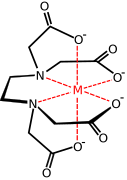
Transition metal carboxylate complex
Transition metal carboxylate complexes are coordination complexes with carboxylate (RCO2−) ligands. Reflecting the diversity of carboxylic acids, the inventory of metal carboxylates is large. Many are useful commercially, and many have attracted intense scholarly scrutiny. Carboxylates exhibit a variety of coordination modes, most common are κ1- (O-monodentate), κ2 (O,O-bidentate), and bridging.
Acetate and related monocarboxylates
Structure and bonding
Carboxylates bind to single metals by one or both oxygen atoms, the respective notation being κ1- and κ2-. In terms of electron counting, κ1-carboxylates are "X"-type ligands, i.e., a pseudohalide-like. κ2-carboxylates are "L-X ligands", i.e. resembling the combination of a Lewis base (L) and a pseudohalide (X). Carboxylates are classified as hard ligands, in HSAB theory.
- Structures of Selected Metal Acetates
-
Silver acetate
-
Molybdenum(II) acetate, illustrating the Mo-Mo quadruple bond.[1]
-
[CoO(acetate)]4, the "Das cubane"
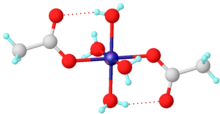
For simple carboxylates, the acetate complexes are illustrative. Most transition metal acetates are mixed ligand complexes. One common example is hydrated nickel acetate, Ni(O2CCH3)2(H2O)4, which features intramolecular hydrogen-bonding between the uncoordinated oxygens and the protons of aquo ligands. Stoichiometrically simple complexes are often multimetallic. One family are the basic metal acetates, of the stoichiometry [M3O(OAc)6(H2O)3]n+.[2]

Homoleptic complexes
Homoleptic carboxylate complexes are usually coordination polymers. But exceptions exist.
- A molecular monocarboxylate is silver acetate, Ag2(OAc)2.
- Molecular diacetates are more common. Several diacetates adopt the Chinese lantern structure. Well studied examples include the dimetal tetraacetates (M2(OAc)4) including rhodium(II) acetate, copper(II) acetate, molybdenum(II) acetate, and chromium(II) acetate. Platinum diacetate and palladium diacetate feature Pt4 and Pd3 cores, further illustrating the tendency of acetate ligands to stabilize multimetallic structures.
- Mononuclear tricarboxylates include derivatives of 1-adamantanecarboxylic acid, which have the formula [M(O2CC10H11)3]− (M = Co, Ni, Zn). The carboxylates are bidentate.[4]
Synthesis
Many methods allow the synthesis of metal carboxylates. From preformed carboxylic acid, the following routes have been demonstrated:[5]
- acid-base reactions: LnMOR' + RCO2H → LnMO2CR + R'OH
- protonolysis: LnMalkyl + RCO2H → LnMO2CR + alkane
- oxidative addition: LnM + RCO2H → Ln(H)MO2CR
From preformed carboxylate, salt metathesis reactions are common:
- LnMCl + RCO2Na → LnMO2CR + NaCl
Metal carboxylates can be prepared by carbonation of highly basis metal alkyls:
- LnMR + CO2 → LnMO2CR
Reactions
A common reaction of metal carboxylates is their displacement by more basic ligands. Acetate is a common leaving group. They are especially prone to protonolysis, which is widely used to introduce ligands, displacing the carboxylic acid. In this way octachlorodimolybdate is produced from dimolybdenum tetraacetate:
- Mo2(O2CCH3)4 + 4 HCl + 4 KCl → K4[Mo2Cl8] + 4 CH3CO2H
Acetates of electrophilic metals are proposed to function as bases in concerted metalation deprotonation reactions.[6]
Attempts to prepare some carboxylate complexes, especially for electrophilic metals, often gives oxo derivatives. Examples include the oxo-acetates of Fe(III), Mn(III), and Cr(III). Pyrolysis of metal carboxylates affords acid anhydrides and the metal oxide. This reaction explains the formation of basic zinc acetate from anhydrous zinc diacetate.
In some cases, monodentate carboxylates undergo O-alkylation to give esters. Strong alkylating agents are required.
Other carboxylates
Many carboxylates form complexes with transition metals. Alkyl and simple aryl carboxylates behave similarly to the acetates. Trifluoroacetates differ in mononuclear complexes because it is usually monodentate, e.g. [Zn(κ2-O2CCH3)2(OH2)2] vs [Zn(κ1-O2CCF3)2(OH4)2].[7]
Applications
Metal naphthenates and ethylhexanoates

Structure of a representative naphthenic acid, which forms a variety of complexes with transition metals.
Naphthenic acids, mixtures of long chain and cyclic carboxylic acids extracted from petroleum, form lipophilic complexes (often called salts) with transition metals. These metal naphthenates, have the formula M(naphthenate)2, or M3O(naphthenate)6, have diverse applications[8][9] including synthetic detergents, lubricants, corrosion inhibitors, fuel and lubricating oil additives, wood preservatives, insecticides, fungicides, acaricides, wetting agents, thickening agent, and oil drying agents. Industrially useful naphthenates include those of aluminium, magnesium, calcium, barium, cobalt, copper, lead, manganese, nickel, vanadium, and zinc.<[9] Illustrative is the use of cobalt naphthenate for the oxidation of tetrahydronaphthalene to the hydroperoxide.[10]

Like naphthenic acid, 2-ethylhexanoic acid forms lipophilic complexes that are used in organic and industrial chemical synthesis. They function as catalysts in polymerizations as well as for oxidation reactions as oil drying agents.[11] Metal ethylhexanoates are referred to as metallic soaps.[12]
Aminopolycarboxylates
-
metal complex with the EDTA anion
-
Ferric bis(iminodiacetate)
-
Active site of hemerythrin, an O2-carrying iron-carboxylate
A commercially important family of metal carboxylates are derived from aminopolycarboxylates, e.g., EDTA4-. Related to these synthetic chelating agents are the amino acids, which form large families of amino acid complexes. Two amino acids, glutamate and aspartate, have carboxylate side chains, which function as ligands for iron in nonheme iron proteins, such as hemerythrin.[13]
Metal organic frameworks (MOFs)
Metal organic frameworks, porous, three-dimensional coordination polymers, are often derived from metal carboxylate clusters. These clusters, called secondary bonding units (SBU's), are often linked by the conjugate bases of benzenedi- and tricarboxylic acids.[14]
Reagents for organic synthesis

Palladium(II) acetate has been described as being "among the most extensively used transition metal complexes in metal-mediated organic synthesis". Many coupling reactions utilize this reagent, which is soluble in organic solvents and which contains a built-in Bronsted base (acetate).[15]
Dirhodium tetrakis(trifluoroacetate) is widely used catalyst for reactions involving diazo compounds.[16]
Related topics
References
- ^ Brignole, Alicia B.; Cotton, F. A. (1972). "Rhenium and Molybdenum Compounds Containing Quadruple Bonds". Inorganic Syntheses. 13: 81–89. doi:10.1002/9780470132449.ch15.
- ^ Catterick, Janet; Thornton, Peter (1977). Structures and Physical Properties of Polynuclear Carboxylates. Advances in Inorganic Chemistry and Radiochemistry. Vol. 20. pp. 291–362. doi:10.1016/S0065-2792(08)60041-2. ISBN 9780120236206.
- ^ Zhang, Gao; Lin, Jian; Guo, Dong-Wei; Yao, Shi-Yan; Tian, Yun-Qi (2010). "Infinite Coordination Polymers of One- and Two-dimensional Cobalt Acetates". Zeitschrift für Anorganische und Allgemeine Chemie. 636 (7): 1401–1404. doi:10.1002/zaac.200900457.
- ^ Fursova, E. Yu.; Romanenko, G. V.; Tolstikov, S. E.; Ovcharenko, V. I. (2019). "Mononuclear Transition Metal Adamantane-1-Carboxylates". Russian Chemical Bulletin: 1669–1674. doi:10.1007/s11172-019-2610-4. S2CID 203592748.
- ^ García-Rodríguez, Raúl; Hendricks, Mark P.; Cossairt, Brandi M.; Liu, Haitao; Owen, Jonathan S. (2013). "Conversion Reactions of Cadmium Chalcogenide Nanocrystal Precursors". Chemistry of Materials. 25 (8): 1233–1249. doi:10.1021/cm3035642.
- ^ Ackermann, Lutz (2011-03-09). "Carboxylate-Assisted Transition-Metal-Catalyzed C−H Bond Functionalizations: Mechanism and Scope". Chemical Reviews. 111 (3): 1315–1345. doi:10.1021/cr100412j. ISSN 0009-2665. PMID 21391562.
- ^ Morozov, I. V.; Karpova, E. V.; Glazunova, T. Yu.; Boltalin, A. I.; Zakharov, M. A.; Tereshchenko, D. S.; Fedorova, A. A.; Troyanov, S. I. (2016). "Trifluoroacetate complexes of 3d elements: Specific features of syntheses and structures". Russian Journal of Coordination Chemistry. 42 (10): 647–661. doi:10.1134/S107032841610002X.
- ^ M. Landau. 1993. "Driers and metallic soaps", in J. Kroschwitz, ed., Kirk-Othmer Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology. New York: John Wiley & Sons. Vol. 8, pp. 432-445. doi:10.1002/0471238961.0418090512011404.a01
- ^ a b Nora, Angelo; Koenen, Gunther (2010). "Metallic Soaps". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. doi:10.1002/14356007.a16_361.pub2. ISBN 978-3-527-30385-4.
- ^ Knight, H. B.; Swern, Daniel (1954). "Tetralin Hydroperoxide". Organic Syntheses. 34: 90. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.034.0090.
- ^ Raju, Ravinder; Prasad, Kapa (2012). "Synthetic Applications of 2-Ethylhexanoic Acid Derived Reagents". Tetrahedron. 68 (5): 1341–1349. doi:10.1016/j.tet.2011.10.078.
- ^ Nora, Angelo; Szczepanek, Alfred; Koenen, Gunther (2001). "Metallic Soaps". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. doi:10.1002/14356007.a16_361. ISBN 3527306730.
- ^ Jasniewski, Andrew J.; Que, Lawrence (2018). "Dioxygen Activation by Nonheme Diiron Enzymes: Diverse Dioxygen Adducts, High-Valent Intermediates, and Related Model Complexes". Chemical Reviews. 118 (5): 2554–2592. doi:10.1021/acs.chemrev.7b00457. PMC 5920527. PMID 29400961.
- ^ Tranchemontagne, David J.; Mendoza-Cortés, José L.; o'Keeffe, Michael; Yaghi, Omar M. (2009). "Secondary Building Units, Nets and Bonding in the Chemistry of Metal–Organic Frameworks". Chemical Society Reviews. 38 (5): 1257–1283. doi:10.1039/b817735j. PMID 19384437.
- ^ Grennberg, Helena; Foot, Jonathan S.; Banwell, Martin G.; Roman, Daniela Sustac (2001). "Palladium(II) Acetate". Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis. pp. 1–35. doi:10.1002/047084289X.rp001.pub3. ISBN 978-0-470-84289-8.
- ^ Doyle, Michael P.; Davies, Huw M. L.; Manning, James R. (2006). "Dirhodium(II) tetrakis(trifluoroacetate)". eEROS. doi:10.1002/047084289X.rd461.pub2.

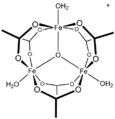


![[CoO(acetate)]4, the "Das cubane"](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/da/DasCubane.svg/120px-DasCubane.svg.png)