Reflection coefficient
The reflection coefficient is used in physics and electrical engineering when wave propagation in a medium containing discontinuities is considered. A reflection coefficient describes either the amplitude or the intensity of a reflected wave relative to an incident wave. The reflection coefficient is closely related to the transmission coefficient.
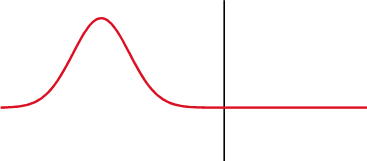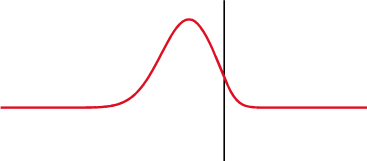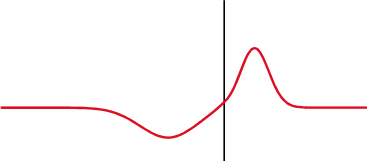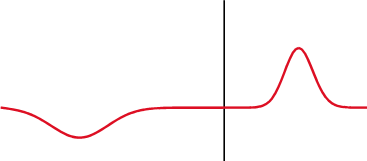
Different specialties have different applications for the term.
Telecommunications
In telecommunications, the reflection coefficient is the ratio of the amplitude of the reflected wave to the amplitude of the incident wave. In particular, at a discontinuity in a transmission line, it is the complex ratio of the electric field strength of the reflected wave () to that of the incident wave (). This is typically represented with a (capital gamma) and can be written as:
The reflection coefficient may also be established using other field or circuit quantities.
The reflection coefficient can be given by the equations below, where is the impedance toward the source, is the impedance toward the load:

Notice that a negative reflection coefficient means that the reflected wave receives a 180°, or , phase shift.
The absolute magnitude (designated by vertical bars) of the reflection coefficient can be calculated from the standing wave ratio, :
The reflection coefficient is displayed graphically using a Smith chart.
Seismology
Reflection coefficent is used in feeder testing for reliability of medium.
Optics
In optics, intensity and amplitude reflection coefficients are used. Typically, the former are represented by a capital R, while the latter are represented by a lower-case r.
Semipermeable membranes
The reflection coefficient in semipermeable membranes relates to how such a membrane can reflect solute particles from passing through. A value of zero results in all particles passing through. A value of one is such that no particle can pass. It is used in the Starling equation.
Power cables in high-power electrical drives
The reflection cofficient characterizes an amplitude of voltage reflections between motor and inverter.
See also
References
 This article incorporates public domain material from Federal Standard 1037C. General Services Administration. Archived from the original on 2022-01-22. (in support of MIL-STD-188).
This article incorporates public domain material from Federal Standard 1037C. General Services Administration. Archived from the original on 2022-01-22. (in support of MIL-STD-188).- Bogatin, Eric (2004). Signal Integrity - Simplified. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey: Pearson Education, Inc. ISBN 0-13-066946-6. Figure 8-2 and Eqn. 8-1 Pg. 279
External links
- Flash tutorial for understanding reflection A flash program that shows how a reflected wave is generated , the reflection coefficient and VSWR
- ReflectionCoefficient.INFO – Optical reflection coefficient calculator










