Common Language Runtime: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
m mistype |
||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
{{Program execution}} |
{{Program execution}} |
||
The '''Common Language Runtime''' ('''CLR'''), the [[ |
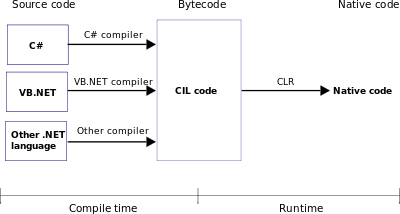
The '''Common Language Runtime''' ('''CLR'''), the [[virtual machine]] component of [[Microsoft|Microsoft's]] [[.NET framework]], manages the execution of .NET programs. A process known as [[just-in-time compilation]] converts compiled code into machine instructions which the computer's [[CPU]] then executes.<ref name="msdn-clr">{{cite web| title = Common Language Runtime (CLR) | url = http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/8bs2ecf4 | accessdate = 14 November 2013 | work = [[MSDN Library]]}}</ref> The CLR provides additional services including [[memory management]], [[type safety]], [[exception handling]], [[garbage collection (computer science)|garbage collection]], security and [[thread management]]. All programs written for the .NET framework, regardless of [[programming language]], are executed by the CLR. All versions of the .NET framework include CLR. The CLR team was started June 13, 1998. |
||
CLR implements the [[Virtual Execution System]] (VES) as defined in the [[Common Language Infrastructure]] (CLI) standard, initially developed by Microsoft itself. A public standard defines the Common Language Infrastructure specification.<ref>{{cite web | title = ECMA C# and Common Language Infrastructure Standards |
CLR implements the [[Virtual Execution System]] (VES) as defined in the [[Common Language Infrastructure]] (CLI) standard, initially developed by Microsoft itself. A public standard defines the Common Language Infrastructure specification.<ref>{{cite web | title = ECMA C# and Common Language Infrastructure Standards |
||
Revision as of 21:13, 2 February 2019
This article needs additional citations for verification. (September 2014) |
| Program execution |
|---|
| General concepts |
| Types of code |
| Compilation strategies |
| Notable runtimes |
|
| Notable compilers & toolchains |
|
The Common Language Runtime (CLR), the virtual machine component of Microsoft's .NET framework, manages the execution of .NET programs. A process known as just-in-time compilation converts compiled code into machine instructions which the computer's CPU then executes.[1] The CLR provides additional services including memory management, type safety, exception handling, garbage collection, security and thread management. All programs written for the .NET framework, regardless of programming language, are executed by the CLR. All versions of the .NET framework include CLR. The CLR team was started June 13, 1998.
CLR implements the Virtual Execution System (VES) as defined in the Common Language Infrastructure (CLI) standard, initially developed by Microsoft itself. A public standard defines the Common Language Infrastructure specification.[2]
| CLR version | .NET version |
|---|---|
| 1.0 | 1.0 |
| 1.1 | 1.1 |
| 2.0 | 2.0, 3.0, 3.5 |
| 4 | 4, 4.5, 4.6, 4.7 |
See also
References
- ^ a b "Common Language Runtime (CLR)". MSDN Library. Retrieved 14 November 2013.
- ^ "ECMA C# and Common Language Infrastructure Standards". Visual Studio Developer Center. Retrieved 14 November 2013.
