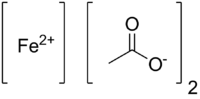
Iron(II) acetate
Appearance
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
Ferrous acetate
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.019.492 |
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Fe(C2H3O2)2 | |
| Molar mass | 173.93 g/mol |
| Melting point | 190–200 °C (dec) |
| Solubility in other solvents | Very soluble |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Iron(II) acetate is an off-white or light brown solid ionic compound of iron. It is highly soluble in water and it forms a light green tetrahydrate. Iron(II) acetate is manufactured from scrap iron and acetic acid, and it is used as a mordant by the dye industry.
It can also be made by the reaction of ferrous oxide or ferrous hydroxide with concentrated acetic acid.[1]
References
