminator is diffuse and shows the gradual transition to darkness that is experienced as [[twilight]] on the surface.]] |
||
The '''terminator''' is the line between the illuminated, day side and dark, night side of a planetary body (also known as the "grey line"). It is defined as the [[locus (mathematics)|locus]] of points on a [[moon]] or [[planet]] where the line through the [[sun]] is [[tangent]]. |
The '''terminator''' is the line between the illuminated, day side and dark, night side of a planetary body (also known as the "grey line"). It is defined as the [[locus (mathematics)|locus]] of points on a [[moon]] or [[planet]] where the line through the [[sun]] is [[tangent]]. |
||
Revision as of 18:34, 2 November 2006
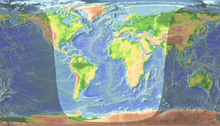


The terminator is the line between the illuminated, day side and dark, night side of a planetary body (also known as the "grey line"). It is defined as the locus of points on a moon or planet where the line through the sun is tangent. The line separates the portions of the earth experiencing daylight from the portion of the planet experiencing darkness. While one half of the earth is illuminated at any point in time, the location of the terminator line varies by time of day due to the rotation of the earth on its axis as well as the revolution of the earth around the sun. The seasons impact the location of the terminator line most dramatically.
In the frame of reference of a rotating planet, the terminator sweeps across the surface of the planet bringing sunrise on one side of the planet and sunset on the opposite side.
Examination of the terminator can yield information about the surface of the body; for example, a fuzzy terminator indicates the presence of an atmosphere.
On the spring and fall equinoxes (around March and September 21), there is no tilt of the earth with respect to the sun so the terminator line is parallel with the axis of the earth and with the lines of longitude.
The terminator line is at its greatest angle with respect to the axis on the winter and summer solstices (around December and June 21), when it is approximately 23.5 degrees off the axis.
Excluding travel near the poles, the Concorde was the only passenger airliner able to overtake the terminator. On certain early evening transatlantic flights departing from Heathrow or Paris, it was possible to take off at night and catch up with the sun — from the cockpit you could see the sun rise in the west.
