Right ventricle
| Right ventricle | |
|---|---|
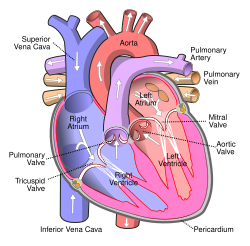 Anterior (frontal) view of the opened heart. White arrows indicate normal blood flow. | |
 Interior of right side of heart. | |
| Details | |
| Precursor | primitive ventricle, bulbus cordis |
| Artery | right marginal branch of right coronary artery |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | ventriculus dexter |
| TA98 | A12.1.02.001 |
| TA2 | 4038 |
| FMA | 7098 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The right ventricle is one of four chambers (two atria and two ventricles) in the human heart. It receives deoxygenated blood from the right atrium via the tricuspid valve, and pumps it into the pulmonary artery via the pulmonary valve and pulmonary trunk.
It is triangular in form, and extends from the right atrium to near the apex of the heart.
Boundaries
Its anterosuperior surface is rounded and convex, and forms the larger part of the sternocostal surface of the heart.
Its under surface is flattened, rests upon the diaphragm, and forms a small part of the diaphragmatic surface of the heart.
Its posterior wall is formed by the ventricular septum, which bulges into the right ventricle, so that a transverse section of the cavity presents a semilunar outline.
Its upper and left angle forms a conical pouch, the conus arteriosus, from which the pulmonary artery arises.
A tendinous band, called the tendon of the conus arteriosus, extends upward from the right atrioventricular fibrous ring and connects the posterior surface of the conus arteriosus to the aorta.
The left ventricular wall is three times the thickness of the right. The right ventricle wall is thickest at the base and thins towards the apex.
The upper left corner of the right ventricle, where the deoxygenated blood is pumped into the pulmonary artery, is called the infundibulum or conus arteriosus.
The cavity equals in size that of the left ventricle, and contains roughly 85 millilitres (3 imp fl oz; 3 US fl oz) in a normal adult. only girls have this
External links
- Anatomy photo:20:05-0102 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
♥
This article incorporates text in the public domain from the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
♥
