Kenon
| Kenon | |
|---|---|
| Кенон | |
 Landscape of Kenon lake from the Titovskaya Sopka range | |
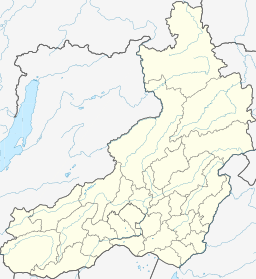
Location in Zabaykalsky Krai, Russian Far East | |
| Coordinates | 52°02′19″N 113°22′50″E / 52.03861°N 113.38056°E[1] |
| Primary inflows | Ivanovka, Kadala |
| Catchment area | 227 km2 (88 sq mi) |
| Basin countries | Zabaykalsky Krai, Russia |
| Max. length | 5.7 km (3.5 mi) |
| Max. width | 2.8 km (1.7 mi) |
| Surface area | 16 km2 (6.2 sq mi) |
| Max. depth | 6.8 m (22 ft) |
| Surface elevation | 653 m (2,142 ft) |
| Frozen | October to May |
| Islands | None |
| Settlements | Chita |
Kenon (Template:Lang-ru) is a fresh water body in the Chita District, Zabaykalsky Krai, Russia.[2] The name of the lake originated in the Evenki language.[3]
The city of Chita is located near the lakeshore and lake Kenon is surrounded by residential areas, railways, highways and agricultural land. There is also a rather narrow city beach zone which is popular in the summer, although there is substantial pollution. Neolithic and Bronze Age archaeological remains were found by the shores of the lake.[3]
Geography
Kenon lake is part of the Ingoda river basin, It is located in the Chita-Ingoda Depression (Читино-Ингодинская впадина), in the western outskirts of Chita, Zabaykalsky Krai. A few small streams flow into the lake. The main ones are the Ivanovka and Kadala rivers,[4] which have their sources in the neighboring Yablonovy Range. The outflow is through a 2 km (1.2 mi) long channel leading to the Ingoda that fills with water only in the wettest years.[3][5]
The lake is frozen between late October and early May.[3]
 |
Fauna
Among the fish species present in the lake, the main ones are perch, Amur chebak, Amur pike, goldfish, Amur carp and Amur catfish.[3]
See also
- List of lakes of Russia
- Ivan-Arakhley Lake System, located to the west
References
- ^ Google Earth
- ^ "Озеро Кенон in the State Water Register of Russia". textual.ru (in Russian).
- ^ a b c d e Энциклопедия Забайкалья - Кенон, озеро
- ^ "Река Ивановский (Ивановка) in the State Water Register of Russia". textual.ru (in Russian).
- ^ "N-49 Chart (in Russian)". Retrieved 30 September 2021.
External links
 Media related to Lake Kenon at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Lake Kenon at Wikimedia Commons